Which DNA test should I buy, and why?
I receive questions like this often. As a reminder, I don’t take private clients anymore, which means I don’t provide this type of individual consulting or advice. However, I’m doing the next best thing! In this article, I’m sharing the step-by-step process that I utilize to evaluate these questions so you can use the process too.
It’s important to know what questions to ask and how to evaluate each situation to arrive at the best answer for each person.
Here’s the question I received from someone I’ll call John. I’ve modified the wording slightly and changed the names for privacy.
I’m a male, and my mother was born in Charleston, SC. My maternal grandmother’s maiden name was Jones and a paternal surname was Davis. The family was supposed to have been Black, Dutch, Pennsylvania Dutch, and Scots-Irish…only once was I told I was 3/16 Indian, with Davis being 3/4 and Jones being full Indian.
Do I have enough reasonable information to buy a test, and which one?
Please note that it’s common for questions to arrive without all the information you need to provide a sound answer – so it’s up to you to ask those questions and obtain clarification.
Multiple Questions
There are actually multiple questions here, so let me parse this a bit.
- John never mentioned what his testing goal was.
- He also never exactly said how the paternal line of Davis was connected, so I’ve made an assumption. For educational purposes, it doesn’t matter because we’re going to walk through the evaluation process, which is the same regardless.
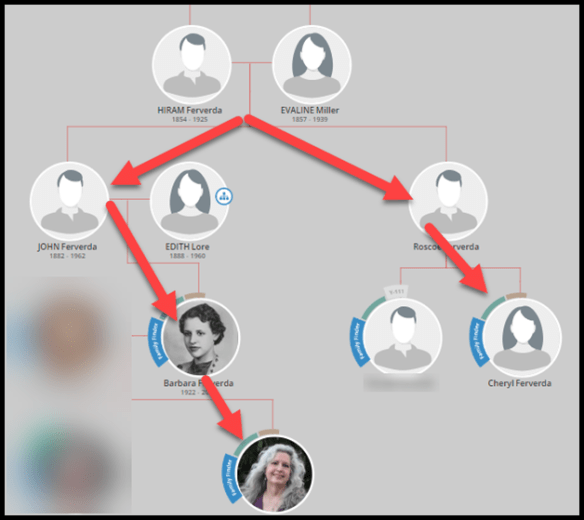
- John did not include a tree or a link to a tree, so I created a rudimentary tree to sort through this. I need the visuals and normally just sketch it out on paper quickly.
- Does John have enough information to purchase a test?
- If so, which test?
There is no “one size fits all” answer, so let’s discuss these one by one.
Easy Answers First
The answer to #4 is easy.
Anyone with any amount of information can purchase a DNA test. Adoptees do it all the time, and they have no prior information.
So, yes, John can purchase a test.
The more difficult question is which test, because that answer depends on John’s goals and whether he’s just looking for some quick information or really wants to delve into genealogy and learn. Neither approach is wrong.
Many people think they want a quick answer – and then quickly figure out that they really want to know much more about their ancestors.
I wrote an article titled DNA Results – First Glances at Ethnicity and Matching for new testers, here.
Goals
Based on what John said, I’m going to presume his goals are probably:
- To prove or disprove the family oral history of Black, Dutch, Pennsylvania Dutch (which is actually German,) Scots-Irish, and potentially Native American.
- John didn’t mention actual genealogy, which would include DNA matches and trees, so we will count that as something John is interested in secondarily. However, he may need genealogy records to reach his primary goal.
If you’re thinking, “The process of answering this seemingly easy question is more complex than I thought,” you’d be right.
Ethnicity in General
It sounds like John is interested in ethnicity testing. Lots of people think that “the answer” will be found there – and sometimes they are right. Often not so much. It depends.
The great news is that John really doesn’t need any information at all to take an autosomal DNA test, and it doesn’t matter if the test-taker is male or female.
To calculate each tester’s ethnicity, every testing company compiles their own reference populations, and John will receive different results at each of the major companies. Each company updates their ethnicity results from time to time as well, and they will change.
Additionally, each company provides different tools for their customers.
