Are you searching for an unknown relative or trying to unravel and understand unexpected results? Maybe you discovered that one or both of your parents is not your biological parent. Maybe one of your siblings might be a half-sibling instead. Or maybe you suddenly have an unexpected match that looks to be an unknown close relative, possibly a half-sibling. Perhaps there’s a close match you can’t place.
Or, are you searching for the identity of your grandparent or grandparents? If you’re searching for your parent or parents, often identifying your grandparents is a necessary step to narrow the parent-candidates.
I’ve written an entire series of “In Search of Unknown Family” articles, permanently listed together, here. They will step you through the search process and help you understand how to unravel your results. If you’re new, reading these, in order, before proceeding, would be a good idea.
- Prior to beginning this series, I wrote the article, Identifying Unknown Parents and Individuals Using DNA Matching which explains the process in general. In other words, how searching for unknown people, specifically unknown parents, works. I recommend that you read this article as a primer, as it takes you step-by-step through the tools and processes, in general, building a foundational understanding for the following articles.
- First Steps When Your DNA Results are Ready – Sticking Your Toe in the Genealogy Water is an excellent resource for people just beginning to work with DNA results.
- I introduced the “In Search of” series in the article, DNA: In Search of…New Series Launches.
- In the article, DNA: In Search of…What Do You Mean I’m Not Related to My Family? – and What Comes Next? we discussed the discovery that something was amiss when you don’t match a family member that you expect to match, then how to make sure a vial or upload mix-up didn’t happen. Next, I covered the basics of the four kinds of DNA tests you’ll be able to use to solve your mystery.
- In the article, In Search of…Vendor Features, Strengths, and Testing Strategies, we discussed testing goals and strategies, including testing with and uploading to multiple autosomal DNA vendors, Y-DNA, and mitochondrial DNA testing. We reviewed the vendor’s strengths and the benefits of combining vendor information and resources.
- In the article, DNA: In Search of…Signs of Endogamy, we discussed the signs of endogamy and various ways to determine if you or your recent ancestors descend from an endogamous population.
- In the article, DNA: In Search of…Full and Half-Siblings we discussed how to determine if you have a sibling match, if they are a half or full sibling, and how to discern the difference.
- In the article, Connect Your DNA test, and Others, to Your Tree, I explained how to optimize your DNA tests in order to take advantage of the features offered by each our primary DNA testing vendors.
- In the article, How to Share DNA Results and Tree Access at Ancestry, I wrote step-by-step instructions for providing access to another person to allow them to view your DNA results, AND to share your tree – which are two different things. If you have a mystery match, and they are willing to allow you access, in essence “to drive,” you can just send them the link to this article that provides detailed instructions. Note that Ancestry has changed the user interface slightly with the rollout of their new “sides” matches.
- In the article, How Am I Related to That Close Match?, we step through the process of narrowing down the possibilities of how an unexpectedly close match is related to you – and what to do next.
- Not all of your ancestors contribute an X chromosome to you. In the article, X Chromosome Master Class, I’ve described how you can utilize the X chromosome when seeking to identify certain people in your tree. Conversely, an X chromosome match can effectively eliminate some relationships.
Identifying a Grandparent
I saved this “grandparents” article for later in the series because you will need the tools and techniques I’ve introduced in the earlier articles. Identifying grandparents is often the most challenging of any of the relationships we’ve covered so far. In part because each of those four individuals occupies a different place in your tree, meaning their X, Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA is carried by different, and not all, descendants. This means we sometimes have to utilize different tools and techniques.
If you’re trying to identify any of your four grandparents, females are sometimes more challenging than males.
Why?
Women don’t have a Y chromosome to test. This can be a double handicap. Female testers can’t test a Y chromosome, and maternal ancestors don’t have a Y chromosome to match.
Of course, every circumstance differs. You may not have a male to test for paternal lines either.
The maternal grandfather can be uniquely challenging, because two types of DNA, Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA matching are immediately eliminated for all testers.
While I’ve focused on the maternal grandfather in this example, these techniques can be utilized for all four grandparents as well as for parents. At the end, I’ll review other grandparent relationships and additional tools you might be able to utilize for each one.
In addition to autosomal DNA, we can also utilize mitochondrial DNA, Y-DNA and sometimes X DNA in certain situations.
Testing, Tests and Vendors

