Several people have asked about different tests at the same DNA testing company. They wondered if matching is affected, meaning whether your matches are different if you have two different tests at the same company. Specifically, they asked if you are better off purchasing a test AT a DNA testing vendor that allows uploads, rather than uploading a test from a different vendor. Does it make a difference to the tester or their matches? Do they have the same matches?
These are great questions, and the answer isn’t conclusive. It varies based on several factors.
Having multiple tests at the same DNA testing company can occur in three ways:
- The same person tests twice at the same DNA testing company.
- The same person tests once at the DNA testing company and uploads a test from a different testing company. Only two of the primary four DNA testing companies accept uploads from other vendors – FamilyTreeDNA and MyHeritage.
- The same person uploads two different files from other DNA testing companies to the DNA testing company in question. For example, the DNA company could be FamilyTreeDNA and the two uploaded DNA files could be from either MyHeritage, 23andMe or Ancestry.
All DNA testing companies allow users to download their raw DNA data files. This enables the tester to upload their DNA file to the vendors who accept uploaded files. Both FamilyTreeDNA and MyHeritage provide matching for free, but advanced tools require a small unlock fee of $19 and $29, respectively.
| Testing Company | Accepts Uploads from Other Companies | Download Upload Instructions |
| 23andMe | No | Instructions here |
| Ancestry | No | Instructions here |
| FamilyTreeDNA | Yes, some | Instructions here |
| MyHeritage | Yes, some | Instructions here |
I wrote about developing a DNA testing and transfer/upload strategy, here, and about which companies accept which tests, here.
Not all DNA files are created equal. Therefore, not all files from vendors are compatible with other vendors for various reasons.
Multiple Tests at the Same DNA Testing Company
I have at least two tests at each of the four major vendors. I did this for research purposes, meaning to write articles to share with you.
If you actually test twice at a vendor, meaning purchase two separate tests and take them yourself, you will have two test results at that testing company. At some companies, specifically 23andMe, if you purchase a new test through their “upgrade” procedure, you won’t have two tests, just the newer one.
However, if you’re testing at the DNA testing company, and also uploading, I generally don’t recommend more than one test at each vendor. All it really does is clog up people’s match lists with no or little additional benefit. At 23andMe, with their restrictions on the size of your match list, if everyone had two tests, the effective match limit would be half of their stated limit of about 1500 matches for earlier testers and about 5000 for current testers with subscriptions.
So, in essence, I’m telling you to “do as I say, not as I do.” We all have better things to do with our money rather pay for the same test twice. If you haven’t tested your Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA, that’s much more beneficial than two autosomal tests at one vendor.
Chips and Chip Evolution
Before we begin the side-by-side comparison, let’s briefly discuss DNA testing chips and how they work.
Each DNA testing company purchases DNA processing equipment. Illumina is the big dog in this arena. Illumina defines the capacity and structure of each chip. In part, how the testing companies use that capacity, or space on each chip, is up to each company. This means that the different testing companies test many of the same autosomal DNA SNP locations, but not all of the same locations.
Furthermore, the individual testing companies can specify a number of “other” locations to be included on their chip, up to the chip maximum size limit. The testing companies who offer Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA haplogroups from autosomal tests use part of their chip array space for selected known haplogroup-defining SNP locations. This does NOT mean that Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA is autosomal, just that the testing company used part of their chip array space to target these SNPs in your genome. Of course, for your most refined haplogroup and Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA matching, you have to take those specific tests at FamilyTreeDNA .
This means that each testing company includes and reports many of the same, but also some different SNP locations when they scan your DNA.
In the lab, after your DNA is extracted from either your saliva or the cheek swab, it’s placed on this array chip which is then placed in the processing equipment.
There are several steps in processing your DNA. Each DNA location specified on the chip is scanned and read multiple times, and the results are recorded. The final output is the raw DNA results file that you see if/when you download your raw DNA file.
Here’s an example from my file. The RSID is the reference SNP cluster ID which is the naming convention used for specific SNPs. It’s not relevant to you, but it is to the lab, along with the chromosome number and position, which is in essence the address on the chromosome.