The ethnicity results at different companies generally won’t match each other exactly, and sometimes the populations look quite different.
Normally, DNA from a specific ancestor can be found for at least 5 or 6 generations. Of course, that means their DNA, along with the DNA from all of your other ancestors is essentially combined in a communal genetic “pot” of your chromosomes, and the DNA testing company needs to sort it out and analyze your DNA for ethnicity.
DNA descended from ancestors, and their populations, further back in people’s trees may not be discerned at all using autosomal DNA tests.
A much more specific “ethnicity” can be obtained for both the Y-DNA line, which is a direct patrilineal line for men (blue arrow,) and the mitochondrial DNA line (pink arrows,) which is a direct matrilineal line for everyone, using those specific tests.
We will discuss both of those tests after we talk about the autosomal tests available from the four major genealogy DNA testing companies. All of these tools can and should be used together.
Let’s Start with Native American
Let’s evaluate the information that John provided.
John was told that he “was 3/16 Indian, with Davis being 3/4 and Jones being full Indian.”
We need to evaluate this part of his question slightly differently.
I discussed this in the article, Ancestral DNA Percentages – How Much of Them is in You?
First, we need to convert generations to 16ths.
You have two ancestors in your parent’s generation, four in your grandparents, and so forth. You have 16 great-great-grandparents. So, if John was 3/16th Native, then three of his great-great-grandparents would have been fully Native, or an equivalent percentage. In other words, six ancestors in that generation could have been half-Native. Based on what John said, they would have come from his mother’s side of the tree. John is fortunate to have that much information to work with.
He told us enough about his tree that we can evaluate the statement that he might be 3/16ths Native.
Here’s the tree I quickly assembled in a spreadsheet based on John’s information.
His father, at left, is not part of the equation based on the information John provided.
On his mother’s side, John said that Grandfather Davis is supposed to be three-quarters Native, which translates to 12/16ths. Please note that it would be extremely beneficial to find a Y-DNA tester from his Davis line, like one of his mother’s brothers, for example.
John said that his Grandmother Jones is supposed to be 100% Native, so 16/16ths.
Added together, those sum to 28/32, which reduces down to 14/16th or 7/8th for John’s mother.
John would have received half of his autosomal DNA from his mother and half from his non-Native father. That means that if John’s father is 100% non-Native, John would be half of 14/16ths or 7/16ths, so just shy of half Native.
Of course, we know that we don’t always receive exactly 50% of each of our ancestors’ DNA (except for our parents,) but we would expect to see something in the ballpark of 40-45% Native for John if his grandmother was 100% Native and his grandfather was 75%.
Using simple logic here, for John’s grandmother to be 100% Native, she would almost assuredly have been a registered tribal member, and the same if his grandfather was 75% Native. I would think that information would be readily available and well-known to the family – so I doubt that this percentage is accurate. It would be easy to check, though, on various census records during their lifetimes where they would likely have been recorded as “Indian.” They might have been in the special “Indian Census” taken and might be living on a reservation.
It should also be relatively easy to find their parents since all family members were listed every ten years in the US beginning with the 1850 census.
The simple answer is that if John’s grandparents had as much Native as reported, he would be more than 3/16th – so both of these factoids cannot simultaneously be accurate. But that does NOT mean neither is accurate.
John could be 7/8th or 40ish%, 3/16th or 18ish%, or some other percentage. Sometimes, where there is smoke, there is fire. And that seems to be the quandary John is seeking to resolve.
Would Ethnicity/Population Tests Show This Much Native?
Any of the four major testing companies would show Native for someone whose percentage would be in the 40% or 18% ballpark.
The easiest ethnicities to tell apart from one another are continental-level populations. John also stated that he thinks he may also have Black ancestry, plus Dutch, Pennsylvania Dutch (German), and Scots-Irish. It’s certainly possible to verify that using genealogy, but what can DNA testing alone tell us?
How far back can we expect to find ethnicities descending from particular ancestors?