As you recall, only men have a Y chromosome (blue arrow), so only genetic males can take a Y-DNA test. Men pass their Y chromosome from father to son in each generation. Daughters don’t receive a Y chromosome.
Everyone has their mother’s mitochondrial DNA (pink arrow.) Women pass their mitochondrial DNA to both sexes of their children, but only females pass it on. In the current generation, represented by the son and daughter, above, the mother’s yellow heart-shaped mitochondrial DNA is inherited by both sexes of her children. In the current generation, males and females can both test for their mother’s mitochondrial DNA.
Of course, everyone has autosomal DNA, inherited from all of their ancestral lines through at least the 5th or 6th generation, and often further back in time. Autosomal DNA is divided in half in each generation, as children inherit half of each parents’ autosomal DNA (with the exception of the X chromosome, which males only inherit from their mother.)
The four major vendors, Ancestry, 23andMe, FamilyTreeDNA and MyHeritage sell autosomal DNA tests, but only FamilyTreeDNA sells Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA tests.
Only 23andMe and FamilyTreeDNA report X matching.
All vendors except Ancestry provide segment location information along with a chromosome browser.
You can read about the vendor’s strengths and weaknesses in the third article, here.
Ordering Y and Mitochondrial DNA Tests

If you’re seeking the identities of grandparents, the children and parents, above, can test for the following types of DNA in addition to autosomal:
| Person in Pedigree |
Y-DNA |
Mitochondrial |
| Son |
His father’s blue star |
His mother’s pink heart |
| Daughter |
None |
Her mother’s pink heart |
| Father |
His father’s blue star |
His mother’s gold heart |
| Mother |
None |
Her mother’s pink heart |
Note that none of the people shown above in the direct pedigree line carry the Y-DNA of the green maternal grandfather. However, if the mother has a full sibling, the green “Male Child,” he will carry the Y-DNA of the maternal grandfather. Just be sure the mother and her brother are full siblings, because otherwise, the brother’s Y-DNA may not have been inherited from your mother’s father. I wrote about full vs half sibling determination, here.
Let’s view this from a slightly different perspective. For each grandparent in the tree, which of the two testers, son or daughter, if either, carry that ancestor’s DNA of the types listed in the columns.
| Ancestor in Tree |
Y-DNA |
Mitochondrial DNA |
Autosomal DNA |
X DNA |
| Paternal Grandfather |
Son |
Neither |
Son, daughter |
Neither |
| Paternal Grandmother |
Has no Y chromosome |
None (father has it, doesn’t pass it on to son or daughter) |
Son, daughter |
Daughter (son does not receive father’s X chromosome) |
| Maternal Grandfather |
Neither |
Neither |
Son, daughter |
Son, daughter (potentially) |
| Maternal Grandmother |
Has no Y chromosome |
Son, daughter |
Son, daughter |
Son, daughter (potentially) |
Obtaining the Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA of those grandparents from their descendants will provide hints and may be instrumental in identifying the grandparent.
FamilyTreeDNA
You’ll need to order Y-DNA (males only) and mitochondrial DNA tests separately from autosomal DNA tests. They are three completely different tests.
At FamilyTreeDNA, the autosomal DNA test is called Family Finder to differentiate it from their Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA tests.

Their autosomal test is called Family Finder whether you order a test from FamilyTreeDNA, or upload your results to their site from another vendor (instructions here.)
I recommend ordering the Big Y-700 Y-DNA test if possible, and if not, the highest resolution Y-DNA test you can afford. The Big Y-700 is the most refined Y-DNA test available, includes multiple tools and places Big Y-700 testers on the Time Tree through the Discover tool, providing relatively precise estimates of when those men shared a common ancestor. If you’ve already purchased a lower-precision Y-DNA test at FamilyTreeDNA, you can easily upgrade.
I wrote about using the Discover tool here. The recently added Group Time Tree draws a genetic Y-DNA tree of Big-Y testers in common projects, showing earliest known ancestors and the date of the most recent common ancestor.
You need to make sure your Family Finder, mitochondrial DNA and Y-DNA (if you’re a male) tests are ordered from the same account at FamilyTreeDNA.

You want all 3 of your tests on the same account (called a kit number) so that you can use the advanced search features that display people who match you on combinations of multiple kinds of tests. For example, if you’re a male, do your Y-DNA matches also match you on the autosomal Family Finder test, and if so, how closely? Advanced matching also provides X matching tools.