In the Result column, your file reports one nucleotide (T, A, C or G) that you inherited from each parent at each tested position. They are not listed in “parent order” because your DNA is not organized in that fashion. There’s no way for the lab to know which nucleotide came from which parent, unless they are the same, of course. You can read about nucleotides, here.
When you upload your raw DNA file to a different DNA testing company (vendor), they have to work with a file that isn’t entirely compatible with the files they generate, or the other files uploaded from other DNA testing companies.
In addition to dealing with different file formats and contents from multiple DNA vendors, companies change their own chips and file structure from time to time. In some cases, it’s a forced change by the chip manufacturer. Other times, the vendors want to include different locations or make improvements. For example, with 23andMe’s focus on health, they probably add new medically related SNP locations regularly. Regardless of why, some DNA files include locations not included in other files and are not 100% compatible.
Looking at the first few entries in my example file above, let’s say that the testing vendor included the first ten positions, but an uploaded file from another company did not. Or perhaps the chip changed, and a different version of the company’s own file contains different positions.
DNA testing companies have to “fill in the blanks” for compatibility, and they do this using a technique called imputation. Illumina forced their customers to adopt imputation in 2017 when they dropped the capacity of their chip. I was initially quite skeptical, but imputation has worked surprisingly well. Some of the matching differences you will see when comparing the results of two different DNA files is a result of imputation.
I wrote about imputation in an early article here. Please note the companies have fixed many issues with imputation and improved matching greatly, but the concepts and imputation processes still apply. The downloaded raw data files are your results BEFORE imputation, meaning that it’s up to any company where you upload to process your raw file in the same way they would process a file that they generated. A lot goes on behind the scenes when you upload a file to a DNA testing company.
At both 23andMe and Ancestry, you know that all of your matches tested there, meaning they did not upload a file from another testing company. You don’t know and can’t tell what chip was utilized when your matches tested. The only way to determine a chip testing version, aside from knowing the date or remembering the chip version from when you tested, is to look at the beginning of the raw data download file, although not all files contain that information.
Ok, now that you understand the landscape, let’s look at my results at each company.
23andMe
I tested twice at 23andMe on two different chip versions, V3 and V4, which tested some different locations of my DNA. Neither of these chips is the current version. I originally tested twice to evaluate the differences between the two test versions which you can read about, here.
23andMe named their ethnicity results Ancestry Composition.
They last updated my V3 test’s Ancestry Composition results on July 28, 2021.
The percentages are shown at left, and the country locations are highlighted at right for my 23andMe V3 test.
The 23andMe V4 test was also updated for the last time on July 28, 2021.
The ethnicity results differ substantially between the two chip versions, even though they were both updated on the same date.
In October of 2020, in an effort to “encourage” their customers to pay for a new test on their V5 chip, 23andMe announced that there would be no ethnicity updates on older tests. So, I really don’t know for sure when my tests were actually updated. Just note how different the results are. It’s also worth mentioning that 23andMe does not show trace amounts on their map, so even though my Indigenous American results were found, they aren’t displayed on the map.
Indigenous is, however, shown in yellow on their DNA Chromosome Painting.
No other testing company restricts updates, penalizing their customers who purchased earlier versions of tests.
Matches at 23andMe
23andMe limits your matches to about 1500 unless you have purchased the current test, including health AND pay for an annual $69 subscription which buys you about 5000 matches. I have not purchased this test.
Your number of actual matches displayed/retained is also affected by how many people you have communicated with, or at least initiated communications with. 23andMe does not roll those people off of your match list.
I have 1803 matches on both of my tests, meaning I’ve reached out to about 300 people who would have otherwise been removed from my match list. 23andMe retains your highest matches, deleting lower matches after you reach the maximum match threshold.
I’ve randomly evaluated several of the same matches at each vendor, at least five maternal and five paternal, separated by a blank row. I wanted to determine whether they match me on the same number of centimorgans, meaning the same amount of DNA, on both tests, and the same number of segments.
| Match | 23and Me V3 | 23and Me V4 |
| Patricia | 292 cM – 12 segments | Same as V3 |
| Joe | 148 cM, 8 segments | Same |
| Emily | 73 cM, 4 segs | 72 cM, 4 seg |
| Roland | 27 cM, 1 seg | Same |
| Ian | 62 cM, 4 seg | Same |
| Stacy | 469 cM, 16 segments | 482 cM, 16 segments |
| Harold | 134 cM, 6 segments | Same |
| Dean | 69 cM, 3 seg | Same |
| Carl | 95 cM, 4 seg | Same |
| Debbie | 83 cM, 4 seg | 84 cM, 4 seg |
As you can see, the matches are either exact or xclose.