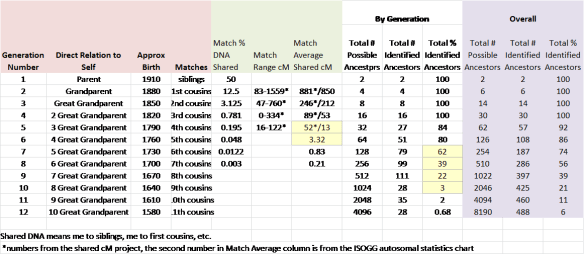
In this table, you can see at each generation how many ancestors you have in that generation, plus the percentage of DNA, on average, you would inherit from each ancestor.
All of the major DNA testing companies can potentially pick up small trace percentages, but they don’t always. Sometimes one company does, and another doesn’t. So, if John has one sixth-generation Native American ancestor, he would carry about 1.56% Native DNA, if any.
- Sometimes a specific ethnicity is not found because, thanks to random recombination, you didn’t inherit any of that DNA from those ancestors. This is why testing your parents, grandparents, aunts, uncles, and siblings can be very important. They share your same ancestors and may have inherited DNA that you didn’t that’s very relevant to your search.
- Sometimes it’s not found because the reference populations and algorithms at that testing company aren’t able to detect that population or identify it accurately, especially at trace levels. Every DNA testing company establishes their own reference populations and writes internal, proprietary ethnicity analysis algorithms.
- Sometimes it’s not found because your ancestor wasn’t Native or from that specific population.
- Sometimes it’s there, but your population is called something you don’t expect.
For example, you may find Scandinavian when your ancestor was from England or Ireland. The Vikings raided the British Isles, so while some small amount of Scandinavian is not what you expect, that doesn’t mean it‘s wrong. However, if all of your family is from England, it’s not reasonable to have entirely Scandinavian ethnicity results.
It’s also less likely as each generation passes by that the information about their origins gets handed down accurately to following generations. Most non-genealogists don’t know the names of their great-grandparents, let alone where their ancestors were from.
Using a 25-year average generation length, by the 4th generation, shown in the chart above, you have 16 ancestors who lived approximately 100 years before your parents were born, so someplace in the mid-1800s. It’s unlikely for oral history from that time to survive intact. It’s even less likely from a century years earlier, where in the 7th generation, you have 128 total ancestors.
The best way to validate the accuracy of your ethnicity estimates is by researching your genealogy. Of course, you need to take an ethnicity test, or two, in order to have results to validate.
Ethnicity has a lot more to offer than just percentages.
Best Autosomal Tests for Native Ethnicity
Based on my experience with people who have confirmed Native ancestry, the two best tests to detect Native American ethnicity, especially in smaller percentages, are both FamilyTreeDNA and 23andMe.
In addition to percentages, both 23andMe and FamilyTreeDNA provide chromosome painting for ethnicity, along with segment information in download files. In other words, they literally paint your ethnicity results on your chromosomes.
They then provide you with a file with the “addresses” of those ethnicities on your chromosomes, which means you can figure out which ancestors contributed those ethnicity segments.
The person in the example above, a tester at FamilyTreeDNA, is highly admixed with ancestors from European regions, African regions and Native people from South America.
Trace amounts of Native American with a majority of European heritage would appear more like this.
You can use this information to paint your chromosome segments at DNAPainter, along with your matching segments to other testers where you can identify your common ancestors. This is why providing trees is critically important – DNA plus ancestor identification with our matches is how we confirm our ancestry.
This combination allows you to identify which Native (or another ethnicity) segments descended from which ancestors. I was able to determine which ancestor provided that pink Native American segment on chromosome 1 on my mother’s side.
I’ve provided instructions for painting ethnicity segments to identify their origins in specific ancestors, here.
Autosomal and Genealogy
You may have noticed that we’ve now drifted into the genealogy realm of autosomal DNA testing. Ethnicity is nice, but if you want to know who those segments came from, you’ll need:
- Autosomal test matching to other people
- To identify your common ancestor with as many matches as you can
- To match at a company who provides you with segment information for each match
- To work with DNAPainter, which is very easy
The great news is that you can do all of that using the autosomal tests you took for ethnicity, except at Ancestry who does not provide segment information.