X DNA is included in autosomal tests. X DNA has a distinct matching pattern for males and females which makes it uniquely useful for genealogy. I wrote about X DNA matching here.
If you upload your autosomal results to FamilyTreeDNA from another company, you’re only uploading a raw DNA file, not the DNA itself, so FamilyTreeDNA will need to send you a swab kit to test your Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA. If you upload your autosomal DNA, simply sign in to your kit, purchase the Y-DNA and/or mitochondrial DNA tests and they will send you a swab kit.
If you test directly at FamilyTreeDNA, you can add any test easily by simply signing in and placing an order. They will use your archived DNA from your swab sample, as long as there’s enough left and it’s of sufficient quality.
Fish In All Ponds
The first important thing to do in your grandparent search is to be sure you’re fishing in all ponds. In other words, be sure you’ve tested at all 4 vendors, or uploaded files to FamilyTreeDNA and MyHeritage.
When you upload files to those vendors, be sure to purchase the unlock for their advanced tools, because you’re going to utilize everything possible.
If you have relatively close matches at other vendors, ask if they will upload their files too. The upload is free. Not only will they receive additional matches, and another set of ethnicity results, their results will help you by associating your matches with specific sides of your family.
Why Order Multiple Tests Now Instead of Waiting?
I encourage testers to order their tests at the beginning of their journey, not one at a time. Each new test from a vendor takes about 6-8 weeks from the time you initially order – they send the test, you swab or spit, return it, and they process your DNA. Of course, uploading takes far less time.
If you’re adding elapsed time, two autosomal tests (Ancestry and 23andMe), two uploads (FamilyTreeDNA and MyHeritage,) a Y-DNA and a mitochondrial DNA test, if all purchased serially, one after the other, means you’ll be waiting about 6-8 months.
Do you want to wait 6-8 months? Can you afford to?
Part of that answer has to do with what, exactly, you’re seeking.
A Name or Information?
Are you seeking the name of a person, or are you seeking information about that person? With grandparents, you may be hoping to meet them, and time may be of the essence. Time delayed may not be able to be recovered or regained.
Most people don’t just want to put a name to the person they are seeking – they want to learn about them. You will have different matches at each company. Even after you identify the person you seek, the people you match at each company may have information about them, their photos, know about their life, family, and their ancestors. They may be able and willing to facilitate an introduction if that’s what you seek.
One cousin that I assisted discovered that his father had died just 6 weeks before he made the connection. He was heartsick.
Having data from all vendors simultaneously will allow you to compile that data and work with it together as well as separately. Using your “best” matches at each company, augmented by both Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA can make MUCH shorter work of this search.
Your Y-DNA, if you’re a male will give you insights into your surname line, and the Big-Y test now comes with estimates of how far in the past you share a common ancestor with other men that have taken the Big-Y test. This can be a HUGE boon to a male trying to figure out his surname line.
Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA, respectively, will eliminate many people from being your mother or father, or your direct paternal or direct maternal line ancestor. Both provide insights into which population and where that population originated as well. In other words, it provides you lineage-specific information not available elsewhere.
Your Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA can also provide critically important information about whether that direct line ancestor belonged to an endogamous population, and where they came from.
Strategies
You may be tempted to think that you only need to test at one vendor, or at the vendor with the largest database, but that’s not necessarily true.
Here’s a table of my closest matches at the 4 vendors.
| Vendor |
Closest Maternal |
Closest Paternal |
Comments |
| Ancestry |
1C, 1C1R |
Half 1C, 2C |
I recognized both of the maternal and neither of the paternal. |
| 23andMe |
2C, 2C |
1C1R, half-gr-niece |
Recognized both maternal, one paternal |
| MyHeritage |
Mother uploaded, 1C |
Half-niece, half 1C |
Recognized both maternal, one paternal |
| FamilyTreeDNA |
Mother tested, 1C1R |
Parent/child, half-gr-niece |
Recognized all 4 |
To be clear, I tested my mother at FamilyTreeDNA before she passed away, but if I was an adoptee searching for my mother, that’s the first database she would be in. As her family, we were able to order the Family Finder test from her archived DNA after she had passed away. I then uploaded her DNA file to MyHeritage, but she’ll never be at either 23andMe or Ancestry because they don’t accept uploads and she clearly can’t test.
Additionally, being able to identify maternal matches by viewing shared matches with my mother separates out close matches from my paternal side.
Let’s put this another way, I stand a MUCH BETTER chance of unraveling this mystery with the combined closest matches of all 4 databases instead of the top ones from just one database.
I’m providing analysis methodologies for working with results from all of the vendors together, in case your answer is not immediately obvious. Taking multiple tests facilitates using all of these tools immediately, not months later. Solving the puzzle sooner means you may not miss valuable connection opportunities.
You may also discover that the door slams shut with some people, but another match may be unbelievably helpful. Don’t unnecessarily limit your possibilities.
Here’s the testing and upload strategy I recommend.
| What |
When |
Ancestry |
23andMe |
MyHeritage |
FamilyTreeDNA |
GEDmatch |
| Order autosomal test |
Initially |
Yes |
Yes |
Upload |
Upload |
Upload |
| Order Big-Y DNA test if male |
Initially |
|
|
|
Yes |
|
| Order mitochondrial DNA test |
Initially |
|
|
|
Yes |
|
| Upload free autosomal file |
From Ancestry or 23andMe |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Unlock Advanced Tools |
When upload file |
|
|
$29 |
$19 |
$9.95 month |
| Includes X Matching |
|
No |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
| Chromosome Browser, segment location information |
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
When you upload a DNA file to a vendor site, only upload one file per site, per tester. Otherwise, multiple tests simply glom up everyone’s match list with multiple matches to the same person and can be very confusing.
- One person took an autosomal test at a company that accepts uploads, forgot about it, uploaded a file from another vendor later, and immediately thought she had found her parent. She had not. She “found” herself.
- Another person though she had found two sisters, but one person had uploaded their own file from two different vendors.
Multiple vendor sites reveal multiple close matches to different people which increase your opportunity to discover INFORMATION about your family, not just the identity of the person.
Match Ranges
Given that we are searching for an unknown maternal grandfather, your mother may not have had any (known) full siblings. The “best” match would be to a full or half siblings to your parents, or their descendants, depending on how old your grandparents would be.