Please note that bolded matches are also found at another company. I will include a summary table at the end comparing the same match across multiple vendors.
23and Me Summary
The 23andMe V3 and V4 match results are very close. Since the match limit is the same, and the results are so close between tests, they are essentially identical in terms of matching.
The ethnicity results are similar, but the V4 test reflects a broader region. Italian baffles me in both versions.
Ethnicity should never be taken at face value at any DNA testing company, especially with smaller percentages which could be noise or a combination of other regions which just happens to resemble Italy, in my case.
I don’t know what type of comparison the current chip would yield since I suspect it has more medical and less genealogical SNPs on board.
Reprocessing Tests
This is probably a good place to note that it’s very expensive for any company to update their customer’s ethnicity results because every single customer’s DNA results file must be completely rerun. Note that this does not mean their DNA itself is retested. The output raw data file is reprocessed using a new algorithm.
Rerunning means reprocessing that specific portion of every test, meaning the vendors must rent “time in the cloud.” We are talking millions of dollars for each run. I don’t know how much it costs per test, but think about the expense if it takes $1 to rerun each test in the vendor’s database. Ancestry has more than 20 million tests.
While we, as consumers, are always chomping at the bit for new and better ethnicity results – the testing companies need to be sure it really is “better,” not just different before they invest the money to reprocess and update results.
This is probably why 23andMe decided to cease updating older kits. The newer tests require a subscription which is recurring revenue.
The same is true when DNA testing companies need to rematch their entire user base. This happens when the criteria for matching changes. For example, Ancestry purged a large number of matches for all of their customers back in 2020. While match algorithm changes necessitate rematching, with associated costs, this change also provided Ancestry with the huge benefit of eliminating approximately half of their customer’s matches. This freed up storage space, either physically in their data center or space rented in the cloud, representing substantial cost-savings.
How long can a DNA testing company reasonably be expected to continue investing in a product which never generates additional revenue but for which the maintenance and reinvestment costs never end?
Ancestry and MyHeritage both hope to offset the expenses of maintaining their customer’s DNA tests and providing free updates by selling subscriptions to their record services. 23andMe wants you to purchase a new test and a yearly subscription. FamilyTreeDNA wants you to purchase a Big Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA test.
OK, now let’s look at my matches at Ancestry.
Ancestry
I’ve taken two Ancestry tests, V1 and V2. There were some differences, which I wrote about here and here. V2 is no longer the current chip.
Except for 23andMe who wants their customers to purchase their most current test, the other companies no longer routinely announce new chip versions. They just go about their business. The only way you know that a vendor actually changed something is when the other companies who accept uploads suddenly encounter an issue with file formats. It always takes a few weeks to sort that out.
My Ancestry V1 test’s ethnicity results don’t show my Native American ethnicity.
Ancestry results were updated in June 2022
However, my V2 results do include Native American ethnicity.
Matches at Ancestry
I have many more matches on my V1 test at Ancestry because I took steps to preserve my smaller matches when Ancestry initiated its massive purge in 2020. I wrote about that here and here.
Ancestry’s SideView breaks matches down into maternal, paternal, and unassigned based on your side selection. You tell Ancestry which side is which. You may be able to determine which “side” is maternal or paternal either by your ethnicity or shared matches. While SideView is not always accurate, it’s a good place to begin.
| Match Category | Ancestry V1 Test | Ancestry V2 Test |
| Maternal | 15,587 | 15,116 |
| Paternal | 42,247 | 41,870 |
| Both | 2 | 2 |
| Unassigned | 48,999 | 4,127 |
| Total | 106,835 | 61,115 |
Ancestry either displays all your matches or your matches by side, which I used to compile the table above. I suspect that Ancestry is not assigning any of the smaller preserved matches to “sides” based on the numbers above.