Best Autosomal Test for Matching Other Testers
The best autosomal test for matching may be different for everyone. Let’s look at some of the differentiators and considerations.
If you’re basing a testing recommendation solely on database size, which will probably correlate to more matches, then the DNA testing vendors fall into this order:
If you’re basing that recommendation on the BEST, generally meaning the closest matches for you, there’s no way of knowing ahead of time. At each of the four DNA testing companies, I have very good matches who have not tested elsewhere. If I weren’t in all four databases, I would have missed many valuable matches.
If you’re basing that recommendation on which vendor began testing earliest, meaning they have many tests from people who are now deceased, so you won’t find their autosomal tests in other databases that don’t accept uploads, the recommended testing company order would be:
- FamilyTreeDNA with tests from people who originally tested two decades ago.
- 23andMe
- Ancestry
- MyHeritage
If you’re basing that recommendation on matches to people who live in other countries, the order would be:
Ancestry and 23andMe are very distant third/fourth because they did not sell widely outside the US initially and still don’t sell in as many countries as the others, meaning their testers’ geography is more limited. However, Ancestry is also prevalent in the UK.
If you’re basing that recommendation on segment information and advanced tools that allow you to triangulate and confirm your genetic link to specific ancestors, the order would be:
Ancestry does NOT provide any segment information.
If you’re basing that recommendation on unique tools provided by each vendor, every vendor has something very beneficial that the others don’t.
In other words, there’s really no clear-cut answer for which single autosomal DNA test to order. The real answer is to be sure you’re fishing in all the ponds. The fish are not the same. Unique people test at each of those companies daily who will never be found in the other databases.
Test at or upload your DNA to all four DNA testing companies, plus GEDmatch. Step-by-step instructions for downloading your raw data file and uploading it to the DNA testing companies who accept uploads can be found, here.
Test or Upload
Not all testing companies accept uploads of raw autosomal DNA data files from other companies. The good news is that some do, and it’s free to upload and receive matches.
Two major DNA testing companies DO NOT accept uploads from other companies. In other words, you have to test at that company:
Two testing companies DO accept uploads from the other three companies. Uploads and matching are free, and advanced features can be unlocked very cost effectively.
- FamilyTreeDNA – free matching and $19 unlock for advanced features
- MyHeritage – free matching and $29 unlock.for advanced features
I recommend testing at both 23andMe and Ancestry and uploading one of those files to both FamilyTreeDNA and MyHeritage, then purchasing the respective unlocks.
GEDmatch
GEDmatch is a third-party matching site, not a DNA testing company. Consider uploading to GEDmatch because you may find matches from Ancestry who have uploaded to GEDmatch, giving you access to matching segment information.
Other Types of DNA
John provided additional information that may prove to be VERY useful. Both Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA can be tested as well and may prove to be more useful than autosomal to positively identify the origins of those two specific lines.
Let’s assume that John takes an autosomal test and discovers that indeed, the 3/16th Native estimate was close. 3/16th equates to about 18% Native which would mean that three of his 16 great-great-grandparents were Native.
John told us that his Grandmother Jones was supposed to be 100% Native.
At the great-great-grandparent level, John has 16 ancestors, so eight on his mother’s side, four from maternal grandmother Jones and four from his maternal grandfather Davis.
John carries the mitochondrial DNA of his mother (red boxes and arrows,) and her mother, through a direct line of females back in time. John also carries the Y-DNA of his father (dark blue box, at left above, and blue arrows below.)
Unlike autosomal DNA which is admixed in every generation, mitochondrial DNA (red arrows) is inherited from that direct matrilineal line ONLY and never combines with the DNA of the father. Mothers give their mitochondrial DNA to both sexes of their children, but men never contribute their mitochondrial DNA to offspring. Everyone has their mother’s mitochondrial DNA.
Because it never recombines with DNA from the father, so is never “watered down,” we can “see” much further back in time, even though we can’t yet identify those ancestors.
However, more importantly, in this situation, John can test his own mitochondrial DNA that he inherited from his mother, who inherited it from her mother, to view her direct matrilineal line.