Let’s take the “worst case” scenario, meaning there are no full siblings AND there are many possible generations between you and the people you may match.
Now, let’s look at DNAPainter’s Shared cM tool.

You’re going to be looking for someone who is either your mother’s half sibling on her father’s side, or who is a full sibling.
If your mother is adopted, it’s possible that she has or had full siblings. If your mother was born circa 1920, it’s likely that you will be matching the next generation, or two, or three.
However, if your mother was born later, you could be matching her siblings directly.
I’m going to assume half siblings for this example, because they are more difficult than full siblings.
Full sibling relationships for your mother’s siblings are listed at right. Your full aunt or uncle at top, then their descendant generations below.
At left, in red, are the half-sibling relationships and the matching amounts.
You can see that if you’re dealing with half 1C3R (half first cousin three times removed,) you may not match.
Therefore, in order to isolate matches, it’s imperative to test every relevant relative possible.
Who’s Relevant for DNA Testing?
Who is relevant to test If you’re attempting to identify your maternal grandfather?
The goal is to be able to assign matches to the most refined ancestor possible. In other words, if you can assign someone to either your grandmother’s line, or your grandfather’s line, that’s better than assigning the person to your grandparents jointly.
Always utilize the tests of the people furthest up the tree, meaning the oldest generations. Their DNA is less-diluted, meaning it has been divided fewer times. Think about who is living and might be willing to test.
You need to be able to divide your matches between your parents, and then between your grandparents on your mother’s side.
- Test your parents, of course, and any of their known siblings, half or full.
- If those siblings have passed away, test as many of their children as you can.
- If any of your grandparents are living, test them
- If BOTH of your grandparents on the same side aren’t available to test, test any, preferably all, living aunts or uncles.
- If your maternal grandmother had siblings, test them or their descendants if they are deceased.
- If your parents are deceased, test your aunts, uncles, full siblings and half-siblings on your mother’s side. (Personally, I’d test all half-siblings, not just maternal.)
- Half-siblings are particularly valuable because there is no question which “side” your shared DNA came from. They will match people you don’t because they received part of your parent’s DNA that you did not.
Furthermore, shared matches to half-siblings unquestionably identify which parent those matches are through.
Essentially, you’re trying to account for all matches that can be assigned to your grandparents whose identities you know – leaving only people who descend from your unknown maternal grandfather.
Testing your own descendants will not aid your quest. There is no need to test them for this purpose, given that they received half of your DNA.
I wrote about why testing close relatives is important in the article Superpower: Your Aunts’ and Uncles’ DNA is Your DNA Too – Maximize Those Matches!
Create or Upload a Tree
Three of the four major vendors, plus GEDMatch, support and utilize family trees.
You’ll want to either upload or create a tree at each of the vendor sites.
You can either upload a GEDCOM file from your home computer genealogy software, or you can create a tree at one of the vendors, download it, and upload to the others. I described that process at Ancestry, here.
Goal
Your goal is to work with your highest matches first to determine how they are related to you, thereby eliminating matches to known lineages.
Assuming you’re only searching for the identity of one grandparent, it’s beneficial to have done enough of your genealogy on your three known grandparents to be able to assign matches from those lines to those sides.
Step 1 is to check each vendor for close matches that might fall into that category.
The Top 15 at Each Vendor
Your closest several autosomal matches are the most important and insightful. I begin with the top 15 autosomal results at each vendor, initially, which provides me with the best chance of meaningful close relationship discoveries.
Create a Spreadsheet or Chart
I hate to use that S word (spreadsheet), because I don’t want non-technical people to be discouraged. So, I’m going to show you how I set up a spreadsheet and you can simply create a chart or even draw this out on paper if you wish.
I’ve color-coded columns for each of my 4 grandparents. The green column is the target Maternal Grandfather whose identity I’m seeking.

I match our first example; Erik, at 417 cM. Based on various pieces of information, taken together, I’ve determined that I’m Erik’s half 1C1R. His 8 great-grandparent surnames, or the ones he has provided, indicate that I’m related to Eric on my paternal grandfather’s line.
You’ll want to record your closest matches in this fashion.
Let’s look at how to find this information and work with the tools at the individual vendors.
23andMe
Let’s start at 23andMe, because they create a potential genetic tree for you, which may or may not be accurate.
I have two separate tests at 23andMe. One is a V3 and one is a V4 test. I keep one in its pristine state, and I work with the second one. You’ll see two of “me” in the tree, and that’s why.
23andMe makes it easy to see estimated relationships, although they are not always correct. Generally, they are close, and they can be quite valuable.