Ancestry implemented a process called Timber that removes DNA that they feel is “too matchy,” meaning you match enough people in this region that they think it’s a pileup region for you personally, and therefore not useful. In some cases, enough DNA is removed causing that person to no longer be considered a match because they fall beneath the match threshold. I am not a fan of Timber.
Your match amount shown is AFTER Timber has removed those segments. Unweighted shared DNA is your pre-Timber match amount.
You can view the Unweighted shared DNA by clicking on the amount of shared DNA on your match list.
You can read Ancestry’s Matching White Paper, here.
Let’s take a look at my matches. I’ve listed both weighted and unweighted where they are different.
| Match | Ancestry V1 | Ancestry V2 |
| Michael | 755 cM, 35 seg | 737 cM, 33 seg |
| Edward | 66 cM, 4 seg (unweighted 86 cM) | 65 cM, 4 seg (unweighted 86 cM) |
| Tom | 59 cM, 3 seg (unweighted 63) | Same |
| Jonathon | 43 cM, 4 seg, (unweighted 52 cM) | Same |
| Matthew | 20 cM, 2 seg (unweighted 35 cM) | Same |
| Harold | 132 cM, 7 seg | 135 cM, 6 seg |
| Dean | 67 cM, 4 seg (unweighted 78 cM) | 66 cM, 4 seg (unweighted 78 cM) |
| Debbie | 93 cM, 5 seg | Same |
| Valli | 142 cM, 3 seg | Same |
| Jared | 20 cM, 1 seg (unweighted 22 cM) | Same |
Timber only removes DNA when the match is under 90 cM. Almost every match under 90 cM has some DNA removed.
Ancestry Summary
The results of the two Ancestry tests are very close.
In some circumstances, no DNA is removed by Timber, so the unweighted is the same as the weighted. However, in other cases, a significant amount is removed. 15 cM of Matthew’s 35 cM was removed by Timber, reducing his total to 20 cM.
Remember that Ancestry does not show shared matches unless they are greater than 20 cM, which is different than any other DNA testing company.
At one point, Ancestry was selling a health test that was also a genealogy test. That test utilized a different chip that is not accepted for uploads by other vendors. The results of that test might well be different that the “normal” Ancestry tests focused on genealogy. The Ancestry health test is no longer offered.
Companies that Accept Uploads
DNA testing companies that accept uploaded DNA files from other DNA testing companies need to process the uploaded file, just like a file that is generated in their own lab. Of course, they must deal with the differences between uploaded files and their own file format. The processing includes imputation and formulates the uploaded file so that it works with the tools that they provide for their customers, including ethnicity (by whatever name they use) matching, family matching (bucketing), advanced matching, the match matrix, triangulation, AutoClusters, Theories of Family Relativity, and other advanced tools.
Of course, the testing company accepting uploads can only work with the DNA locations provided by the original DNA testing company in the uploaded file.
Matching and some additional tools are free to uploaders, but advanced tools require an inexpensive unlock.
FamilyTreeDNA
I took a test at FamilyTreeDNA, plus uploaded a copy of both of my Ancestry DNA files.
FamilyTreeDNA named their population (ethnicity) test myOrigins and the current version is V3. I wrote about the rollout and comparison in September of 2020, here.
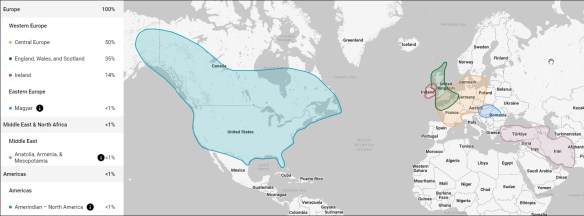
My DNA test taken at FamilyTreeDNA, above, reveals Native American segments that match reference populations found both in North and South America and the Caribbean Islands.
At FamilyTreeDNA, my Ancestry V1 uploaded file results show Native American population matches only in North America.
Interestingly, my Ancestry V1 file processed AT Ancestry did not reveal Native American ancestry, but the same file uploaded to and processed at FamilyTreeDNA did show Native American results, reflecting the difference between the vendors’ internal algorithms and reference populations utilized.
