People have been asking for a step-by-step guide for mitochondrial DNA, and here it is!
This article steps testers through all their results, page by page, including a dozen Discover reports, explaining what the information in each tool means. There’s SO MUCH great content provided, and you’ll want to absorb every tidbit.
This is meant to be a roadmap for you – a recipe card to follow to get the most out of your results.
You can either read through this article once, then sign on to your own account, or sign on now and follow along. Yes, this article is long, but it’s also a one-stop shop when you want information about any page or feature. Refer back to this article as needed, and feel free to forward it to others when they receive their results.
I’ve also provided additional resources for you at each step of the way, along with many tips and suggestions to help you help yourself.
I’m using the LeJeune sisters of Acadia as my example – in part because there were several questions about their heritage – including whether they were actually sisters, whether they were Native American, and if a third woman was also a sister.
Think about why you tested, and what you hope to learn so you know where to focus.
Everyone has their own motivation for testing, and we all want to extract as much information as possible. Some answers are genetic – thanks to mitochondrial, Y-DNA, and autosomal testing. Some answers are historical and genealogical. All of them need to mesh nicely together and confirm each other.
When they don’t, if they don’t, we need to understand how to discern the truth.
Every Ancestor Has a Mitochondrial DNA Story to Tell You
Sometimes it’s not our own results we’re analyzing, but the results of another tester – a cousin whose mitochondrial DNA represents a particular shared ancestor. We aren’t restricted to just our own mitochondrial DNA to decipher our ancestors’ stories.
What messages and secrets do those ancestors have to tell us? Our results read like the very best mystery novel ever – except it’s not a novel – it’s fact. And it’s ours!
Mitochondrial DNA is only passed from mothers to their children, never admixed or combined with the DNA of the father, so your mitochondrial DNA today is either exactly the same as that of your ancestors a few generations ago, or very close if a mutation has occurred between when they lived and today’s tester.
One of mitochondrial DNA’s strengths is that it can reach far back in time, it’s message undiluted and uninterrupted by recombination.
The messages from our ancestors are very clear. We just need to understand how to hear what they are telling us.
Step-by-Step Soup to Nuts
We will analyze the mitochondrial DNA results of multiple testers who descend from the LeJeune sisters, Edmee and Catherine, born in 1624 and 1633, respectively, to see what they have to tell their descendants. For a very long time, rumors abounded that their mother was Native American, so we will keep that in mind as we review all matching, Mitotree and mtDNA Discover tools provided by FamilyTreeDNA.
We will also learn how to evaluate seemingly conflicting information.
Soup to nuts – we will incorporate every sliver of information along the way and extract every morsel that can help you. Think of this article as your recipe and the reports and information as ingredients!
To be clear, you don’t HAVE to read all of this or decipher anything if you don’t want to. You can just glance at the matches and be on your way – but if you do – you’re leaving an incredible amount of useful information on the table, along with MANY hints that you can’t find elsewhere.
If there was an out-of-print book about this ancestral line in a rare book collection someplace, as a genealogist, you would drive half-way across the country to access that information. This is your rare book, that updates itself, and you don’t have to do anything other than take a mitochondrial DNA test, or find a cousin to take one for lines you don’t carry..
Come along and join the fun! Your ancestors are waiting!
The LeJeune Question
Recently, I wrote about my ancestor Catherine LeJeune, who was born about 1633, probably in France before her family settled in Acadia, present-day Nova Scotia.
The identity of her parents has been hotly contested and widely debated for a long time.
I intentionally did not address her DNA results in that article because I wanted to establish the historical facts about her life and address her mitochondrial DNA separately. The process we are following to analyze her DNA results is the same process everyone should follow, which is why we are taking this step-by-step approach, complete with detailed explanations.
Often, when people hit a brick wall with an ancestor, especially during European colonization of the Americas, someone suggests that the person surely “must be” Native American. Lack of records is interpreted to add layers of evidence, when, in fact, absence of evidence is not evidence of absence.
For example, for many of the earliest French Acadians, birth and baptism records have NOT been located in France, where massive record loss has been experienced.
Additionally, not all records that do exist have been indexed, transcribed, or digitized. Many are damaged and/or nearly impossible to read. Lack of records does NOT mean that those settlers weren’t French, or in this case, it does NOT indicate that they were Native American. It simply means we are lacking that piece of evidence.
Enter mitochondrial DNA.
This article is focused on how to use mitochondrial DNA to decode these messages from our ancestors. I’m providing a very short summary of the relevant historical factors about the LeJeune sisters so readers can keep this in mind as we review the 17+ tools waiting for us when mitochondrial DNA results are ready.
The First Acadian Settlers
The Acadians were French settlers in what is today Nova Scotia. The first Acadians arrived in LaHeve (LaHave), on the southern coast of Acadia, in 1632 after Acadia was returned to France from English control. There may or may not have been any French families in the original group, but if so, very few. In 1636, another group of settlers arrived, but no LeJeune is on the roster.
At the end of 1636, the fledgling Acadian colony was moved from LaHeve, on the southern coast, to Port Royal, a more protected environment.
While we don’t know exactly when the family of Catherine and Edmee LeJeune arrived, we can bracket the dates. We know that Catherine’s sister, Edmee LeJeune, born about 1624, married another settler, Francois Gautrot, about 1644 in Port Royal, so they had arrived by that time.
Edmee’s 1624 birth year is important for two reasons. First, there were no French settlers in the part of Acadia that became Nova Scotia in 1624, so that clearly demonstrates that Edmee was born in France.
It’s unlikely that Catherine was born in Acadia in 1633 given that the first known families arrived in 1636, and we have their names from the ship roster. Pierre Martin was on the 1636 ship, and Acadian history tells us that his son, Mathieu Martin, was the first French child born in Acadia, about 1636, based on the 1671 census.
We also know that there was an early Acadian man, Jean LeJeune, who was granted land at BelleIsle, near Port Royal, among other Acadian families, but he was deceased before the first Acadian census in 1671. Acadia was under English control again from 1654 to 1670, so Jean LeJeune’s land grant had to have occurred after 1636 and prior to 1654, and is where Catherine LeJeune is found as an adult.
Another source of confusion is that there is a third LeJeune woman, Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard, born about 1659. Her daughter, Catherine Joseph’s 1720 marriage record in Port Royal refers to her mother, Jeanne, as being “d’un nation sauvagé”, giving her parents’ names as Francois Joseph and Jeanne LeJeune “of the Indian Nation.” Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard lived with her first husband in Port Royal, but had relocated to LaHeve by 1708.
You can see why this led to confusion about LeJeune females.
Another male, Pierre LeJeune was associated with LaHeve, which suggests he may have been awarded land there, possibly before the colony moved to Port Royal. One of the reasons that the rumor that Catherine LeJeune had a Native mother is so persistent is the belief that Pierre came over early, as a laborer or soldier, and married a Native woman because there weren’t any European women available.
Pierre may well have arrived as a single man, but there is no shred of evidence to suggest Pierre is the father of the sisters, Catherine LeJeune and Edmee LeJeune. In fact, given that Jeanne was born about 1659, Pierre, if he was her father, may have been born as late as 1627, which makes it impossible for him to have been Catherine and Edmee’s father.
That speculation was before the advent of DNA testing, and before Stephen White discovered that there was also a Jean LeJeune who was awarded land exactly where Catherine is known to have been living a few years later.
While it would be nice to unravel this entire cat’s cradle of confusion, the questions we are seeking to answer definitively here are:
- Are Catherine LeJeune (born 1633) and Edmee LeJeune (born 1624) actually sisters?
- Is the mother of Catherine LeJeune and her sister, Edmee LeJeune, Native American or European?
- Is Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard, born about 1659, “d’un nation sauvagé” another sister of the LeJeune sisters?
- What else is revealed about the LeJeune sisters and their ancestors? Is there something else we should know?
I’ll provide a summary of the combined evidence after our step-by-step mitochondrial analysis.
Testing for Sisters
Mitochondrial DNA is passed from mothers to all of their children, but only females pass it on.
Since we have two LeJeune females, believed to be sisters, we need mitochondrial DNA from direct matrilineal testers for each woman. This is particularly important because we know unquestionably that Edmee was born in France in 1624, prior to Acadian settlement in New France, so her DNA should be European. If they match, it means that Catherine was born to the same mother who was not Native. If they don’t match, there’s a different message.
In some cases, a match might mean that they were born to females related on the matrilineal line, like first cousins, for example. But in the early days of Acadia, there were no European females other than the handful, less than a dozen, who arrived on the Saint-Jehan in 1636.
Fortunately, we have multiple testers for each woman in two DNA projects at FamilyTreeDNA, the only DNA testing company that provides mitochondrial DNA testing and matching. Testers can join special interest projects, and both the Mothers of Acadia Project, and the Acadian AmerIndian Project have testers who descend from the LeJeune sisters.
I’ve identified 28 descendants of Catherine, and 25 from Edmee, giving us a total of 53 known matrilineal descendants to work with. Not all are shown publicly, in projects. Catherine has a known total of 14 testers, and Edmee has 17 that are shown publicly. All testers are members of haplogroup U6a7a1a.
The fact that the descendants of these women match each other, often exactly, combined with Catholic parish register dispensations for their descendants, when taken together, prove conclusively that Catherine and Edmee were sisters, not paternal half-sisters.
Let’s look at each piece of evidence.
Mitochondrial DNA Results
When the lab finishes processing the mtFull test, the results are posted to the account of the test taker.
You’ll see the Maternal Line Ancestry section which displays your mitochondrial mtDNA Results.
The three tabs we will be primarily working with are:
- mtDNA Matches
- Matches Maps
- Discover Haplogroup Reports, which includes another dozen+ reports and an updated Migration Map
- Advanced Matching
At the bottom right of your page, you’ll see two haplogroup badges.
The one at right is called the “Legacy” haplogroup, which means the haplogroup you were assigned prior to the release of the new Mitotree.
The Mitotree mtDNA Haplogroup, with the green “Beta” at the bottom, is the new Mitotree haplogroup, which I wrote about in a series of articles:
- Mitotree is Born
- New Mitotree Haplogroups and How to Use Them for Genealogy
- Mitochondrial DNA: What is a Haplotype Cluster and How Do I Find and Use Mine?
- Mitotree Q&A for Everyone
Your old Legacy haplogroup will never change, because it’s the 2016 version that was not updated by the previous tree-keepers. That’s why the FamilyTreeDNA R&D team, me included, developed and birthed the new Mitotree. There were thousands of new haplogroups that could be defined to kick-start our genealogy, so we did.
The mitochondrial tree went from about 5000 branches to over 40,000 in the new Mitotree, each providing additional information to testers.
Not everyone received a new haplogroup, but about 75% of testers did, and another new Mitotree version will be released soon. In order to receive a new haplogroup, testers needed to:
- Have at least one qualifying, stable mutation that had not been previously used to define a haplogroup
- Match at least one other person in the same haplogroup branch with the same mutation(s)
In the case of the LeJeune sisters, there were no mutations that met all of the qualifications, so their known descendants did not receive a new haplogroup. That’s fine, though, because it’s not the name but the messages held by the information that’s important – and there’s a LOT to work with.
Let’s start with matches.
Matches
Of course, the first thing everyone does is click to see their matches.
The default is Detail View, but I prefer Table View (top left) because you can see more matches on the same page.
Catherine’s descendant whose matches are shown here has 108 Full Sequence matches, which are labeled as the “Coding Region.” The Coding Regions is the mtFULL test and includes both the HVR1 and HVR2 regions. Viewing Coding Region matches means they have taken the mtFull test, which sequences all 16,569 locations of the mitochondria.
When you click on the “Coding Region”, you are seeing matches to people who took all three test levels, not just the first one or two.
There are three test levels to view:
- HVR1
- HVR1+HVR2 both
- Coding Region, which is in addition to the HVR1+HVR2 regions
You can no longer order three different test levels today, although at one time you could. As costs decreased, it no longer made sense to offer multiple testing levels, and often the HVR1 or HVR1+HVR2 results, which only tested about 500 locations each, would confuse people.