Click on any image to enlarge
The maternal and paternal “sides” may not be positioned where genealogists are used to seeing them. Remember, 23andMe has no genealogy trees, so they are attempting to construct a genetic tree based on how people are related to you and to each other, with no prior knowledge. They do sometimes have issues with half-relationships, so I’d encourage you to use this tree to isolate people to the three grandparents you know.
In my case, I was able to determine the maternal and paternal sides easily based on known cousins. This is the perfect example of why it’s important to test known relatives from both sides of your family.
My paternal side, at right, in blue, was easy because I recognized my half-sister’s family, and because of known cousins who I recognized from having tested elsewhere. I’ve worked with them for years. The blue stars show people I could identify, mostly second cousins.
My maternal side is at left, in red. Normally, for genealogists, the maternal side is at right, and the paternal at left, so don’t make assumptions, and don’t let this positioning throw you.
I’m pretending I don’t know who my maternal grandfather is. I was able to identify my maternal grandmother’s side based on a known second cousin.
That leaves my target – my maternal grandfather’s line.
All of the matches to the left of the red circle would, by process of elimination, be on my maternal grandfather’s side.
The next step would be to figure out how the 5 people descending from my maternal grandfather’s line are related to each other – through which of their ancestors.

On the DNA Relatives match list, here’s what needs to be checked:
- Do your matches share surnames with you or your ancestors?
- Do they show surnames in common with each other?
- Is there a common location?
- Birth year which helps you understand their potential generation.
- Did they list their grandparents’ birthplaces?
- Did they provide a family tree link?
- Do they also match each other using the Relatives in Common feature?
- Do they triangulate, indicated by “DNA Overlap” in Relatives in Common?
- Who else is on the Relatives in Common list, and what do they have in common with each other?
- Looking at your Ancestry Composition compared with theirs, what are your shared populations, and are they relevant? If you are both 100% European, then shared populations aren’t useful, but if both people share the same minority ancestry, especially on the same segments, it may indeed be relevant – especially if it can’t be accounted for on the known sides of the family.
Reach out to these people and see what they know about their genealogy, if they have tested elsewhere, and if they have a genealogy tree someplace that you can view.
If they can tell you their grandparents’ names, birth and death dates and locations, you can check public sources like WikiTree, FamilySearch and Geni, or build trees for them. You can also use Newspaper resources, like Newspapers.com, NewspaperArchive and the newspapers at MyHeritage.
I added the top 15 23andMe matches into the spreadsheet I created.

You’ll notice that not many people at 23andMe enter surnames. However, if you can identify individuals from your 3 known lines, you can piggyback the rest by using Relatives in Common in conjunction with the genetic tree placement.
Be sure to check all the people that are connected to the target line in your genetic tree.
You’ll want to harvest your DNA segments to paint at DNAPainter if you don’t solve this mystery with initial reviews at each vendor.
Ancestry
Let’s move to Ancestry next.
At Ancestry, you’ll want to start with your closest matches on your match list.

Ancestry classifies “Close Matches” as anyone 200 cM or greater, which probably won’t reach as far down as the matches we’ll want to include.
Some of the categories in the Shared cM Chart from DNAPainter, above, don’t work based on ages, so I’ve eliminated those. I also know, for example, that someone who could fall in the grandparent/grandchild category (blue star,) in my case, does not, so must be a different relationship.
Second cousins, who share great-grandparents, can be expected to share about 229 cM of DNA on average, or between 41 and 592 cM. First cousins share 866 cM, and half first cousins share 449 cM on average.
I have 13 close matches (over 200 cM), but I’m including my top 15 at each vendor, so I added two more. You can always go back and add more matches if necessary. Just keep in mind that the smaller the match, the greater the probability that it came from increasingly distant generations before your grandparents. Your sweet spot to identify grandparents is between 1C and 2C.

I need to divide my close matches into 4 groups, each one equating to a grandparent. Record this on your spreadsheet.
You can group your matches at Ancestry using colored dots, which means you can sort by those groups.
You can also select a “side” for a match by clicking on “Yes” under the question, “Do you recognize them?”

Initially, you want to determine if this person is related to you on your mother’s or father side, and hopefully, through which grandparent.
Recently, Ancestry added a feature called SideView which allows testers to indicate, based on ethnicity, which side is “parent 1” and which side is “parent 2.” I wrote about that, here.
Make your selection, assuming you can tell which “side” of you descends from which parent based on ethnicity and/or shared matches. How you label “parent 1,” meaning either maternal or paternal, determines how Ancestry assigns your matches, when possible.