My myOrigins results from my Ancestry V2 uploaded file at FamilyTreeDNA also include my North American Native American segments. The V2 test also showed Native American ethnicity at Ancestry, so clearly something changed in Ancestry’s algorithm, locations tested, and/or reference populations between V1 and V2.
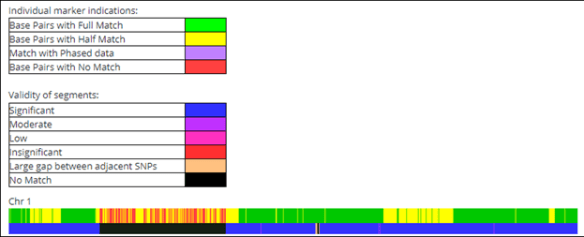
Fortunately, FamilyTreeDNA provides both chromosome painting and a population download file so I can match those Native segments with my autosomal matches to identify which of my ancestors contributed those specific segments.
One of my Native segments is shown in pink on Chromosome1. My mother has a Native segment in exactly the same location, so I know that this segment originated with my mother’s ancestors.
I downloaded the myOrigins population segment file and painted my results at DNAPainter, along with the matches where I can identify our common ancestor. This allowed me to pinpoint the ancestral line that contributed this Native segment in my maternal line. You can read about using DNAPainter, here.
FamilyTreeDNA Matches
I have significantly more matches at FamilyTreeDNA on their test than on either of my Ancestry tests that I uploaded. However, nearly the same number are maternally or paternally assigned through Family Matching, with the remainder unassigned. You can read about Family Matching here.
| Match Category | FamilyTreeDNA Test | Ancestry V1 at FamilyTreeDNA | Ancestry V2 at FamilyTreeDNA |
| Paternal | 3,479 | 3,572 | 3,422 |
| Maternal | 1,549 | 1,536 | 1,477 |
| Both | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| All | 8,154 | 6,397 | 6,579 |
Family matching, aka bucketing, automatically assigns my matches as maternal and paternal by linking known relatives to their place in my tree.
I completed the following match chart using my original test taken at FamilyTreeDNA, plus the same match at FamilyTreeDNA for both of my Ancestry tests.
In other words, Cheryl matched me at 467 cM on 21 segments on the original test taken at FamilyTreeDNA. She matched me on 473 cM and 21 segments on my Ancestry V1 test uploaded to FamilyTreeDNA and on 483 cM and 22 segments on the Ancestry V2 test uploaded to FamilyTreeDNA.
| Match | FamilyTreeDNA | Ancestry V1 at FTDNA | Ancestry V2 at FTDNA |
| Cheryl | 467 cM, 21 seg | 473 cM, 21 seg | 483 cM, 22 seg |
| Patricia | 195 cM, 11 seg | 189 cM, 11 seg | 188 cM, 11 seg |
| Tom | 77 cM, 4 seg | 71 cM, 4 seg | 76 cM, 4 seg |
| Thomas | 72 cM, 3 seg | 71 cM, 3 seg | 74 cM, 3 seg |
| Roland | 29 cM, 1 seg | 35 cM, 2 seg | 35 cM, 2 seg |
| Rex | 62 cM, 4 seg | 55 cM, 3 seg | 57 cM, 3 seg |
| Don | 395 cM, 18 seg | 362 cM, 15 seg | 398 cM, 18 seg |
| Ian | 64 cM, 4 seg | 56 cM, 4 seg | 64 cM, 4 seg |
| Stacy | 490 cM, 18 seg | 494 cM, 15 seg | 489 cM, 14 seg |
| Harold | 127 cM, 5 cM | 133 cM, 6 seg | 143 cM, 6 seg |
| Dean | 81 cM, 4 seg | 75 cM, 3 seg | 83 cM, 4 seg |
| Carl | 103 cM, 4 seg | 101 cM, 4 seg | 102 cM, 4 seg |
| Debbie | 99 cM, 5 seg | 97 cM, 5 seg | 99 cM, 5 seg |
| David | 373 cM, 16 seg | 435 cM, 19 seg | 417 cM, 18 seg |
| Amos | 176 cM, 7 seg | 177 cM. 8 seg | 177 cM, 7 seg |
| Buster | 387 cM, 15 seg | 396 cM, 16 seg | 402 cM, 17 seg |
| Charlene | 461 cM, 21 seg | 450 cM, 21 seg | 448 cM, 20 seg |
| Carol | 65 cM, 6 seg | 64 cM, 6 seg | 65 cM, 6 seg |
I have tested many of my cousins at FamilyTreeDNA and encouraged others to test or upload. I’ve attempted to include enough people so that I can have common matches at least at one other DNA testing company for comparison.