People at the lower HVR1 or HVR1+HVR2 levels, known as mtPlus, can upgrade to the complete mtFull level, and should.
However, because some people only tested at those lower levels, matches are still shown at three levels, with different match thresholds for each level.
Matches at the HVR1 or HVR1+HVR2 levels *might* be entirely irrelevant, reaching back thousands of years. They could also be much more current, and critical to your genealogy, so don’t assume. Just one unstable mutation can cause a mismatch though, and at lower levels, cause you not to match someone with the same ancestor, which is why the full sequence test is so critically important.
For some testers, matches at lower levels sometimes provide the ONLY match to your known ancestor. So don’t skip over them. If you find a critical match there, you can email the tester to see if they will upgrade to the mtFull test.
People who test only at the HVR1 or HVR1+HVR2 level receive a more refined haplogroup after they upgrade, so the haplogroups between the HVR1/HVR2 testers and the full sequence test won’t match exactly. For the LeJeune sisters, the haplogroup for HVR1/HVR2-only testers is U6a and for full sequence testers, it’s U6a7a1a.
While full sequence matches are wonderful, if you’re searching for a particular ancestor and the ONLY place they appear is the HVR1 or HVR1+HVR2 testing levels, you’ll want to pursue the match. You may also want to evaluate lower level matches if their ancestors are from a specific location – like France – even if their earliest known ancestor (EKA) is not your ancestor.
To view your HVR1 or HVR1+HVR2 matches, just click on either of those links. You’ll see ALL of the results, including everyone who took the full sequence test. In this case, that means that the 217 HVR1 (hypervariable region 1) results will include the 120 coding region (full sequence) tests. I’ve already looked through the full sequence matches, so that’s not what I want.
If you ONLY want to see testers who did NOT take the Full Sequence test, use the Filter option. Select Filter, then the features you seek.
Fortunately, the LeJeune sisters have lots of known descendants at the mtFull level to work with, so we will focus on their full sequence matches.
Your Focus
On the matches page, you’ll be immediately interested in two fields:
- Maternal Earliest Known Ancestor (EKA) – the direct matrilineal ancestor of your match – unless they got confused and entered someone else
- Their Tree
Viewing the first several matches only produced one match to someone whose earliest known ancestor (EKA) is listed as Catherine or Edmee LeJeune, but perhaps the next group will be more productive. Note that females’ EKAs, earliest known ancestors, are sometimes challenging, given surname changes. So unfamiliar EKAs could represent generational differences and sometimes offer other hints based on their information.
Shifting to the detail view for a minute, you’ll want to review the genetic distance, meaning whether you’re an exact match or not.
If you’re not an exact match, a genetic distance of “1 step” means that you match except for one mutation at a specific location.
If you have a genetic distance greater than 3, meaning 4 mutations or more, you won’t be shown as a match on this match list. However, you can still be a haplogroup match, which we’ll discuss in the Discover section.
Essentially, with more than 3 mutations difference, it’s unlikely (but not impossible) that your match is genealogically relevant – meaning you probably won’t be able to identify your most recent common ancestor (MRCA).
However, that doesn’t mean that haplogroup-only matches can’t provide important clues, and we will look under every rock!
A Slight Detour – Confirmation Bias
This is a good place to mention that both ancestors and their location (country) of origin are provided by (some) testers to the best of their ability and understanding.
This tester selected “United States Native American” as the location for their earliest known ancestor. We don’t know why they entered that information. It could be that:
- The tester did not understand that the maternal country of origin means the direct MATRILINEAL line, not just someplace on the maternal side
- Selina Sinott was Native on her father’s side, or any line OTHER than her direct matrilineal line.
- They relied on oral history or made a guess
- They found the information in someone else’s tree
- They found all of the LeJeune information confusing (because it is)
The tester has provided no tree, so we can’t do any sleuthing here, but an Ancestry search shows a woman by that name born in 1855 in Starksboro, VT to Louis Senott and Victoria Reya. A further search on Victoria leads me to Marie Lussier who leads me to Marguerite Michel who leads me to Marie Anne Lord (Lore, Laure), who lived in Acadia, whose ancestor is…drum roll…Catherine LeJeune. You get the idea.
Yes, you may need to extend other people’s trees.
The Point
However, and this is the point – if you’re looking for confirmation that the LeJeune sisters were Native American, this ONE tester who entered Native American for an unknown reason is NOT the confirmation you’re looking for. Don’t get sucked into confirmation bias, or into categorically believing what someone else entered without additional information.
You need haplogroup confirmation, but, in this case, you don’t have it. However, if you’re new to genetic genealogy, you don’t know that yet, so hold on. We’re still getting there. This is why we need to review all of the reports.
And trust me, I’m not being critical because there isn’t a single seasoned genealogist who has NOT fallen down the rathole of excited confirmation bias or accepting information without further analysis – me included. We all need to actively guard against it, all the time. Confirm and weigh all of the evidence we do have, and seek missing evidence.
Let’s go back to the match results.
Matches – Haplogroups and Haplotypes
Scrolling down the Table View, the next group of matches shows many more matches to descendants of both Catherine and Edmee LeJeune.
Next, you’ll notice that there’s a Mitotree haplogroup, U6a7a1a, AND an F number. In this case, they are both checked in blue, which means you share the exact same haplogroup with that tester, and the exact same haplotype cluster, which is the F number.
I wrote about haplotype clusters, here.
If NEITHER box is checked, you don’t share either the haplogroup nor the haplotype cluster.
You can match the haplogroup, but not the haplotype cluster, which means the haplogroup box will be checked, but the haplotype cluster will not. If you share the same haplotype cluster, you WILL share the same haplogroup, but the reverse is not true.
What is a Haplotype Cluster, and why do they matter?
Haplotype Clusters
We need to talk about exact matches and what they mean. Yes, I know it seems intuitive, but it isn’t.
There are three types of matches
- Matching and Genetic Distance on your Match List
- Haplotype matching
- Haplogroup matching
Without getting (too much) into the weeds, an Exact Match in the Genetic Distance column on your match list excludes locations 309 and 315 because they are too unstable to be considered reliable for matching. So, 309 and 315 are EXCLUDED from this type of matching. In other words, you may or may not match at either or both of those locations. They are ignored for matching on your match list.
Locations 309 and 315 are also EXCLUDED from haplogroup definitions.
A haplotype F cluster match indicates that everyone in that cluster is an exact match, taking into consideration EVERY mutation, INCLUDING 309 and 315.
| 309 and 315 | Why | |
| Matching and Genetic Distance | Excluded | Unstable, probably not genealogically relevant and may be deceptive, leading you down a rathole |
| Haplogroup Definition | Excluded | Too unstable for tree branching and definition |
| Haplotype F Clusters | Included | Might be genealogically useful, so everyone can evaluate the rathole for themselves |
Some people think that if they don’t match someone exactly, they can’t have the same ancestor as people who do match exactly, but that’s not true. “Mutations happen” whenever they darned well please. Downstream mutations in stable locations that match between two or more testers will form their own haplogroup branch.
The most distant matches are shown on the last match page, and as you can see below, some descendants of Catherine and Edmee LeJeune have a 1-step difference with our tester, meaning a genetic distance of one, or one mutation (disregarding 309 and 315). One match has a 2-step mutation.
The fact that their F numbers are not the same tells you that their mutations are different from each other, too. If two of those people also matched each other, their F# would be identical.
The mutations that do not (yet) form a haplogroup, and are included in your haplotype cluster, are called Private Variants, and you cannot see the private variants of other people. Clearly, you and anyone in your haplotype cluster share all of the same mutations, including Private Variants.
Evaluating Trees and EKAs
By reviewing the matches, their EKAs, and the trees for the matches of Catherine’s descendants, I was able to create a little mini-tree of sorts. Keep in mind that not everyone with an EKA has a tree, and certainly not everyone who uploaded a tree listed an EKA. So be sure to check both resources. Here’s how to add your EKA, and a one-minute video, here.
The good news is that if your match has a WikiTree link when you click on their tree icon, you know their tree actually reaches back to either Edmee or Catherine if that’s their ancestor, and you’re not dealing with a frustrating, truncated two or three-generation tree, or a private tree. You can add your WikiTree link at FamilyTreeDNA here, in addition to any other tree you’ve linked.
Takeaways from Matches
- You can identify your common ancestor with other testers. By viewing people’s trees and emailing other testers, you can often reconstruct the trees from the tester back through either Catherine or Edmee LeJeune.
- Your primary focus should be on the people in your haplotype cluster, but don’t neglect other clusters where you may find descendants of your ancestor.
- If you see a male EKA name, or something other than a female name in the EKA field, like a location, the tester was confused. Only females pass their mitochondrial DNA to their descendants.
- If you’re searching for an ancestor whose mitochondrial DNA you don’t carry, use projects and WikiTree to see if you can determine if someone has tested from that line. From viewing the project results, I already knew that the LeJeune sisters had several descendants who had tested.
- If you’re searching for your ancestor on your match list, and you don’t find them in the full sequence results, use the filter to view people who ONLY took the HVR1 and HVR1+HVR2 tests to see if the results you seek are there. They won’t be on your full sequence match list because they didn’t test at that level. Testers at the lower levels will only have a partial, estimated haplogroup – in this case, U6a.
- For Edmee and Catherine LeJeune, we have enough testers to ensure that we don’t have just one or two people with the same erroneous genealogy. If you do find someone in a project or at WikiTree claiming descent from the same ancestor, but with a different haplogroup, you’ll need to focus on additional research to verify each step for all testers.
Resources:
- Ancestors: What Constitutes Proof
- Genealogy Proof Series – Creating Genealogy Proof Tables
- Lineages Versus Ancestors – How to Find and Leverage Yours
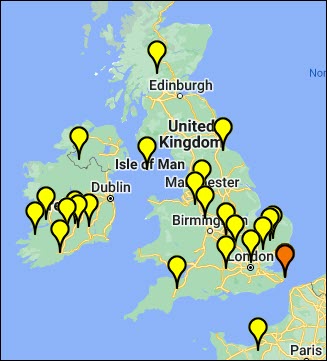
Matches Maps
The Matches Map is a great visual resource. That “picture is worth 1000 words” tidbit of wisdom definitely applies here.
Clicking on the Matches Maps displays the locations that your matches entered for their EKA.
In the upper left-hand corner, select “Full Sequence,” and only the full sequence matches will be displayed on the map. All full sequence testers also have HVR1/HVR2 results, so those results will be displayed under that selection, along with people who ONLY took the HVR1 or HVR1/HVR2 tests.
We know that the Acadians originally came from France, and their descendants were forcibly expelled from Nova Scotia in 1755. Families found themselves scattered to various locations along the eastern seaboard, culminating with settlements in Louisiana, Quebec, and in some cases, back in France, so this match distribution makes sense in that context.
Be sure to enlarge the map in case pins are on top of or obscuring each other.
Some people from other locations may be a match, too. Reviewing their information may assist with breaking down the next brick wall. Sometimes, additional analysis reveals that the tester providing the information was confused about what to complete, e.g., male names, and you should disregard that pin.
Takeaways from the Matches Map
- These results make sense for the LeJeune sisters. I would specifically look for testers with other French EKAs, just in case their information can provide a (desperately needed) clue as to where the LeJeune family was from in France.
- Reviewing other matches in unexpected locations may provide clues about where ancestors of your ancestor came from, or in this case, where descendants of the LeJeune sisters wound up – such as Marie Josephe Surette in Salem, Massachusetts, Catherine LeJeune’s great-granddaughter.
- Finding large clusters of pins in an unexpected location suggests a story waiting to be uncovered. My matrilineal ancestor was confirmed in church records in Wirbenz, Germany, in 1647 when she married, but the fact that almost all of my full sequence matches are in Scandinavia, clustered in Sweden and Norway, suggests an untold story, probably involving the 30 Years War in Germany that saw Swedish troop movement in the area where my ancestor lived.
- For my own mitochondrial DNA test, by viewing trees, EKAs, and other hints, including email addresses, I was able to identify at least a country for 30 of 36 full sequence matches and created my own Google map.