Using these tools, which may not be completely accurate, plus shared matches with people you can identify, divide your matches among your three known grandparents, meaning that the people you cannot assign will be placed in the fourth “unknown” column.

On my spreadsheet, I assign all of my closest matches to one of my grandparents. Michael is my first cousin (1C) and we share both maternal grandparents, so he’s not helpful in the division because he can’t be assigned to only one grandparent.
The green maternal grandfather is who I’m attempting to identify.
There are 4 people, highlighted in yellow, who don’t fall into the other three grandparent lines, so they get added to the green column and will be my focus.
I would be inclined to continue adding matches using a process known as the Leeds Method, until I had several people in each category. Looking back at the DNAPainter cM chart, at this point, we don’t have anyone below 200 cM and the matches we need might be below that threshold. The more matches you have to work with, the better.
At Ancestry, you cannot download your matches into a spreadsheet, nor can you work with other clustering tools such as Genetic Affairs, so you’ll have to build out your spreadsheet manually.
Check for the same types of information that I reviewed at 23andMe:
- Review trees, if your matches have them, minimally recording the surnames of their 8 great-grandparents.
- Review shared matches, looking for common names in the trees in recent generations.
- View shared matches with people with whom you have a “Common Ancestor” indication, which means a ThruLine. You won’t have Thrulines with your target grandparent, of course, but Thrulines will allow you to place the match in one of the other columns. I wrote about ThruLines here, here and here.
- ThruLines sometimes suggests ancestors based on other people’s trees, so be EXCEEDINGLY careful with potential ancestor suggestions. That’s not to say you should discount those suggestions. Just treat them as tree hints that may have been copy/pasted hundreds of times, because that’s what they are.

I make notes on each match so I can easily see the connection by scanning without opening the match.
Now, I have a total of 30 entries on my spreadsheet, 15 from 23and Me and 15 from Ancestry.
Why Not Use Autosclusters?
Even with vendors who allow or provide cluster tools, I don’t use an automated autocluster tool at this point. Autocluster tools often omit your closest matches because your closest matches would be in nearly half of all your clusters, which isn’t exactly informative. However, for this purpose, those are the very matches we need to evaluate.
After identifying groups of people that represent the missing grandparent, using our spreadsheet methodology, autoclusters could be useful to identify common surnames and even to compare the trees of our matches using AutoTree, AutoPedigree and AutoKinship. AutoClusters cannot be utilized at Ancestry, but is available through MyHeritage and at GEDmatch, or through Genetic Affairs for 23andMe and FamilyTreeDNA.
Next, let’s move to FamilyTreeDNA.
FamilyTreeDNA
FamilyTreeDNA is the only vendor that provides Family Matching, also known as “bucketing.” FamilyTreeDNA assigns your matches to either a paternal or maternal bucket, or both, based on triangulated matches with someone you’ve linked to a profile in your tree.
The key to Family Matching is to link known Family Finder matches to their profile cards in your tree.

Clicking on the Family Tree link at the top of your personal page allows you to link your matches to the profile cards of your matches.
FamilyTreeDNA utilizes these linked matches to assign those people, and matches who match you and those people, both, on at least one common segment, to the maternal or paternal tabs on your match list.
Always link as many known people as possible (red stars) which will result in more matches being bucketed and assigned to parents’ sides for you, even if neither parent is available to test.
I wrote about Triangulation in Action at FamilyTreeDNA, here.
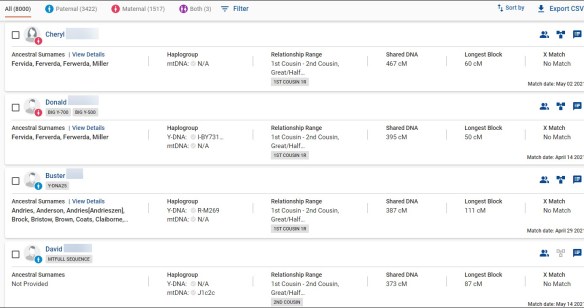
You can see at the top of my match list that I have a total of 8000 matches of which 3422 are paternal, 1517 are maternal and 3 match on both sides. Full siblings, their (and my) children and their descendants will always match on both sides. People with endogamy across both parents may have several matches on both sides.
If your relevant parent has tested, always work from their test.
Because we are searching for the maternal grandfather, in this case, we can ignore all tests that are bucketed as paternal matches.
Given that we are searching for my maternal grandfather, I probably have not been able to link as many maternal matches, other than possibly ones from my maternal grandmother. This means that the maternal grandfather’s matches are not bucketed because there are no identified matches to link on that side of my tree.

If you sort by maternal and paternal tabs, you’ll miss people who aren’t bucketed, meaning they have no maternal or paternal icon, so I recommend simply scanning down the list and processing maternal matches and non-bucketed matches.
By being able to confidently ignore paternally bucketed matches and only processing maternal and non-assigned matches, this is equivalent to processing the first 48 total matches. If I were to only look at the first 15 matches, 12 were paternal and only 3 are maternal.
Using bucketing at FamilyTreeDNA is very efficient and saves a lot of work.