FamilyTreeDNA Summary
The matches are relatively close, with a few being exact.
Interestingly, some of the segment counts are different. In most cases, this results from one segment being broken into multiple segments by one or more of the tests, but not always. In the couple that I checked, the entire segment seems to descend from the same ancestral couple, so the break is likely a result of not all of the same DNA locations being tested, plus the limits of imputation.
MyHeritage
I have two tests at MyHeritage. One taken at MyHeritage, and an uploaded file from FamilyTreeDNA.
MyHeritage displays both ethnicity results and Genetic Groups which maps groups of people that you match. I left the Genetic Groups setting at the highest confidence level. Shifting it to lower displays additional Genetic Groups, some of which overlap with or are within ethnicity regions.
My test taken at MyHeritage, above, shows several ethnicities and Genetic Groups, but no Native American.
My FamilyTreeDNA kit processed at MyHeritage shows the same ethnicity regions, one additional Genetic Group, plus Native American heritage in the Amazon which is rather surprising given that I don’t show Native in North American regions where I’m positive my Native ancestors lived.
MyHeritage Matching
At MyHeritage, I compared the results of the test I took with MyHeritage, and a test I uploaded from FamilyTreeDNA. Fewer than half of my matches can be assigned to a parent via shared matching.
| Matches | MyHeritage Test | FamilyTreeDNA at MyHeritage |
| Paternal | 4,422 | 6,501 |
| Maternal | 2,660 | 3,655 |
| Total | 13,233 | 16,147 |
I have rounded my matches at MyHeritage to the closest cM.
| Match | MyHeritage Test | FamilyTreeDNA at MyHeritage |
| Michael | 801 cM, 32 seg | 823 cM, 31 segments |
| Cheryl | 467 cM, 23 seg | 477 cM, 23 seg |
| Roland | No match | 28 cM, 1 seg |
| Patty | 156 cM, 9 seg | 151 cM, 9 seg |
| Rex | 43 cM, 4 seg | 53 cM, 3 seg |
| Don | 369 cM, 16 seg | 382 cM, 17 seg |
| David | 449 cM, 17 seg | 460 cM, 17 seg |
| Charlene | 454 cM, 23 seg | 477 cM, 24 seg |
| Buster | 408 cM, 15 seg | 410 cM, 16 seg |
| Amos | 183 cM, 8 seg | Same |
| Carol | 78 cM, 6 seg | 87 cM, 7 seg |
MyHeritage Summary
I was surprised to discover that Roland had no match with the MyHeritage test, but did with the FamilyTreeDNA test. I wonder if this is a searching or matching glitch, especially since both companies use the same chip. 28 cM in one segment is a reasonably large match, and even if it was divided in two, it would still be over the matching threshold. I know this is a valid match because Roland triangulates with me and several cousins, I’m positive of our common ancestor, and he also matches me at both FamilyTreeDNA and 23andMe.
Other than that, the matches are reasonably close, with one being exact.
Your Matches Aren’t Everyplace
I unsuccessfully searched for someone who was a match to me in all four databases. Ancestry does not permit match downloads, so I had to search manually. People don’t always use the same names in different databases.
Surprisingly, I was unable to find one match who is in all of the databases. Many people only suggest testing at Ancestry because they have the largest database, but if you look at the following comparison chart that I’ve created, you’ll see that 16 of 26 people, or 62% were not at Ancestry. Conversely, many people were at Ancestry and not elsewhere. I could not find five maternal and five paternal matches at Ancestry that I could identify as matches in another database. 40% were not elsewhere.