- You can often add to the locations by creating your own map and including everyone’s results.
Resources:
Mitochondrial DNA Part 4 – Techniques for Doubling Your Useful Matches
Mitochondrial DNA Myth – Mitochondrial DNA is not Useful because the Haplogroups are “Too Old”
Before we move to the Discover Reports, I’m going to dispel a myth about haplogroups, ages, genealogical usefulness, and most recent common ancestors known as MRCAs.
Let me start by saying this out loud. YES, MITOCHONDRIAL DNA IS USEFUL FOR GENEALOGY and NO, OLDER HAPLOGROUPS DO NOT PREVENT MITOCHONDRIAL DNA FROM BEING USEFUL.
Here’s why.
The most recent common ancestor (MRCA) is the person who is the closest common ancestor of any two people.
For example, the mitochondrial DNA MRCA of you and your sibling is your mother.
For your mother and her first cousin, the mitochondrial MRCA is their grandmother on the same side, assuming they both descend from a different daughter. Both daughters carry their mother’s undiluted mitochondrial DNA.
A common complaint about mitochondrial DNA is that “it’s not genealogically useful because the haplogroups are so old” – which is absolutely untrue.
Let’s unravel this a bit more.
The MRCA of a GROUP of people is the first common ancestor of EVERY person in the group with each other.
So, if you’re looking at your tree, the MRCA of you, your sibling, and your mother’s 1C in the example above is also your mother’s grandmother, because your mother’s grandmother is the first person in your tree that ALL of the people in the comparison group descend from.
Taking this even further back in time, your mother’s GGG-grandmother is the MRCA for these five people bolded, and maybe a lot more descendants, too.
At that distance in your tree, you may or may not know the name of the GGG-grandmother and you probably don’t know all of her descendants either.
Eventually, you will hit a genealogical brick wall, but the descendants of that unknown “grandmother” will still match. You have NOT hit a genetic brick wall.
A haplogroup name is assigned to the woman who had a mutation that forms a new haplogroup branch, and she is the MRCA of every person in that haplogroup and all descendant haplogroups.
However, and this is important, the MRCA of any two people, or a group of people may very well be downstream, in your tree, of that haplogroup mother.
As you can clearly see from our example, there are four different MRCAs, depending on who you are comparing with each other.
- Mom – MRCA of you and your sibling
- Grandmother – MRCA of you, your sibling, your mom and your mom’s 1C
- GGG-Grandmother – MRCA of all five bolded descendants
- Haplogroup formation – MRCA of ALL tested descendants, and all downstream haplogroups, many of whom are not pictured
Many of the testers may, and probably do, form haplotype clusters beneath this haplogroup.
When you are seeking a common ancestor, you really don’t care when everyone in that haplogroup was related, what you seek is the common ancestor between you and another person, or group of people.
If the haplogroup is formed more recently in time, it may define a specific lineage, and in that case, you will care because that haplogroup equates to a woman you can identify genealogically. For example, let’s say that one of Catherine LeJeune’s children formed a specific haplogroup. That would be important because it would be easy to assign testers with that haplogroup to their appropriate lineage. That may well be the case for the two people in haplogroup U6a7a1a2, but lack of a more recent haplogroup for the other testers does not hinder our analysis or reduce mitochondrial DNA’s benefits.
That said, the more people who test, the more possibilities for downstream haplogroup formation. Currently, haplogroup U6a7a1a has 34 unnamed lineages, just waiting for more testers.
Haplogroup ages are useful in a number of ways, but haplogroup usefulness is IN NO WAY DEPRICATED BY THEIR AGE. The haplogroup age is when every single person in that haplogroup shares a common ancestor. That might be useful to know, but it’s not a barrier to genealogy. Unfortunately, hearing that persistent myth causes people to become discouraged, give up and not even bother to test, which is clearly self-defeating behavior. You’ll never know what you don’t know, and you won’t know if you don’t test. That’s my mantra!
The LeJeune sisters provide a clear example.
OK, now on to Discover.
mtDNA Discover
Next, we are going to click through from the mtDNA Results and Tools area on your personal page to Discover Haplogroup Reports. These reports are chapters in your own personal book, handed down from your ancestors.
Discover is also a freely available public tool, but you’ll receive additional and personalized information by clicking through when you are signed into your page at FamilyTreeDNA. Only a subset is available publicly.
mtDNA Discover was released with the new Mitotree and provides fresh information weekly.
Think of Discover as a set of a dozen reports just for your results, with one more, Globetrekker, an interactive haplogroup map, coming soon.
Resources:
- Mitotree is Born
- Mitotree Q&A for Everyone
- Updated mtDNA Haplotree: 35,000 New Branches for Genealogy Research– FamilyTreeDNA’s announcement article
- Accessing mtDNA Discover™
- Using the mtDNA Discover™ Haplogroup Story Report
- Using the mtDNA Discover™ Classic Tree
- Understanding the mtDNA Haplotree
When you click through to Discover from your results, Discover defaults to your haplogroup. In this case, that’s U6a7a1a for the LeJeune sisters.
Let’s begin with the first report, Haplogroup Story.
Haplogroup Story
The Haplogroup Story is a landing page that summarizes information about your ancestor’s haplogroup relevant to understanding your ancestor’s history. Please take the time to actually READ the Discover reports, including the information buttons, not just skim them.
Think of Discover as your own personalized book about your ancestors – so you don’t want to miss a word.
You’ll see facts on the left, each one with a little “i” button. Click there or mouse over for more information about how that fact was determined.
When we’re talking about haplogroup U6a7a1a, it sounds impersonal, but we’re really talking about an actual person whose name, in this case, we will never know. We can determine the ancestor of some haplogroups that formed within a genealogical timeframe. The LeJeune ancestor in question is the person in whose generation the final mutation in a long string of mutations created the final “a” in haplogroup U6a7a1a.
Think of these as a long line of breadcrumbs. By following them backwards in time and determining when and where those breadcrumbs were dropped, meaning when and where the mutation occurred, we begin to understand the history of our ancestor – where she was, when, and which cultures and events shaped her life.
U6a7a1a was formed, meaning this ancestor was born, about 50 CE, so about 1950 years ago. This means that the ancestor of ANY ONE PERSON with this haplogroup could have lived anytime between the year 50 CE and the year of their mother’s birth.
This is VERY important, because there is an incredible amount of misunderstanding about haplogroup ages and what they mean to you.
The year 50 CE is the year that the common ancestor of EVERY PERSON in the haplogroup was born, NOT the year that the common ancestor of any two or more people was born.
By way of illustration, the LeJeune sisters were born in about 1624 and 1633, respectively, not 50 CE, and their most recent common ancestor (MRCA) is their mother, who would have been born between about 1590 and 1608, based on their birth years.
For reference, I’ve created this genealogical tree from individuals who took the mitochondrial DNA test and have identified their mitochondrial lineage on the LeJeune mother’s profile at Wikitree
You can see that both Edmee and Catherine have mitochondrial DNA testers through multiple daughters. I’ve color coded the MRCA individuals within each group, and of course their mother is the MRCA between any two people who each descend from Edmee and Catherine.
Mitochondrial DNA matches to the LeJeune sisters’ descendants could be related to each other anywhere from the current generation (parent/child) to when the haplogroup formed, about 50 CE.
You can easily see that all of these testers, even compared with their most distant relatives in the group, share a common ancestor born between 1590 and about 1608. Other people when compared within the group share MCRAs born about 1717 (blue), 1778 (peach), 1752 (green), 1684 (pink), 1658 (mustard), and 1633 (red).
Soooooo…a haplogroup born in 50 CE does NOT mean that you won’t be able to find any genealogical connection because your common ancestor with another tester was born more than 1900 years ago. It means that the common ancestor of EVERYONE who is a member of haplogroup U6a7a1a (and downstream haplogroups) was born about 50 CE.
The parent haplogroup of U6a7a1a is haplogroup U6a7a1, which was born about 1450 BCE, or about 3450 years ago.
In the graphic, I’ve shown other unknown genealogical lineages from U6a7a1 and also downstream haplogroups.
Haplogroup U6a7a1 is the MRCA, or most recent common ancestor of haplogroup U6a7a1a, and anyone who descends from haplogroup U6a7a1 or any of the 23 downstream lineages from U6a7a1, including 5 descendant haplogroups and 18 unnamed lineages.
The LeJeune haplogroup, U6a7a1a, has 35 descendant lineages. One downstream haplogroup has already been identified – U6a7a1a2 – which means two or more people share at least one common, stable, mutation, in addition to the mutations that form U6a7a1a. Thirty-four other lineages are as yet unnamed.
The fact that there are 34 unnamed lineages means that people with one or more private variants, or unique mutations, are candidates for a new branch to form when someone else tests and matches them, including those variants.
You’re a candidate for a new haplogroup in the future if no one else matches your haplotype cluster number, or, potentially, as the tree splits and branches upstream.
When a second person in a lineage tests, those two people will not only share a common haplotype cluster F#, they will share a new haplogroup too if their common mutation is not excluded because it’s unstable and therefore unreliable.
There are 127 members of haplogroup U6a7a1a today, and their EKAs are noted as being from France, Canada, the US, and other countries that we’ll view on other pages.
Haplogroup U6a7a1a has been assigned two Discover badges:
- Imperial Age – “an age noted for the formation and global impact of expansive empires in many parts of the world.” In other words, colonization, which is certainly true of the French who battled with the English to colonize New England, Acadia, and New France.
- mtFull Confirmed (for testers only)
Additionally, the LeJeune sisters have one Rare Notable Connection, and three Rare Ancient Connections, all of which may shed light on their history.
Takeaways from the Haplogroup Story
- The Haplogroup Story provides an overview of the haplogroup
- You can easily see how many testers fall into this haplogroup and where they have indicated as the origin of their matrilineal line.
- The haplogroup may have several new haplogroup seeds – 34 in this case – the number of unnamed lineages
- You can share this or other Discover pages with others by using the “share page” link in the upper right-hand corner.
- Don’t be discouraged by the age of the haplogroup, whether it’s recent or older.
Next, let’s look at Country Frequency.
Country Frequency
Country Frequency shows the locations where testers in haplogroup U6a7a1a indicate that their EKA, or earliest known matrilineal ancestor, is found. The Country Frequency information is NOT limited to just your matches, but all testers in haplogroup U6a7a1a, some of whom may not be on your match list. Remember, only people with 3 mutations difference, or fewer, are on your match list.
Haplogroup distribution around the world is very informative as to where your ancestors came from.
There are two tabs under Country Frequency, and I’d like to start with the second one – Table View.
Table View displays all of the user-provided country locations. Note that the Haplogroup Frequency is the percentage of total testers in which this haplogroup is found in this particular country. These frequencies are almost always quite small and are location-based, NOT haplogroup based.
There are now 40,000 haplogroups, and in haplogroup U, the LeJeune sisters are 6 branches down the tree with U6a7a1a.
In total, 127 testers are members of haplogroup U6a7a1a, and 42 of those claim that their ancestor is from France, which comprises 1% of the people who have taken the full sequence mitochondrial DNA test whose ancestor is from that location.
Let’s do the math so you can see how this is calculated and why it’s typically so small. For our example, let’s say that 8000 people in the database have said their matrilineal ancestor is from France. Of the 127 haplogroup U6a7a1a members, 42 say their ancestor is from France. Divide 42 by 8,000, which is 0.00525, and round to the nearest percentage – which is 1%.
The best aspect of this page is that you can see a nice summary of the locations where people indicate that their earliest known U6a7a1a ancestor was found.
Please note that the last entry, “Unknown Origins,” is the bucket that everyone who doesn’t provide a location falls into. That row is not a total but includes everyone who didn’t provide location information.
These location results make sense for the LeJeune sisters – maybe except for Ireland and Belgium. Some people don’t understand the directions, meaning that a matrilineal ancestor or direct maternal ancestor is NOT your literal “oldest” ancestor on your mother’s side of the tree who lived to be 105, but your mother-to-mother-to-mother-to-mother ancestor, so check to see if these people with unusual locations are in your match list and view their tree or reach out to them.