John’s mitochondrial DNA haplogroup that will be assigned during testing tells us unquestionably whether or not his direct matrilineal ancestor was Native on her mother’s line, or not. If not, it may well tell us where that specific line originated.
You can view the countries around the world where Y-DNA haplogroups are found, here, and mitochondrial haplogroups, here.
If John’s mitochondrial DNA haplogroup is Native, that confirms that one specific line is Native. If he can find other testers in his various lines to test either their Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA, John can determine if other ancestors were Native too. If not, those tests will reveal the origins of that line, separate from the rest of his genealogical lines.
Although John didn’t mention his father’s line, if he takes a Y-DNA test, especially at the Big Y-700 level, that will also reveal the origins of his direct paternal line. Y-DNA doesn’t combine with the other parent’s DNA either, so it reaches far back in time too.
Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA tests are laser-focused on one line each, and only one line. You don’t have to try to sort it out of the ethnicity “pot,” wondering which ancestor was or was not Native.
My Recommendation
When putting together a testing strategy, I recommend taking advantage of free uploads and inexpensive unlocks when possible.
- To confirm Native American ancestry via ethnicity testing, I recommend testing at 23andMe and uploading to FamilyTreeDNA, then purchasing the $19 unlock. The free upload and $19 unlock are less expensive than testing there directly.
- For matching, I recommend testing at Ancestry and uploading to MyHeritage, then unlocking the MyHeritage advanced features for $29, which is less expensive than retesting. Ancestry does not provide segment information, but MyHeritage (and the others) do.
At this point, John will have taken two DNA tests, but is now in all four databases, plus GEDmatch if he uploads there.
- For genealogy research on John’s lines to determine whether or not his mother’s lines were Native, I recommend an Ancestry and a MyHeritage records subscription, plus using WikiTree, which is free.
- To determine if John’s mother’s direct matrilineal female line was Native, I recommend that John order the mitochondrial DNA test at FamilyTreeDNA.
- When ordering multiple tests, or uploading at FamilyTreeDNA, be sure to upload/order all of one person’s tests on the same DNA kit so that those results can be used in combination with each other.
Both males and females can take autosomal and mitochondrial DNA tests.
- To discover what he doesn’t know about his direct paternal, meaning John’s surname line – I recommend the Big Y-700 test at FamilyTreeDNA.
Only males can take a Y-DNA test, so women would need to ask their father, brother, or paternal uncle, for example, to test their direct paternal line.
- If John can find a male Davis from his mother’s line, I recommend that he purchase the Big Y-700 test at FamilyTreeDNA for that person, or check to see if someone from his Davis line may have already tested by viewing the Davis DNA Project. Like with mitochondrial DNA, the Y-DNA haplogroup will tell John the origins of his direct Davis male ancestor – plus matching of course. He will be able to determine if they were Native, and if not, discover the origins of the Davis line.
- For assigning segments to ancestors and triangulating to confirm descent from a common ancestor, I recommend 23andMe, MyHeritage, FamilyTreeDNA and GEDmatch, paired with DNAPainter as a tool.
Shopping and Research List
Here are the tests and links recommended above:
- 23andMe
- Ancestry
- MyHeritage Upload with free matching, then $29 unlock
- FamilyTreeDNA Upload with free matching, then $19 unlock
- GEDmatch free upload, then $9.95 monthly subscription for advanced tools if needed
- FamilyTreeDNA mitochondrial DNA test (using the same kit number as the upload)
- FamilyTreeDNA Big Y-700 for John and also for Davis male tester if he can find one
- DNAPainter for uploading ethnicity painting plus segments that can be identified to specific ancestors to determine which ancestors provided which ethnicity segments
- MyHeritage records subscription (free trial) (for genealogy research)
- Ancestry subscription for genealogy research
More Than He Asked
I realize this answer is way more than John expected or even knew to ask. That’s because there is often no “one” or “one best” answer. There are many ways to approach the question after the goal is defined, and the first “answer” received may be a bit out of context.