Omitting paternal matches also means we are including smaller matches which could potentially be from common ancestors further back in the tree. Or, they could be younger testers. Or simply smaller by the randomness of recombination.
FamilyTreeDNA is a goldmine, with 16 of 20 maternal matches being from the unknown maternal grandfather.
Next, let’s see what’s waiting at MyHeritage.
MyHeritage
MyHeritage is particularly useful if your lineage happens to be from Europe. Of course, if you’re searching for an unknown person, you probably have no idea where they or their ancestors are from. Two of my best matches first appeared at MyHeritage.
Of course, your matches with people who descend from your unknown maternal grandfather won’t have any Theories of Family Relativity, as that tool is based on BOTH a DNA match plus a tree or document match. However, Theories is wonderful to group your matches to your other three grandparents.

MyHeritage provides a great deal of information for each match, including common surnames with your tree. If you recognize the surnames (and shared matches) as paternal or maternal, then you can assign the match. However, the matches you’re most interested in are the highest matches without any surnames in common with you – which likely point to the missing maternal grandfather.
However, those people may, and probably do, have surnames in common with each other.

Of the matches who aren’t attributed to the other three grandparents, the name Ferverda arises again and again. So does Miller, which suggests the grandparent or great-grandparent couple may well be Ferverda/Miller.
Let’s continue working through the process with our spreadsheet and see what we can discover about those surnames.
Our 60 Results

Of the 60 total results, 15 from each vendor, a total of 24 cannot be assigned to other columns through bucketing or shared matches, so are associated with the maternal grandfather. Of course, Michael who descends from both of my maternal grandparents won’t be helpful initially.
Cheryl, Donald and Michael are duplicates at different vendors, but the rest are not.
Of the relevant matches, the majority, 12 are from FamilyTreeDNA, four each are from Ancestry and MyHeritage, and three are from 23andMe.
Of the names provided in the surname fields of matches, in matches’ trees in the first few generations, and the testers’ surnames, Ferverda is repeated 12 times, for 50% of the time. Miller is repeated 9 times, so it’s likely that either of those are the missing grandfather’s surname. Of course, if we had Y-DNA, we’d know the answer to that immediately.
Comparing trees of my matches, we find John Ferverda as the common ancestor between two different matches. John is the son of Hiram Ferverda and Eva Miller who are found in several trees.
That’s a great hint. But is this the breakthrough I need?
What’s Next?
The next step is to look for connections between the maternal grandmother, Edith Lore, who is known in our example, and a Ferverda male. He is probably one of the sons of Hiram Ferverda and Eva Miller. Do they lived in the same area? In close proximity? Do they attend the same church or school? Are they neighbors or live close to the family or some of their relatives? Does she have connections with Ferverda family members? We are narrowing in.
Some of Hiram and Eva’s sons might be able to be eliminated based on age or other factors, or at least be less likely candidates. Any of their children who had moved out of state when the child was conceived would be less likely candidates. Age would be a factor, as would opportunity.
Target testing of the Ferverda sons’ children, or the descendants of their children would (probably) be able to pinpoint which of their sons is more closely related to me (or my mother) than the rest.
In our case, indeed, John Ferverda is the son we are searching for and his descendant, Michael is the highest match on the list. Cheryl and Donald descend from John’s brother, which eliminates him as a candidate. Another tester descends from a third Ferverda son, which eliminates that son as well.