We don’t know why the person who selected Native American made that choice, but I’d bet it has to do with confusion about the “other” LeJeune female, Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard. Based on Catherine and her sister, Edmee LeJeune’s haplogroup through more than 50 testers, U6a7a1a, Native is incorrect.
Of course, that tester wouldn’t have known that if they completed their EKA information before they tested. Perhaps they entered information based on the stories they had heard, or flawed genealogy, and didn’t think to go back and correct it when their results were ready, indicating that Native was mistaken.
On the “Map View” tab, the locations are shown using a heat map, where the highest percentages are the darkest. Here, both France and Canada are the darkest because that’s the most common selection for this haplogroup with 1% each, while the rest of the countries registered with less <1%.
These colors are comparative to each other, meaning that there is no hard and fast line in the sand that says some percentage or greater is always red.
To summarize these two tables, because this is important:
- The Table View shows you how many people selected a specific country for their ancestor’s location, but the frequency is almost always very low because it’s based on the total number of testers in the entire database, comprised of all haplogroups, with ancestors from that country.
- The Map View shows you a heat map for how frequently a particular location was selected, as compared to other locations, for this haplogroup.
To view the difference between adjacent haplogroups, I always compare at least one haplogroup upstream. In this case, that’s the parent haplogroup, U6a7a1.
The Parent Haplogroup
If you look at haplogroup U6a7a1, just one haplogroup upstream, you’ll see that for Mauritania, the total number of U6a7a1 descendants tested is only “1”, but the haplogroup frequency in Mauritania is 10% which means that there are only 10 people who have been tested in the database altogether from Mauritania – and one person is haplogroup U6a7a1.
However, due to substantial under-sampling of the Mauritania population, the frequency for Mauritania, 10%, is higher than any other location.
Also, remember, these are user-reported ancestor locations, and we have no idea if or how these people determined that their ancestor is actually from Mauritania.
Please only enter actual known locations. For example, we don’t want haplogroup U6a7a1 members to look at this informatoin, then add Mauritania as their location because now they “know” that their ancestor is from Mauritania.
On the Map View, Mauritania is dark red because the percentage is so high – never mind that there are only 10 testers who report matrilineal ancestors from there, and only one was U6a7a1.
This map illustrates one reason why taking the full sequence test is important. Viewing partial haplogroups can be deceiving.
Catherine and Edmee LeJeune’s matrilineal descendants who only tested at the HVR1 or HVR1+HVR2 level receive a predicted haplogroup of U6a, born about 21,000 years ago. That’s because the full 16,569 locations of the mitochondria need to be tested in order to obtain a full haplogroup, as opposed to about 500 locations in the HVR1 and HVR1/2, each, respectively.
U6a – The Result for HVR1/HVR2-Only Testers
So, let’s look at what haplogroup U6a reveals, given that it’s what early LeJeune descendants who ordered the lower-level tests will see.
In the Table View for U6a, below, you see that the top 5 counties listed by haplogroup frequency are five North African countries.
A total of 801 people are assigned to haplogroup U6a, meaning the majority, 757, report their ancestors to be from someplace else. If two people from the Western Sahara (Sahrawi) comprise 67% of the people who tested, we know there are only three people who have tested and selected that location for their ancestors.
If you didn’t understand how the display works, you’d look at this report and see that the “top 5” countries are North African, and it would be easy to interpret this to mean that’s where Catherine and Edmee’s ancestors are from. That’s exactly how some people have interpreted their results.
Scrolling on down the Table View, 50 testers report France, and 10 report the US, respectively, with France showing a Haplogroup Frequency of 1% and the US <1%.
The balance of U6a testers’ ancestors are from a total of 57 other countries, plus another 366 who did not select a location. Not to mention that U6a was born 21,000 years ago, and a lot has happened between then and the 1620/1630s when Catherine and Edmee were born to a French mother.
The real “problem” of course is that haplogroup U6a is only a partial haplogroup.
The U6a map shows the highest frequency based on the number of testers per country, which is why it’s dark red, but the Table View reports that the actual number of U6a testers reporting any specific country. France has 50. Next is the US, also with 50, which often means people are brick-walled here. You can view the U6a table for yourself, here.
Why is this relevant for Catherine and Edmee LeJeune? It’s very easy to misinterpret the map, and for anyone viewing U6a results instead of U6a7a1a results, it’s potentially genealogically misleading.
Use Country Frequency with discretion and a full understanding of what you’re viewing, especially for partial haplogroups from HVR1/HVR2 results or autosomal results from any vendor.
If someone tells you that the LeJeune sisters are from someplace other than France, ask where they found the information. If they mention Africa, Morocco or Portugal, you’ll know precisely where they derived the information.
This information is also available on your Maternal Line Ancestry page, under “See More,” just beneath the Matches tab. Haplogroup Origins and Ancestral Origins present the same information in a different format.
Discover is a significant improvement over those reports, but you’ll still need to read carefully, understand the message, and digest the information.
Takeaways from Country Frequency
- Evaluate the results carefully and be sure to understand how the reports work.
- Use complete, not partial haplogroups when possible.
- The Haplogroup Frequency is the number of people assigned to this haplogroup divided by the entire number of people in the database who report that country location for their matrilineal ancestor. It is NOT the percentage of people in ONLY haplogroup U6a7a1a from a specific country.
- Table view shows the number of testers with this haplogroup, with the percentage calculated per the number of people who have tested in that country location.
- The Map shows the highest frequency based on the number of testers per country.
- Use the map in conjunction with the haplogroup age to better understand the context of the message.
Globetrekker, which has not yet been released, will help by tracking your ancestors’ paths from their genesis in Africa to where you initially find that lineage.
Before we move on to the Mitotree, let’s take a minute to understand genetic trees.
About Genetic Trees
The Mitotree is a genetic tree, also called a phylogenetic tree, that generally correlates relatively closely with a genealogical tree. The more testers in a particular haplogroup, the more accurate the tree.
FamilyTreeDNA provides this disclaimer information about the genetic tree. The Mitotree you see is a nice and neat published tree. The process of building the tree is somewhat like making sausage – messy. In this case, the more ingredients, the better the result.
The more people that test, the more genetic information is available to build and expand the tree, and the more accurate it becomes.
The recent Mitotree releases have moved the haplogroup “dates” for the LeJeune sisters from about 21,000 years ago for HVR1/HVR2 U6a testers to 50 CE for full sequence testers, and this may well be refined in future tree releases.
Mutations
Mutations and how to interpret them can be tricky – and this short section is meant to be general, not specific.
Sometimes mutations occur, then reverse themselves, forming a “back mutation”, which is usually counted as a branch defining a new haplogroup. If a back mutation happens repeatedly in the same haplogroup, like a drunken sailor staggering back and forth, that mutation is then omitted from haplogroup branch formation, but is still counted as a mismatch between two testers.
A heteroplasmy is the presence of two or more distinct results for a specific location in different mitochondria in our bodies. Heteroplasmy readings often “come and go” in results for different family members, because they are found at varying threshold levels in different family members, causing mismatches. Heteroplasmies are currently counted only if any person has 20% or greater of two different nucleotides. So, if you have a 19% heteroplasmy read for a particular location, and your sister has 21%, you will “not” have a heteroplasmic condition reported, but she will, and the location will be reported as a mismatch.
If you have a heteroplasmy and another family member does not, or vice versa, it’s counted as as a “mismatch,” meaning you and that family member will find yourselves in different haplotype clusters. Hetroplasmies do not presently define new tree branches. I wrote about heteroplasmies, here.
Takeaways from the Genetic Tree Disclaimer
- DNA is fluid, mutations happen, and all mutations are not created equal.
- Thankfully, you really don’t need to understand the nitty-gritty underpinnings of this because the scientists at FamilyTreeDNA have translated your results into reports and features that take all of this into consideration.
- Testing more people helps refine the tree, which fills in the genetic blanks, refining the dates, and expanding branches of the tree.
Resources:
- Mitochondrial DNA Resource Page
- What is a Heteroplasmy and Why Do I Care?
- Understanding mtDNA Haplogroups
- I covered the basics of DNA, including the different types of mutations in my book, The Complete Guide To FamilyTreeDNA: Y-DNA, Mitochondrial, Autoisomal and X-DNA
Ok, now let’s look at the Time Tree
Time Tree
The Time Tree displays your haplogroup on the Mitotree timeline. In other words, it shows us how old the haplogroup is in relation to other haplogroups, and testers.
The Time Tree displays the country locations of the ancestors of testers who are members of that and descendant or nearby haplogroups. You can view the haplogroup U6a7a1a Time Tree, here, and follow along if you wish. Of course, keep in mind that the tree is a living, evolving entity and will change and evolve over time as updated tree versions are released.
Mousing over the little black profile image, which is the person in whom this haplogroup was born, pops up information about the haplogroup. Additionally, you’ll see black bars with a hashed line between them. This is the range of the haplogroup formation date. Additional details about the range can be found on the Scientific Details tab, which we’ll visit shortly.
On your Matches tab, remember that each match has both a haplogroup and a haplogroup cluster F# listed.
On the Time Tree, individual testers are shown at right, with their selected country of origin. In this case, you’ll see the person who selected “Native American” at the top, followed by France, Canada, the US, and other flags.
Haplogroup U6a7a1a includes several haplotype clusters, designated by the rounded red brackets. In this view, we can see several people who have haplotype cluster matches. Everyone has a haplotype assignment, but a haplotype cluster is not formed until two people match exactly.
In the Time Tree view, above, you can see two clusters with two members each, and the top of a third cluster at the bottom.
In case you’re wondering why some of the globes are offset a bit, they positionally reflect the birth era of the tester, rounded to the closest 25 years, if the birth year is provided under Account Settings. If not, the current tester position defaults to 1950.
Scrolling down to the next portion of the window shows that the third cluster is VERY large. Inside the cluster, we see Belgium, Canada, and France, but we aren’t even halfway through the cluster yet.
Continuing to scroll, we see the cluster number, F7753329, in the middle of the cluster, along with the French flag, two from Ireland, four from the US, and the beginning of the large unknown group.
In this fourth screenshot, at the bottom of the display, we see the balance of haplotype cluster #F7753329, along with eight more people who are not members of that haplotype cluster, nor any other haplotype cluster.
Finally, at the bottom, we find haplogroup U6a7a1a2, a descendant haplogroup of U6a7a1a. Are they descendants of the LeJeune sisters?
Looking back at our tester’s match list, the two people who belong to the new haplogroup U6a7a1a2 haven’t provided any genealogical information. No EKA or tree, unfortunately. The haplogroup formation date is estimated as about 1483, but the range extends from about 1244-1679 at the 95th percentile. In other words, these two people could be descendants of:
- Either Catherine or Edmee LeJeune, but not both, since all of their descendants would be in U6a7a1a2.
- An unknown sister to Catherine and Edmee.
- A descendant line of an ancestor upstream of Catherine and Edmee.
Takeaways from the Time Tree
- The visualization of the matches and haplotype clusters illustrates that the majority of the haplogroup members are in the same haplogroup cluster.
- Given that two women, sisters, are involved, we can infer that all of the mutations in this haplotype cluster were common to their mother as well.
- Haplotype cluster #F7753329 includes 19 testers from Catherine and 17 from Edmee.
- Downstream haplogroup U6a7a1a2 was born in a daughter of haplogroup U6a7a1a, as early as 1244 or as late as 1679. Genealogy information from the two testers could potentially tell us who the mutation arose in, and when.
- As more haplogroup U6a7a1a2 testers provide information, the better the information about the haplogroup will become, and the formation date can be further refined.
Smaller haplotype clusters have a story to tell too, but for those, we’ll move to the Match Time Tree.
Match Time Tree
The Match Time Tree is one of my favorite reports and displays your matches on the Time Tree. This feature is only available for testers, and you must be signed in to view your Match Time Tree.
By selecting “Share Mode”, the system obfuscates first names and photos so you can share without revealing the identity of your matches. I wrote about using “Share Mode” here. I have further blurred surnames for this article.