For example, let’s say John has 2% Native ancestry and took a test at a vendor who didn’t detect it. John would believe he had none. But a different vendor might find that 2%. If it’s on his mother’s direct matrilineal line, mitochondrial DNA testing will confirm, or refute Native, beyond any doubt, regardless of autosomal ethnicity results – but only for that specific ancestral line.
Autosomal DNA can suggest Native across all your DNA, but Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA confirm it for each individual ancestor.
Even when autosomal testing does NOT show Native American, or African, for example, it’s certainly possible that it’s just too far back in time or has not been passed down during random recombination, but either Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA will unquestionably confirm (or refute) the ancestry in question if the right person is tested.
This is exactly why I attempt to find a cousin who descends appropriately from every ancestor and provide testing scholarships. It’s important to obtain Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA information for each ancestor.
Which Test Should I Order?
What steps will help you decide which test or tests to take?
- Define your testing goal.
- Determine if your Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA will help answer the question.
- Determine if you need to find ancestors another generation or two back in time to get the most benefit from DNA testing. In our example, if John discovered that both of his grandparents were enrolled tribal members, that’s huge, and the tribe might have additional information about his family.
- Subscribe to Ancestry and MyHeritage records collections as appropriate to perform genealogical research. Additional information not only provides context for your family, it also provides you with the ability to confirm or better understand your ethnicity results.
- Extend your tree so that you can obtain the best results from the three vendors who support trees; Ancestry, FamilyTreeDNA, and MyHeritage. All three use trees combined with DNA tests to provide you with additional information.
- Order 23andMe and Ancestry autosomal DNA tests.
- Either test at or upload one of those tests to MyHeritage, FamilyTreeDNA, and GEDmatch.
- If a male, order the Big Y-700 DNA test. Or, find a male from your ancestral line who has taken or will take that test. I always offer a testing scholarship and, of course, share the exciting results!
- Order a mitochondrial DNA test for yourself and for appropriately descended family members to represent other ancestors. Remember that your father (and his siblings) all carry your paternal grandmother’s mitochondrial DNA. That’s often a good place to start after testing your own DNA.
- If your parents or grandparents are alive, or aunts and uncles, test their autosomal DNA too. They are (at least) one generation closer to your ancestors than you are and will carry more of your ancestors’ DNA.
- Your siblings will carry some of your ancestors’ DNA that you do not, so test them too if both of your parents aren’t available for testing.
Enjoy!!!
_____________________________________________________________
Follow DNAexplain on Facebook, here.
Share the Love!
You’re always welcome to forward articles or links to friends and share on social media.
If you haven’t already subscribed (it’s free,) you can receive an email whenever I publish by clicking the “follow” button on the main blog page, here.
You Can Help Keep This Blog Free
I receive a small contribution when you click on some of the links to vendors in my articles. This does NOT increase the price you pay but helps me to keep the lights on and this informational blog free for everyone. Please click on the links in the articles or to the vendors below if you are purchasing products or DNA testing.
Thank you so much.
DNA Purchases and Free Uploads
- FamilyTreeDNA – Y, mitochondrial and autosomal DNA testing
- MyHeritage DNA – Autosomal DNA test
- MyHeritage FREE DNA file upload – Upload your DNA file from other vendors free
- AncestryDNA – Autosomal DNA test
- 23andMe Ancestry – Autosomal DNA only, no Health
- 23andMe Ancestry Plus Health
Genealogy Products and Services
- MyHeritage FREE Tree Builder – Genealogy software for your computer
- MyHeritage Subscription with Free Trial
- Legacy Family Tree Webinars – Genealogy and DNA classes, subscription-based, some free
- Legacy Family Tree Software – Genealogy software for your computer
- Newspapers.com – Search newspapers for your ancestors
- NewspaperArchive – Search different newspapers for your ancestors
My Book
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – by Roberta Estes, for those ordering the e-book from anyplace, or paperback within the United States
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – for those ordering the paperback outside the US
Genealogy Books
- Genealogical.com – Lots of wonderful genealogy research books
Genealogy Research
- Legacy Tree Genealogists – Professional genealogy research