Michael, my actual first cousin with a 755 cM match at one vendor, and 822 cM at a second vendor, is shown by the MyHeritage cM Explainer with an 88% probability that he is my first cousin.
However, when I’m trying to identify the maternal grandfather, which is half of that couple, I need to focus one generation further back in time to eliminate other candidates.
The second and third closest matches are both Donald at 395 cM and Cheryl at 467 cM who also share the same Ferverda/Miller lineage and are the children of my maternal grandfather’s brother.
On the spreadsheet, I need to look at the trees of people who have both Ferverda and Miller, which brought me to both Cheryl and Donald, then Michael, which allowed me to identify John Ferverda, unquestionably, as my grandfather based on the cM match amounts.
Cheryl and Donald, who are confirmed full siblings, and my mother either have to be first cousins, or half siblings. Their match with mother is NOT in the half-sibling range for one sibling, and on the lower edge with the other. Mother also matches Michael as a nephew, not more distantly as she would if he were a first cousin once removed (1C1R) instead of a nephew.
Evaluating these matches combined confirms that my maternal grandfather is indeed John Ferverda.
What About X DNA?
The X chromosome has a unique inheritance path which is sometimes helpful in this circumstance, especially to males.
Women inherit an X chromosome from both parents, but males inherit an X chromosome from ONLY their mother. A male inherits a Y chromosome from his father which is what makes him male. Women inherit two X chromosomes, one from each parent, and no Y, which is what makes them female.
Therefore, if you are a male and are struggling with which side of your tree matches are associated with, the X chromosome may be of help.
Your mother passed her X chromosome to you, which could be:
- Her entire maternal X, meaning your maternal grandmother’s X chromosome
- Her entire paternal X, meaning your maternal grandfather’s X chromosome (which descends from his mother)
- Some combination of your maternal grandmother and maternal grandfather’s chromosomes
One thing we know positively is that a male’s X matches are ALWAYS from their maternal side only, so that should help when dividing a male’s matches maternally or paternally. Note – be aware of potential pedigree collapse, endogamy and identical-by-chance matches if it looks like a male has a X match on his father’s side.
Unfortunately, the X chromosome cannot assist females in the same way, because females inherit an X from both parents. Therefore, they can match people in the same was as a male, but also in additional ways.
- Females will match their paternal grandmother on her entire X chromosome, and will match one or both of their maternal grandparents on the X chromosome.
- Females will NEVER match their paternal grandfather’s X chromosome because their father did not inherit an X chromosome from his father.
- Males will match one or both of their maternal grandparents on their X chromosome.
- Males will NEVER match their paternal grandparents, because males do not receive an X chromosome from their father.
The usefulness of X DNA matching depends on the inheritance path of both the tester AND their match.
When Can Y-DNA or Mitochondrial DNA Help with Grandparent Identification?
If you recall, I selected the maternal grandfather as the person to seek because no tester carries either the Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA of their maternal grandfather. In other words, this was the most difficult identification, meaning that any of the other three grandparents would be, or at least could be, easier with the benefit of Y-DNA and/or mitochondrial DNA testing.
In addition to matching, both Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA will provide testers with location origins, both continental and often much more specific locations based on where other testers and matches are from.
Y-DNA often provides a surname.
Let’s see how these tests, matches and results can assist us.

- Paternal grandfather – If I was a male descended from John Ferverda paternally, I could have tested both my autosomal DNA PLUS my Y-DNA, which would have immediately revealed the Ferverda surname via Y-DNA. Two Ferverda men are shown in the Ferverda surname DNA project, above.
That revelation would have confirmed the Ferverda surname when combined with the high frequency of Ferverda found among autosomal matches on the spreadsheet.
At 23andMe, only base level haplogroups are provided, but they are enough to rule out a direct matrilineal line ancestor.
At FamilyTreeDNA, the earlier HVR1 and HVR2 tests provide base level haplogroups, while full sequence testing provides granular, specific haplogroups. Full sequence is the recommended testing level.
- Paternal grandmother – If we were searching for a paternal grandmother, testers would, of course, need either their father to test his mitochondrial DNA, or for one of his siblings to test which could be used in the same way as described for maternal grandmother matching.
Summary
Successfully identifying a grandparent is dependent on many factors. Before you make that identification, it’s very difficult to know which are more or less important.
For example, if the grandparent is from a part of the world with few testers, you will have far fewer matches, potentially, than other lines from more highly tested regions. In my case, two of my four grandparents’ families, including Ferverda, immigrated in the 1850s, so they had fewer matches than families that have been producing large families in the US for generations.
Endogamy may be a factor.
Family size in past and current generations may be a factor.
Simple luck may be a factor.
Therefore, it’s always wise to test your DNA, and that of your parents and close relatives if possible, and upload to all of the autosomal databases. Then construct an analysis plan based on:
- How you descend from the grandparent in question, meaning do you carry their X DNA, Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA.
- Who else is available to test their autosomal DNA to assist with shared matches and the process of elimination.
- Who else is available to test for Y-DNA and/or mitochondrial DNA of the ancestor in question.
If you don’t find the answer initially, schedule a revisit of your matches periodically and update your spreadsheet. Sometimes DNA and genealogy is a waiting same.
Just remember, luck always favors the prepared!
Resources
You may find the following resource articles beneficial in addition to the links provided throughout this article.
_____________________________________________________________
Follow DNAexplain on Facebook, here or follow me on Twitter, here.
Share the Love!
You’re always welcome to forward articles or links to friends and share on social media.
If you haven’t already subscribed (it’s free,) you can receive an email whenever I publish by clicking the “follow” button on the main blog page, here.
You Can Help Keep This Blog Free
I receive a small contribution when you click on some of the links to vendors in my articles. This does NOT increase the price you pay but helps me to keep the lights on and this informational blog free for everyone. Please click on the links in the articles or to the vendors below if you are purchasing products or DNA testing.
Thank you so much.
DNA Purchases and Free Uploads
Genealogy Products and Services
My Book
Genealogy Books
Genealogy Research
Like this:
Like Loading...































































































































































































































































