The Match Time Tree incorporates the tree view, with time, the names of your matches PLUS their EKA name and country, assuming they have entered that information. This is one of the reasons why the EKA information is so important.
This display is slightly different than the Time Tree, because it’s one of the features you only receive if you’ve taken the mtFull test and click through to Discover from your account.
The Time Tree view is the same for everyone, but the Match Time Tree is customized for each tester.
Your result is shown first, along with your haplotype cluster if you are a member of one.
You can easily see the names of the EKAs below the obfuscated testers’ names.
While we immediately know that descendants of both Catherine and Edmee are found in the large cluster #F7753329, we don’t yet know which ancestors are included in other haplotype clusters.
Haplogroup U6a7a1a includes two smaller haplotype clusters with 2 people each.
We know a few things about each of these clusters:
- The people in each cluster have mutations that separate them from everyone else except the other person in their cluster
- The results are identical matches to the other person in the cluster, including less reliable locations such as 309 and 315
- There are other locations that are excluded from haplogroup formation, but are included in matching, unlike 309 and 315.
- Given that they match only each other exactly, AND they did not form a new haplogroup, we know that their common unique mutation that causes them to match only each other exactly is unreliable or unstable, regardless of whether it’s 309, 315, a heteroplasmy, or another marker on the list of filtered or excluded variants.
Only the tester can see their own mutations. By inference, they know the mutations of the people in their haplotype cluster, because they match exactly.
If you’re a member of a cluster and you’re seeking to determine your common ancestor, you’ll want to analyze each cluster. I’ve provided two examples, below, one each for the red and purple clusters.
Red Haplotype Cluster #F3714849
Only one person in the red cluster has included their EKA, and the tree of the second person only reaches to three generations. Tracking that line backwards was not straightforward due to the 1755 expulsion of the Acadians from Nova Scotia.
The second person listed their EKA as Edmee LeJeune, but they have a private tree at MyHeritage, so their matches can’t see anything. I wonder if they realize that their matches can’t view their tree.
We are left to wonder if both people descend from Edmee LeJeune, and more specifically, a common ancestor more recently – or if the unstable mutation that they share with each other is simply happenstance.
E-mailing these testers would be a good idea.
Purple Haplotype Cluster #F2149611
Evaluating the purple cluster reveals that the common ancestor is Catherine LeJeune. The question is twofold – how are these two people related downstream from Catherine, and how unstable is their common mutation or mutations.
Fortunately, both people have nice trees that track all the way back to Catherine.
Unfortunately, their MRCA is Francoise, the daughter of Catherine. I say unfortunately, because two additional testers also descend from Francoise, and they don’t have the haplotype cluster mutation. This tells us that the cluster mutation is unreliable and probably not genealogically relevant because it occurred in two of Francoise’s children’s lines independently, but not all four.
In other words, that specific mutation just happened to occur in those two people.
This is exactly why some mutations are not relied upon for haplogroup definition.
Takeaways from the Match Time Tree
- The time tree is a wonderful visualization tool that shows all of your matches, their EKAs and countries, if provided, in haplotype clusters, on the Time Tree. This makes it easy to see how closely people are related and groups them together.
- On your match page, you can easily click through to view your matches’ trees.
- You can use both haplotype clusters (sometimes reliable) and downstream haplogroups (reliable) to identify and define lineages on your family tree. For example, if a third person matches the two in haplogroup U6a7a1a2, the child haplogroup of U6a7a1a, and you could determine the common ancestor of any two of the three, you have a good idea of the genealogical placement of the third person as well.
- You know that if people form a haplotype cluster, but not a new haplogroup, that their common haplotype cluster-defining mutation is less reliable and may not be genealogically relevant.
- On the other hand, those less reliable mutations may not be reliable enough for haplogroup definition, but may be relevant to your genealogy and could possibly define lineage splits. Notice all my weasel words like “may,” “may not” and “possibly.” Also, remember our purple cluster example where we know that the mutation in question probably formed independently and is simply chance.
- I can’t unravel the ancestors of the red cluster – and if I were one of those two people, especially if I didn’t know who my ancestor was, I’d care a lot that the other person didn’t provide a useful tree. Don’t forget that you can always reach out via email, offer to collaborate, and ask nicely for information.
- We need EKAs, so please encourage your matches to enter their EKA, upload a tree or link to a MyHeritage tree, and enter a Wikitree ID in their FamilyTreeDNA profile, all of which help to identify common ancestors.
Resources:
Classic Tree
FamilyTreeDNA invented the Time Tree and Match Time Tree to display your results in a genealogically friendly way, but there is important information to be gleaned from other tree formats as well.
The Classic Tree presents the Mitotree, haplogroup and haplotype information in the more traditional format of viewing phylogenetic trees, combining their beneficial features. There’s a lot packed in here.
In this default view, all of the Display Options are enabled. We are viewing the LeJeune haplogroup, U6a7a1a, with additional information that lots of people miss.
The countries identified as the location of testers’ earliest known ancestors (EKA) are shown.
Listed just beneath the haplogroup name, five people are members of this haplogroup and are NOT in a haplotype cluster with anyone else, meaning they have unique mutations. When someone else tests and matches them, depending on their mutation(s), a new haplogroup may be formed. If they match exactly, then at least a new haplotype cluster will be formed.
Portions of three haplotype clusters are shown in this screenshot, designated by the F numbers in the little boxes.
Additional information is available by mousing over the images to the right of the haplogroup name.
Mousing over the badge explains the era in which the haplogroup was born. Rapid expansion was taking place, meaning that people were moving into new areas.
Mousing over the date explains that the scientists behind the Mitotree are 95% certain about the date range of the birth of this haplogroup, rounded to 50 CE. Remember, your common ancestor with ALL haplogroup members reaches back to this approximate date, but your common ancestor with any one, or a group, of testers is sometime between the haplogroup formation date, 50 CE, and the present day.
Mousing over the year shows the confidence level, and the date range at that level. These dates will probably be refined somewhat in the future.
If haplogroup members have private variants, it’s likely or at least possible that a new branch will split from this one as more people test
Mousing over the star displays the confidence level of the structure of this portion of the Mitotree based on what could be either confusing or conflicting mutations in the tree. For haplogroup U6a7a1a, there’s no question about the topology, because it has a 10 of 10 confidence rating. In other words, this branch is very stable and not going to fall off the tree.
Every haplogroup is defined by at least one mutation that is absent in upstream branches of the tree. Mutations are called variants, because they define how this sample, or branch, varies from the rest of the branches in the Mitotree.
These two mutations, A2672G and T11929C, are the haplogroup-defining mutations for U6a7a1a. Everyone in haplogroup U6a7a1a will have these two mutations in addition to all of the mutations that define directly upstream haplogroups (with extremely rare exceptions). Haplogroup-defining mutations are additive.
There may be more haplogroup-defining mutations than are displayed, so click on the little paper icons to copy to your clipboard.
You can view upstream haplogroups and downstream haplogroups, if there are any, by following the back arrows to upstream haplogroups, and lines to downstream haplogroups.
For example, I clicked on the arrow beside haplogroup U6a7a1a to view its parent haplogroup, U6a7a1, and a second time to view its parent, haplogroup U6a7a. If I click on the back arrow for U6a7a, I’ll continue to climb up the tree.
Beneath U6a7a, you can see the haplogroup branches, U6a7a1a and U6a7a2.
Beneath U6a7a1, you’ll notice:
- People who don’t share haplotype clusters with anyone
- Three haplotype clusters
- Five descendant haplogroups from U6a7a1, including the LeJeune sister’s haplogroup U6a7a1a.
To expand any haplogroup, just click on the “+”.
You may see icons that are unfamiliar. Mouse over the image or click on the “Show Legend” slider at upper right to reveal the decoder ring, I mean, legend.
You can read more about the symbols and how haplogroups are named, here, and see more about types of mutations in the Scientific Details section.
Takeaways from the Classic Tree
- The Classic Tree provides a quick summary that includes important aspects of a haplogroup, including when it was formed, which mutations caused it’s formation, and each branch’s confidence level.
- It’s easy to back your way up the tree to see where your ancestor’s founding haplogroups were located, which speaks to your ancestor’s history. Patterns, paths, and consistency are the key.
- Ancient DNA locations in your tree can provide a very specific location where a haplogroup was found at a given point in time, but that doesn’t necessarily mean that’s where the haplogroup was born, or that they are your ancestor. We will get to that shortly.
- You can share this page with others using the “Share Page” function at the top right.
Ancestral Path
The Ancestral Path is a stepping-stone chart where you can view essential information about each haplogroup in one row, including:
- Age and era
- Number of years between haplogroups
- Number of subclades
- Number of modern-day testers who belong to this haplogroup
- Number of Ancient Connections that belong to this haplogroup, including all downstream haplogroups
This “at a glance” history of your haplogroup is the “at a glance” history of your ancestors.
The number in the column titled “Immediate Descendants”, which is the number of descendant haplogroups, tells a story.
If you see a large, or “larger” number there, that indicates that several “child” haplogroups have been identified. Translated, this means that nothing universally terrible has occurred to wipe most of the line out, like a volcano erupting, or a famine or plague that would constitute a constraining bottleneck event. Your ancestors’ children survived and apparently thrived, creating many descendant downstream haplogroups, known as an expansion event.
If you see a smaller number, such as rows 5, 7, 8, 9, and 13, each of which have only two surviving branches, yours and another, several branches probably didn’t survive to the present day. This may reflect a bottleneck where only a few people survived or the lines became extinct over time, having no descendants today. Either that, or the right people haven’t yet tested. Perhaps they are living in a particularly undersampled region of the world, a tiny village someplace, or there aren’t many left.
The two most recent haplogroups have the most subclades, indicating that your ancestors were successfully reproducing in the not-too-distant past. Mutations occurred because they randomly do, creating new haplogroups, and several haplogroup members have tested today. Hopefully, genealogy can connect us further.
The next column, “Tested Modern Descendants,” tallies the total number of testers as it rolls up the tree. So, each haplogroup includes the testers in its downstream (child) haplogroups. The 127 people in haplogroup U6a7a1a include the two people in haplogroup U6a7a1a2, and the 226 people in haplogroup U6a7a1 include the 127 people in haplogroup U6a7a1a.
Looking at other types of trees and resources for each haplogroup can suggest where our ancestors were at that time, perhaps correlating with world or regional history that pertains to the lives of those ancestors.
In our case, the LeJeune sisters’ ancestors did well between 3450 years ago through the formation of U6a7a1a, about 1950 years ago. 3500 years ago, in Europe, settlements were being fortified, leadership was emerging as complex social patterns formed, and trade networks developed that spanned the continent and beyond.
Between 20,000 and 3,450 years ago, not so much. This correlates to the time when early European farmers were moving from Anatolia, bringing agriculture to Europe en masse. However, they were not the first people in Europe. Early modern humans arrived and lived in small groups about 50,000 years ago.
And they very nearly didn’t survive. Many lines perished.
Takeaways from the Ancestral Path
- The Ancestral Path shows the stepping stones back to Mitochondrial Eve, dropping hints along the way where expansions occurred, meaning that your ancestors were particularly successful, or conversely, where a bottleneck occurred and the lineage was in jeopardy of extinction.
- In some cases, where a lot of time has passed between haplogroups, such as 8,000 years between U and U6, we’re seeing the effect of lineages dying out. However, with each new tester, there’s the possibility of a previously undiscovered branch split being discovered. That’s precisely what happened with haplogroup L7.
Migration Map
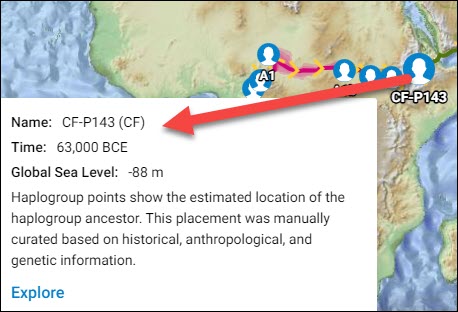
The Discover Migration Map shows the path that your ancestor took out of Africa, and where your base ancestral haplogroup was formed.