If you think for one minute that it doesn’t matter for genealogy if you’re in all four major databases, please reconsider. It surely does matter.
Every single vendor has matches that the others don’t. Substantial, important matches. I have found first and second-cousin matches in every database that weren’t elsewhere.
Many of the original testers have passed away and can’t test again. My mother can never test at either 23andMe or Ancestry, but she is at both FamilyTreeDNA and MyHeritage because I could upgrade her kit at FamilyTreeDNA after she died. I uploaded her to MyHeritage. Of course, because she is a generation closer to our ancestors, she has many valuable matches that I don’t.
Each vendor provides either an email address or a messaging platform for you to contact your matches. Don’t be discouraged if they don’t answer. Just today, I received a reply that was years in the making.
Genealogists hope for immediate gratification, but we are actually in this for the long game. Play it with every tool at your disposal.
The Answer
Does it matter if you test at a DNA testing company, or upload a file?
I know this was a very long answer to what my readers hoped was a simple yes or no question.
There is no consistent answer at either FamilyTreeDNA or MyHeritage, the two DNA testing companies that accept uploads. Be sure you’re in both databases. My closest two matches that I did not test were found at MyHeritage. Here’s a direct link to upload at MyHeritage.
Of the vendors, those two should be the closest to each other because they are both processed in the GenebyGene lab, but again, the actual chip version, when the test was originally taken, and each vendor’s internal processing will result in differences. Neither the original test at the DNA testing company nor the uploaded files have consistently higher or lower matches. Neither type of test or upload appears to be universally more or less accurate. Differences in either direction seem to occur on a match-by-match basis. Many are so close as to be virtually equivalent, with a few seemingly random exceptions. Of course, we always have to consider Timber.
If you upload, unlock the advanced features at both FamilyTreeDNA and MyHeritage.
If you upload to a DNA testing company, you may discover in the future that some features and functions will only be available to original testers.
Personally, if I had the option, I would test at the company directly simply because it eliminates or at least reduces the possibility of future incompatibilities – with the exception of 23andMe which has chosen to not provide consistent updates to older tests. I’m incredibly grateful I didn’t test my mother or now deceased family members at 23andMe, and only there. I would be heartsick, heartbroken, and furious.
Our DNA is an extremely valuable resource for our genealogy. It’s the gift that truly keeps on giving, day after day, even when other records don’t exist. Be sure you and your family members are in each database one way or another, and test your Y-DNA (for males) and mitochondrial DNA (for everyone) to have a complete arsenal at your disposal.
_____________________________________________________________
Follow DNAexplain on Facebook, here.
Share the Love!
You’re always welcome to forward articles or links to friends and share on social media.
If you haven’t already subscribed (it’s free,) you can receive an email whenever I publish by clicking the “follow” button on the main blog page, here.
You Can Help Keep This Blog Free
I receive a small contribution when you click on some of the links to vendors in my articles. This does NOT increase the price you pay but helps me to keep the lights on and this informational blog free for everyone. Please click on the links in the articles or to the vendors below if you are purchasing products or DNA testing.
Thank you so much.
DNA Purchases and Free Uploads
- FamilyTreeDNA – Y, mitochondrial and autosomal DNA testing
- MyHeritage DNA – Autosomal DNA test
- MyHeritage FREE DNA file upload – Upload your DNA file from other vendors free
- AncestryDNA – Autosomal DNA test
- 23andMe Ancestry – Autosomal DNA only, no Health
- 23andMe Ancestry Plus Health
Genealogy Products and Services
- MyHeritage FREE Tree Builder – Genealogy software for your computer
- MyHeritage Subscription with Free Trial
- Legacy Family Tree Webinars – Genealogy and DNA classes, subscription-based, some free
- Legacy Family Tree Software – Genealogy software for your computer
- Newspapers.com – Search newspapers for your ancestors
- NewspaperArchive – Search different newspapers for your ancestors
My Book
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – by Roberta Estes, for those ordering the e-book from anyplace, or paperback within the United States
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – for those ordering the paperback outside the US
Genealogy Books
- Genealogical.com – Lots of wonderful genealogy research books
Genealogy Research
- Legacy Tree Genealogists – Professional genealogy research