Mousing over the little red circle displays the haplogroup, and the area where it originated. Based on this location where U6 was found some 31,000 years ago, we would expect to find U6 and subgroups scattered across North Africa, the Levant, and of course, parts of Eurasia and Europe.
It’s interesting that, based on what we know using multiple tools, it appears that haplogroup U initially crossed between the Horn of Africa and the Arabian Peninsula, at the present-day Strait of Bab-el-Mandeb. Today, that crossing is about 15 nautical miles, but the sea level was much lower during earlier times in history, including the last glacial maximum. Humans would have seen land across the water, and could potentially have swum, drifted, or perhaps used early boats.
Over the next 10,000+ years, haplogroup U trekked across the Arabian peninsula into what is present-day Iran, probably moving slowly, generation by generation, then turning back westward, likely in a small group of hunter-gatherers, crossing the Nile Delta into North Africa, present-day Egypt.
They probably fished along the Nile. Food would have been plentiful along rivers and the sea.
It’s exciting to know that the ancestors of the LeJeune sisters lived right here, perhaps for millennia.
There’s more, however.
The Migration Map shows the location of the genetically closest Ancient DNA results to your haplogroup, obtained from archaeological excavations. This mapped information essentially anchors haplogroup branches in locations in both space and time.
Ancient DNA samples are represented by tiny brown trowels. Clicking on each trowel provides summary information about the associated sample(s) in that location.
Takeaways from the Migration Map
- Scientists have estimated the location where your base haplogroup originated. For the LeJeune sisters, that’s haplogroup U6 in North Africa along the Mediterranean Sea.
- The trowels show the locations of the genetically closest archaeological samples, aka Ancient Connections, in the FamilyTreeDNA data base.
- These Ancient Connections displayed on the map may change. New samples are added regularly, so your older samples, except for the oldest two, which remain in place for each tester, will roll off your list when genetically closer Ancient Connections become available.
- There are no Ancient Connections for the LeJeune sisters in France today, but keep in mind that Europe is closely connected. Today’s French border is only about 25 miles as the crow flies from Goyet, Belgium. France, sea to sea, is only about 500 miles across, and at its closest two points, less than 250 miles.
- Samples found at these locations span a large timeframe.
There’s a LOT more information to be found in the Ancient Connections.
Ancient Connections
Ancient Connections is one of my favorite Discover features. This information would never have been available, nor synthesized into a usable format, prior to the introduction of Mitotree and mtDNA Discover. Ancient Connections unite archaeology with genealogy.
- The first thing I need to say about Ancient Connections is that it’s unlikely that these individuals are YOUR direct ancestors. Unlikely does not mean impossible, but several factors, such as location and timeframe need to be considered.
- What is certain is that, based on their mitochondrial haplogroup, you SHARE a common ancestor at some point in time.
- Ancient samples can be degraded, with missing genetic location coverage. That means that not every mutation or variant may be able to be read.
- Different labs maintain different quality criteria, and location alignments may vary, at least somewhat, lab to lab. While this is always true, it’s particularly relevant when comparing ancient DNA results which are already degraded.
- Samples are dated by archaeologists using a variety of methodologies. FamilyTreeDNA relies on the dates and historical eras provided in the academic papers, but those dates may be a range, or contain errors.
- Obtaining information from ancient DNA samples isn’t as easy or straightforward as testing living people.
However, the resulting information is still VERY useful and incredibly interesting – filling in blanks with data that could never be discerned otherwise.
Many people mistakenly assume that these Ancient Connections are their ancestors, and most of the time, not only is that not the case, it’s also impossible. For example, a woman who lived in 1725 cannot be the ancestor of two sisters who were born in 1624 and 1633, respectively.
When you click on Ancient Connections, you see a maximum of about 30 Ancient Connections. Information about the genetically closest burial is displayed first, with the most distant last on the list.
Please note that the final two are the oldest and will (likely) never change, or “roll off” your list, unless an even older sample is discovered. When new samples become available and are genetically closer, the oldest other samples, other than the oldest two, do roll off to make space for the closer haplogroups and their corresponding samples.
Obviously, you’ll want to read every word about these burials, because nuggets are buried there. I strongly encourage you to read the associated papers, because these publications reveal snippets of the lives of your haplogroup ancestors and their descendants.
The small pedigree at right illustrates the relationship between the ancient sample and the haplogroup of the tester. Three things are listed:
- El Agujero 8, the name assigned by the authors of the paper that published the information about this ancient sample
- The haplogroup of the LeJeune descendant who tested
- The haplogroup of their common ancestor.
If no haplogroup is specifically stated for the ancient sample, the sample is the same haplogroup as the common shared ancestor (MRCA), meaning the tester and the ancient sample share the same haplogroup.
The Time Tree beneath the description shows the tester’s haplogroup, (or the haplogroup being queried), the ancient sample, and their common ancestral haplogroup.
Let’s analyze this first sample, El Agujero 8.
- The person whose remains were sampled lived about 1375 years ago (I’ve averaged the range), in the Canary Islands, and is part of the Guanche culture.
- The Guanche are the indigenous people of the Canary Islands, already established there before the arrival of Europeans and the Spanish conquest of the 1400s.
- The Guanche people are believed to have arrived in the Canaries sometime in the first millennium BCE (2000-3000 years ago) and were related to the Berbers of North Africa.
- This makes sense if you consider the Migration map and geographic proximity.
- Haplogroup U6a7a1, the haplogroup of El Agujero 8, is the shared ancestral haplogroup with the LeJeune sisters.
- That woman, U6a7a1, lived around 1450 BCE, or 3450 years ago, probably someplace in North Africa, the Mediterranean basin, or even in the Nile Delta region, given the correlation between the Canary Islands settlement, the Berbers, and the Migration Map.
- This does NOT mean that the ancestor of the LeJeune sisters lived in the Canary Islands. It means that a descendant of their MRCA, haplogroup U6a6a1, the shared common ancestor with the LeJeune sisters, lived in the Canary Islands.
Ancient Connections Chart Analysis Methodology
I create an Ancient Connection chart for each haplogroup I’m dealing with. We’re analyzing the LeJeune sisters today, but I track and analyze the haplogroup for every ancestor whose haplogroup I can find, or for whom I can find a descendant to test.
In this chart, YA=years ago and is based on the year 2000. KYA=thousand years ago, so 10 KYA is 10,000 years ago.
| Name | Person Lived | Location & Culture | Haplogroup, Date & Age | Shared (MRCA) Haplogroup, Date & Age | Note |
| LeJeune Sisters | Born 1624 & 1633 | French Acadian | U6a7a1a,
50 CE, 1950 YA |
U6a7a1a,
50 CE, 1950 YA |
In Acadia by 1643/44 |
| El Agujero 8 | 1375 CE | Canary Islands, Guanche | U6a7a1
1450 BCE, 3450 YA |
U6a7a1 1450 BCE, 3450 YA | Guanche arrived in Canaries in 1st millennium BCE, related to Berbers |
| Djebba 20824 | 6000 BCE | Jebba, Bājah, Tunisia, Neolithic | U6a3f3’4’5
c 5000 BCE, 7000 YA |
U6a1”9
19,000 BCE, 21,000 YA |
This archaeology site is on the northernmost point of North Africa |
| Djebba 20825 | 5900 BCE | Djebba, Bājah, Tunisia, Neolithic | U6a1”9
19,000 BCE, 21,000 YA |
U6a1”9
19,000 BCE, 21,000 YA |
This archaeology site is on the northernmost point of North Africa |
| Egyptian Mummy 2973 | 200 BCE | Abusir el-Meleq, Giza, Egypt, Ptolemaic Kingdom | U6a3h^,
1450 BCE, 3450 YA |
U6a1”9
19,000 BCE, 21,000 YA |
Nile Delta probably, paper says they share ancestry with near easterners |
| Egyptian Mummy 2888 | 100 BCE | Abusir el-Meleq, Giza, Egypt, Ptolemaic Kingdom | U6a2a’c,
11,000 BCE, 13,000 YA |
U6a1”9
19,000 BCE, 21,000 YA |
Nile Delta probably, paper says they share ancestry with near easterners |
| Segorbe Giant (6’3”) | 1050 CE | Plaza del Almudín, Valencia, Spain, Islamic necropolis burial | U6a1a1, 14,000 BCE, 16,000 YA
|
U6a1”9
19,000 BCE, 21,000 YA |
Paper says his genetic makeup is Berber and Islamic Spain, buried in Islamic style on right side facing Mecca. |
| Sweden Skara | 1050 CE | Varnhem, Skara, Sweden, Viking Swedish culture | U6a1a3a, 7350 BCE, 9350 YA, | U6a1”9
19,000 BCE, 21,000 YA |
Viking burial
|
| Chapelfield 696 | 1180 CE | Chapelfield, Norwich, England, Ashkenazi Jewish Medieval age | U6a1b1b. 400 BCE,
2400 YA
|
U6a1”9
19,000 BCE, 21,000KYA |
Possibly the 1190 antisemitic Norwich massacre |
| Montana Mina 38 | 1200 CE | Montana Mina, Lanzarote, Spain (Canary Islands), Guanche culture | U6a1a1b1 | U6a1”9
19,000 BCE, 21,000 YA |
Guanche arrived in Canaries in 1st millennium BCE, related to Berbers |
| Amina | 1725 CE | Gaillard Center, Charleston, South Carolina, Enslaved African American burials | U6a5b’f’g,
9550 BCE, 11,550 YA, |
U6a1”9
19,000 BCE, 21,000 YA |
Remains of pre-Civil War enslaved Africans unearthed in Charleston, SC |
| Doukanet el Khoutifa 22577 | 4400 BCE | Doukanet el Khoutifa, Mars, Tunisia, Maghrebi cultural group | U6b,
6500 BCE, 8500 YA
|
U6a’b’d’e, 23,000 BCE, 25,000 YA | Late Stone Age, shows some admixture with European Hunter-Gatherers, possibly back and forth from Sicily |
| Guanche 12 | 625 CE | Tenerife, Spain (Canary Islands), Guanche, Medieval | U6b1a1’6’8’9, 1 BCE,
2100 YA |
U6a’b’d’e, 23,000 BCE, 25,000 YA | Guanche arrived in the Canaries in 1st millennium BCE, related to Berbers |
| Guanche 14 | 775 CE | Tenerife, Spain (Canary Islands), Guanche, Medieval | U6b1a1’6’8’9, 1 BCE,
2100 YA |
U6a’b’d’e, 23,000 BCE, 25,000 YA | Ditto above |
| Antocojo 27 | 875 CE | Antocojo, La Gomera, Spain (Canary Islands) | U6b1a1’6’8’9, 1 BCE,
2100 YA |
U6a’b’d’e, 23,000 BCE, 25,000 YA | Ditto above |
| Guanche 13 | 900 CE | Cave, Tenerife, Spain (Canary Islands), Medieval | U6b1a1’6’8’9, 1 BCE,
2100 YA |
U6a’b’d’e, 23,000 BCE, 25,000 YA | Ditto above |
| Guanche 1 | 1090 CE | Cave, Tenerife, Spain (Canary Islands), Medieval | U6b1a1’6’8’9, 1 BCE,
2100 YA |
U6a’b’d’e, 23,000 BCE, 25,000 YA | Ditto above |
| Barranco Majona 30 | 1325 CE | Barranco Majona, La Gomera, Spain (Canary Islands), Guanche late Medieval | U6b1a1’6’8’9, 1 BCE,
2100 YA |
U6a’b’d’e, 23,000 BCE, 25,000 YA | Ditto above |
| Kostenki 14 | 36,000 BCE | Markina Gora, Kostyonki, Voronezh Oblast, Russia | U2,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA
|
U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
European/Asian steppe earliest hunter-gatherers. Farming didn’t arrive until 10 KYA. Admixture from Asia as well. |
| Kostenki 12 | 31,000 BCE | Volkovskaya, Voronezh region, Russian Federation. | U2c’e,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA
|
U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
Early hunter-gatherer |
| Krems 3 | 29,000 BCE | Wachtberg in Krems, Lower Austria, Austria, Gravettian culture | U5,
32,000 BCE, 34,000 YA |
U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
Endured the ice age, sophisticated toolmaking, Venus figures, mobile lifestyle, mammoth hunters |
| Krems Twin 1 | 28,800 BCE | Left bank of the Danube, Krems-Wachtberg, Austria, Gravettian culture | U5,
32,000 BCE, 34,000 YA |
U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
Double grave for twins, 1 newborn, one age about 50 days |
| Krems Twin 2 | 28,800 BCE | Left bank of the Danube, Krems-Wachtberg, Austria, Gravettian culture | U5,
32,000 BCE, 34,000 YA |
U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
Ditto above |
| Vestonice 13 | 28,900 BCE | Pavlovské Hills, South Moravia, Czech Republic, Grevettian culture | U8b^,
37,000 BCE, 39,000 YA
|
U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
Ice Age Europe, few samples before farming introduced. Believe these Gravettian individuals are from a single founder population before being displaced across a wide European region. |
| Vestonice 14 | 28,900 BCE | Dolni Vestonice, Brezi, Czech Republic, Gravettian culture | U5,
32,000 BCE, 34,000 YA |
U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
Ditto above |
| Vestonice 16 | 28,900 BCE | Dolni Vestonice, Brezi, Czech Republic, Gravettian culture | U5,
32,000 BCE, 34,000 YA |
U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
Ditto above |
| Grotta delle Mura child | 15,100 BCE | Grotta delle Mura, Bari, Italy, Paleolithic Italian culture | U2”10,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
This baby, interred in a small shoreline cave, was less than 9 months old and had blue eyes |
| Goyette Q2 | 13,100 BCE | Troisième Caverne, Goyet, Belgium, Magdaleian culture named after the La Madeleine rock shelter in France | U8a,
10,000 BCE, 12,000 YA
|
U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
These hunter-gatherer people may have been responsible for the repopulation of Northern Europe. Cave art, such as that at Altamira, in Northern Spain is attributed to the Magdalenian culture. |
| Villabruna 1 | 12,000 BCE | Villabruna, Italy, Paleolithic culture | U5b2b,
9700 BCE, 11,700 YA
|
U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
Rock shelter in northern Italy where this man was buried with grave goods typical of a hunter and covered in painted stones with drawings. The walls were painted in red ochre. |
| Oberkasel 998 | 12,000 BCE | Oberkassel , Bonn, Germany, Western Hunter-Gatherer culture | U5b1 | U,
43,000 BCE, 45,000 YA |
Double burial found in a quarry with 2 domesticated dogs and grave goods. Genis classification was uncertain initially as they were deemed, “close to Neanderthals.” |
Creating a chart serves multiple functions.
- First, it allows you to track connections methodically. As more become available, older ones fall off the list, but not off your chart.
- Second, it allows you to analyze the results more carefully.
- Third, it “encourages” you to spend enough time with these ancient humans to understand and absorb information about their lives, travels, and migrations – all of which relate in some way to your ancestors.
When creating this chart, I looked up every shared haplogroup to determine their location and what could be discerned about each one, because their story is the history of the LeJeune sisters, and my history too.
Ok, so I can’t help myself for a minute here. Bear with me while we go on a little Ancient Connections tour. After all, history dovetails with genetics.
How cool is it that the LeJeune sisters’ ancestor, around 20,000 years ago, who lived someplace in the Nile Delta, gave birth to the next 1000 (or so) generations?
Of course, the Great Pyramids weren’t there yet. They were built abotu 4600 years ago.
Those women gave birth to two women about 2200 years ago whose mummified remains were found in the Pyramids at Giza. The associated paper described Egypt in this timeframe as a cultural crossroads which both suffered and benefitted from foreign trade, conquest and immigration from both the Greeks and Romans.
You can read more about burials from this timeframe in The Beautiful Burial in Roman Egypt, here. A crossroads is not exactly what I was expecting, but reading the papers is critically important in understanding the context of the remains. This book is but one of 70 references provided in the paper.
Some burials have already been excavated, and work continues in the expansive pyramid complex.
The Egyptian sun is unforgiving, but Giza eventually gives up her secrets. Will more distant cousins of the LeJeune sisters be discovered as burial chambers continue to be excavated?
We know little about the lives of the women interred at Giza, but the life of another Ancient Connection, Amina, strikes chords much closer to home.
Amina, an enslaved woman, is another descendant of that woman who lived 20,000 years ago. She too is related to the Giza mummies.
Amina was discovered in a previously unknown burial ground in downtown Charleston, SC, that held the remains of enslaved people who had been brought, shackled, from Africa to be sold. Amina’s remains convey her story – that she was kidnapped, forced into the Middle Passage, and miraculously survived. She succumbed around 1725 in Charleston, SC, near the wharf, probably where her prison ship docked.
Charleston was a seaport where more than a quarter million enslaved people disembarked at Gadsden’s Wharf, awaiting their fate on the auction block. The location where Amina’s burial was found is only about 1000 feet from the wharf and is now, appropriately, considered sacred ground. Ohhh, how I’d like to share this information with Amina.
A hundred years earlier, a different ancestor of that women who lived 20,000 years ago gave birth to the mother of the LeJeune sisters, someplace in France.
Moving further back in time, another distant cousin was unearthed at the Kostyonki–Borshchyovo archaeological complex near the Don River in Russia.

Photographed by Andreas Franzkowiak (User:Bullenwächter) – Archäologisches Museum Hamburg und Stadtmuseum Harburg, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=58260865
Markina Gora is an incredibly famous location yielding both specimens included here, as well as this famous Venus figurine from the Gravettian culture, dating from about 27,000 years ago.
Bust of Kostenki 14 reconstructed from the burial.
The earliest of these hunter-gatherers in Europe, believed to be a small group of humans, interbred with Neanderthals. Kostenki 14 carried Neanderthal introgression dating back to about 54,000 years ago.
A layer of volcanic ash, thought to be from a volcano near Naples that erupted about 39,000 years ago, is found above the remains, speaking to events that our ancestors survived after this man lived.
I know we’ve traveled far back in history from the LeJeune sisters, but these ancient humans, the MRCA of each upstream haplogroup, are our ancestors, too.
What does all this mean?
At first glance, it’s easy to assume that all of the locations are relevant to our direct ancestors. Not only that, many people assume that all of these people ARE our ancestors. They aren’t.
Creating the Ancient Conenctions Chart should help you gain perspective about how these people are related to you, your ancestors, and each other.
Each individual person is connected to you and your ancestors in various ways – and their stories weave into yours.
Discover provides everyone has a mini-Timeline for each Ancient Connection. It’s easy to see that the tester, who tested in the modern era, since the year 1950, is not descended from El Agujaro 8, who lived in the 1300s and whose common (shared) haplogroup with the tester, U6a7a1, was born between 2100 BCE and 900 BCE, or between 4100 and 2900 years ago. The most probable date is about 3450 years ago.
The Timeline for each ancient sample includes:
- Your haplogroup’s mean birth year
- Ancient Connection’s birth year
- Ancient Connection’s haplogroup mean birth year, if different from the common haplogroup (in the example above, 3 and 4 are the same)
- Birth year of your common ancestor (MRCA), which is your common haplogroup
It’s easy to see the relevant information for each sample, but it’s not easy to visualize the trees together, so I’m creating a “rough” tree in Excel to help visualize the “big picture”, meaning all of the Ancient Connections.
How Do I Know Which Ancient Connections Even MIGHT Be My Ancestors and How We Are All Related?
That’s a great question and is exactly why I created this chart in an ancient haplogroup spreadsheet.
In this chart, you can see the LeJeune sisters, in red, at the bottom, and their direct line hereditary haplogroups, in purple, descending from haplogroup U at the top.
Branching to the left and right from intersections with their purple hereditary haplogroups are other branches that the LeJeune sisters don’t share directly. However, the ancient remains that carry those haplogroups are “haplocousins” at a distant point in time, with our LeJeune sisters.
There only two burials that carry the same ancestral haplogroup as the LeJeune sisters:
- El Agujero 8, haplogroup U6a7a1 who lived in the Canary Islands in the year 1275
- Djebba 20825, who lived in Tunisia about 6,100 years ago
Clearly, Djebba, with a common haplogroup that lived about 21,000 years ago cannot be the ancestor of the LeJeune sisters, but they share a common ancestor. If Djebba was an ancestor of the LeJeune sisters, then Djebba would also descend from haplogroup U6a7, born about 20,600 years ago, like the LeJeune sisters do.
A cursory glance might suggest that since the sample, El Agujero 8 lived in the Canary Islands about 1275, haplogroup U6a7a1 was born there. However, if you read the papers associated with all of the samples found in the Canaries, Tunisia, Spain and other locations, you’ll discover that these populations moved back and forth across the Mediterranean. You’ll also discover that the earliest European haplogroup U samples found in Europe are believed to be the founders of haplogroup U in Europe. It’s possible that U6 dispersed into Italy and Spain, regions with significant exchange with North Africa.
It’s extremely unlikely that El Agujero 8, who lived about the year 1275 CE, was the ancestor of the LeJeune sisters, but it’s not entirely impossible. What’s more likely is that they descended from a common population that moved between Spain, the Canaries, and North Africa where other similar burials are found, like Tunisia. We know that Rome largely conquered France during the Gallic Wars (56-50 BCE), so it’s not terribly surprising that we find haplogroup U6a7a1 and descendants scattered throughout Europe, the Iberian peninsula, the Roman empire, and North Africa.
Sometime between the birth of haplogroup U6a7a1, about 3450 years ago, the descendants of that woman found their way both to France before the 1600s and also to the Canaries before 1275.
Takeaways from Ancient Connections
- I recommend that you read the associated academic papers and publications that provide the Ancient Connections mitochondrial haplogroups. Those publications are chock full of important cultural information.
- Globetrekker, which won’t be released until some time after the next release of the Mitotree, will help with tracking the path of your ancestors, especially where it’s complex and uncertain.
- The “haplosisters” and “haplocousins” of the French LeJeune sisters are quite diverse, including Egyptian pyramid burials in Giza, a Muslim necropolis burial in Spain, a Viking in Sweden, indigenous Canary Islanders, a Tunisian site on the Northern-most tip of Africa, a Jewish burial in England, an enslaved woman in South Carolina, the Markina Gora site in Russia, caves in Austria, the Czech Republic, Belgium, Germany and Italy.
- Ancient Connections are more than just interesting. On another genealogical line, I found a necropolis burial with my ancestor’s haplogroup located about 9 km from where my ancestor is believed to have lived, dating from just a few hundred years earlier.
- FamilyTreeDNA adds more Ancient Connections weekly.
Resources
- Svante Pääbo Wins Nobel Prize in Medicine for Ancient DNA Reconstruction Methods
- Unlocking Our Ancestry: The Fascinating Science of Ancient DNA Analysis
- What’s New in Ancient DNA and Ancient Discover Connections
- Ancient Connections of the Maternal Kind
- Unlocking Our Ancestry: The Fascinating Science of Ancient DNA
Notable Connections
Notable Connections are similar to Ancient Connections, except they are generally based on modern-day or relatively contemporary testers and associated genealogy. Some samples are included in both categories.
Three Notable Connections are included with the public version of Discover, and additional Notable Connections are provided, when available, for testers who click through from their account.
Some Notable Connections may be close enough in time to be useful for genealogy based on their haplogroup, their haplogroup history, and the tester’s history as well.
In this case, the closest two Notable Connections are both included in Ancient Connections, so we know that the rest won’t be closer in time.
The common ancestor, meaning common haplogroup, of Cheddar Man and the rest, reaches all the way back to haplogroup U, born about 45,000 years ago, so these particular Notable Connections can be considered “fun facts.”
However, if the first (closest) notable connection was a famous person who lived in France in the 1600s, and was the same or a close haplogroup, that could be VERY beneficial information.
Takeaways from Notable Connections
- Mostly, Notable Connections are just for fun – a way to meet your haplocousins.
- Notable Connections are a nice way to emphasize that we are all connected – it’s only a matter of how far back in time.
- That said, based on the haplogroup, location and date, you may find Notable Connections that hold hints relevant to your ancestry.
Scientific Details
Scientific Details includes two pages: Age Estimates and Variants.
Scientific Details Age Estimates
Haplogroup ages are calculated using a molecular clock that estimates when the mutation defining a particular haplogroup first arose in a woman.
Since we can’t go back in time, test everyone, and count every single generation between then and now – scientists have to reconstruct the phylogenetic tree.
The more people who test, the more actual samples available to use to construct and refine the Mitotree.
The “mean” is the date calculated as the most likely haplogroup formation date.
The next most likely haplogroup formation range is the 68% band. As you can see, it’s closest to the center.
The 95% and 99% likelihood bands are most distant.
I know that 99% sounds “better” than 68%, but in this case, it isn’t. In fact, it’s just the opposite – 99% takes in the widest range, so it includes nearly all possibile dates, but the center of the range is the location most likely to be accurate.
The full certainty range is the entire 100% range, but is extremely broad. The mean is the date I normally use, UNLESS WE ARE DEALING WITH CONTEMPORARY DATES.
For example, if the LeJeune sisters’ haplogroup was formed in 1550 CE at the mean, I’d be looking at the entire range. Do their approximate birth years of 1624 and 1633 fall into the 68% range, or the 95% range, and what are the years that define those ranges?
Scientific Details Variants
Next, click on the Variants tab.
To view your haplotype cluster, the F#, and your private variants, slide “Show private variants” at upper right above the black bar to “on.” This feature is only available for testers who sign in and click through to mtDNA Discover from their page.
The Variants tab provides lots of information, beginning with a summary of your:
- Haplotype cluster F number, which I’ve blurred
- Private variants, if any
- End-of-branch haplogroup information
The most granular information is shown first.
Your haplotype cluster number is listed along with any private variants available to form a new haplogroup. In this case, there are no private variants for these haplotype cluster members. Every cluster is different.
Just beneath that, listed individually, are the variants, aka SNPs, aka mutations that identify each haplogroup. The haplogroup with the red square is yours.
Everyone in this haplogroup shares these two mutations: A2672G and T11929C. Because two variants define this haplogroup, it’s possible that one day it will split if future testers have one but not the other variant.
Information in the following columns provides details about each mutation. For example, the first mutation shown for haplogroup U6a7a1a is a transition type SNP mutation in the coding region, meaning it’s only reported in the full sequence test, where the A (Adenine) nucleotide, which is ancestral, mutated to a G (Guanine) nucleotide which is derived. This is essentially before (reference) and after (derived).
If you mouse over the Weight column, you’ll see a brief explanation of how each mutation is ranked. Essentially, rarer mutation types and locations are given more weight than common or less stable mutation types and/or locations.
Mutations with orange and red colors are less stable than green mutations.
Following this list from top to bottom essentially moves you back in time from the most recently born haplogroup, yours, to haplogroup L1”7, the first haplogroup in this line to branch from Mitochondrial Eve, our common ancestor who lived about 143,000 years ago in Africa.
View More
Clicking on the “View More” dropdown exposes additional information about the various types of mutations and Filtered Variants. Filtered Variants, in the current version of the Mitotree, are locations combined with specific mutation types that are excluded from branch formation.
Please note that this list may change from time to time as the tree is updated.
Takeaways from Scientific Details
- Based on the Age Estimate for haplogroup U6a7a1a, it’s most likely to have formed about the year 29, but could have formed anytime between about 186 BCE and 230 CE. While this range may not be terribly relevant for older haplogroups, ranges are very important for haplogroups formed in a genealogical era.
- People who are members of this example haplotype cluster do not have any private variants, so they are not candidates to receive a new haplogroup unless the upstream tree structure itself changes, which is always possible.
- A significant amount of additional scientific information is available on these two tabs.
- A list of locations currently excluded from haplogroup formation is displayed by clicking on the “View more” dropdown, along with information about various types of mutations. This list will probably change from time to time as the tree is refined.
Compare
Compare is a feature that allows you to compare two haplogroups side by side.
Let’s say we have an additional woman named LeJeune in Acadia, aside from Catherine and Edmee. As it happens, we do, and for a very long time, assumptions were made that these three women were all sisters.
Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard was born about 1659 and died after 1708. She is the daughter of unknown parents, but her father is purported to be Pierre LeJeune born about 1656, but there’s no conclusive evidence about any of that.
Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard married twice, first to Francois Joseph. Their daughter, Catherine Joseph’s marriage record in 1720 lists Jeanne, Catherine’s mother, as “of the Indian Nation.”
Several direct matrilineal descendants of Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard have joined the Acadian AmerIndian DNA Project, revealing her new Mitotree haplogroup as haplogroup A2f1a4+12092, which is Native American.
If Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard born about 1659, and Edmee and Catherine LeJeune, born about 1624 and 1633, respectively, are full or matrilineal half-siblings, their mitochondrial DNA haplogroups would match, or very closely if a new branch had formed in a descendant since they lived.
Let’s use the Compare feature to see if these two haplogroups are even remotely close to each other.
Click on “Compare.”
The first haplogroup is the one you’re searching from, and you’ll choose the one to compare to.
Click on “Search a haplogroup” and either select or type a haplogroup.
The two haplogroups are shown in the little pedigree chart. The origin dates of both haplogroups are shown, with their common shared ancestor (MRCA) positioned at the top. The most recent common, or shared, ancestor between Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard, who was “of the Indian Nation” and Catherine and Edmee LeJeune is haplogroup N+8701, a woman born about 53,000 years ago.
There is absolutely NO QUESTION that these three women DO NOT share the same mother.
Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard is matrilineally Native, and sisters Caterine and Edmee LeJeune are matrilineally European.
Takeaways from Compare
- The MRCA between Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard and sisters, Edmee and Catherine LeJeune is about 53,000 years ago.
- Jeanne was clearly not their full or maternal sister.
- Compare provides an easy way to compare two haplogroups.
Suggested Projects
Projects at FamilyTreeDNA are run by volunteer project administrators. Some projects are publicly viewable, and some are not. Some project results pages are only visible to project members or are completely private, based on settings selected by the administrator.
When testers join projects, they can elect to include or exclude their results from the public project display pages, along with other options.
The “Suggested Projects” report in Discover provides a compilation of projects that others with the haplogroup you’re viewing have joined. Keep in mind that they might NOT have joined due to their mitochondrial DNA. They may have joined because of other genealogical lines.
While these projects aren’t actually “suggested”, per se, for you to join, they may be quite relevant. Viewing projects that other people with this haplogroup have joined can sometimes provide clues about the history of the haplogroup, or their ancestors, and therefore, your ancestors’ journey.
Remember, you (probably) won’t match everyone in your haplogroup on your matches page, or the Match Time Tree, so projects are another avenue to view information about the ancestors and locations of other people in this haplogroup. The projects themselves may provide clues. The haplogroup projects will be relevant to either your haplogroup, or a partial upstream haplogroup.
The haplogroup U6 project includes multiple U6 daughter haplogroups, not just U6a7a1a, and includes testers whose ancestors are from many locations.
The U6 project has labeled one group of 38 members the “Acadian cluster.” Of course, we find many descendants of Catherine and Edmee LeJeune here, along with testers who list their earliest known ancestor (EKA) as a non-Acadian woman from a different location.
The ancestors of Martha Hughes, who lived in Lynn, Massachusetts, and Mary Grant from Bathhurst, New Brunswick may well be descendants of Edmee or Catherine.
Or, perhaps they are a descendant of another person who might be a connection back to France. If you’re the Hughes or Grant tester, you may just have tested your way through a brick wall – and found your way to your LeJeune ancestors. If you’re a LeJeune descendant, you might have found a link through one of those women to France. Clearly, in either case, additional research is warranted.
For descendants of Catherine and Edmee, you’re looking for other testers, probably from France, whose ancestors are unknown or different from Edmee and Catherine. That doesn’t mean their genealogy is accurate, but it does merit investigation.
Check to see if someone with that EKA is on your match list, then check their tree.
For Catherine and Edmee LeJeune, other than Martha and Mary, above, there was only one EKA name of interest – a name of royalty born in 1606. However, research on Marie Bourbon shows that she was not the mother of the LeJeune sisters, so that tester is either incorrect, or confused about what was supposed to be entered in the EKA field – the earliest known direct matrilineal ancestor.
You may also find people in these projects who share your ancestor, but have not upgraded to the full sequence test. They will have a shorter version of the haplogroup – in this case, just U6a. If they are on your match list and their results are important to your research, you can reach out to them and ask if they will upgrade.
If you’re working on an ancestor whose mitochondrial DNA you don’t carry, you can contact the project administrator and ask them to contact that person, offering an upgrade.
Takeaways from Suggested Projects
- Suggested Projects is a compilation of projects that other people with this haplogroup have joined. Haplogroup-specific projects will be relevant, but others may or may not be.
- Testers may have joined other projects based on different lineages that are not related to their mitochondrial line.
We’re finished reviewing the 12 Discover reports, but we aren’t finished yet with the LeJeune analysis.
Another wonderful feature offered by FamilyTreeDNA is Advanced Matching, which allows you to search using combinations of tests and criteria. You’ll find Advanced Matching on your dashboard.
Advanced Matching
Advanced Matching, found under “Additional Tests and Tools,” is a matching tool for mitochondrial DNA and other tests that is often overlooked.
You select any combination of tests to view people who match you on ALL of the combined tests or criteria.
Be sure to select “yes” for “show only people I match in all selected tests,” which means BOTH tests. Let’s say you match 10 people on both the mitochondrial DNA and Family Finder tests. By selecting “Yes,” you’ll see only those 10 people. Otherwise you’ll get the list of everyone who matches you on both tests individually. If you have 100 mitochondrial matches, and 2000 autosomal matches, you’ll see all 2100 people – which is not at all what you want. You wanted ONLY the people who match you on both tests – so be sure to select “yes.”
The combination of the FMS, full sequence test, plus Family Finder displays just the people you match on both tests – but keep in mind that it’s certainly possible that you match those people because of different ancestors. This does NOT mean you match on both tests thanks to the LeJeune sisters. You could match another tester because of a different Acadian, or other, ancestor.
This is especially true in endogamous populations, or groups, like the Acadians, with a significant degree of pedigree collapse.
Advanced Matching Tip
You can also select to match within specific projects. This may be especially useful for people who don’t carry the mitochondrial DNA of the LeJeune sisters, but descend from them.
Switching to my own test, I’ve selected Family Finder, and the Acadian AmerIndian Project, which means I’ll see everyone who matches me on the Family Finder test AND is a member of that project.
Given that I’ve already identified the haplogroup of Catherine LeJeune, I can use known haplogroups to filter autosomal matches, especially in focused projects such as the Acadian AmerIndian Project. This helps immensely to identify at least one way you’re related to other testers.
By clicking on the match’s name, I can see their EKA information. By clicking on their trees, I can verify the ancestral line of descent.
Of course, in Acadian genealogy, I’m probably related to these cousins through more than one ancestor, but using Advanced Matching, then sorting by haplogroup is a great way to identify at least one common ancestor!
Takeaways from Advanced Matching
- Advanced Matching is a wonderful tool, but make sure you’re using it correctly. Click “Yes” to “Show only people I match in all selected tests.” Please note that if you select all three levels of mtDNA test, and you don’t match at the HVR1 level due to a mutation, that person won’t be shown as a match because you don’t match them on all test levels selected. I only select “FMS” and then my second test.
- You may match someone on either Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA and the autosomal Family Finder through different ancestral lines.
- Advanced Matching is a great way to see who you match within a project of specific interest – like the Acadian AmerIndian Project for the LeJeune sisters.
- You will match people outside of projects, so don’t limit your analysis.
Drum Roll – LeJeune Analysis
It’s finally time to wrap up our analysis.
The original questions we wanted to answer were:
- Were Edmee and Catherine LeJeune actually sisters?
- Was their mother Native American?
- Was the third woman, Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard, also their sister?
- Are there any other surprises we need to know about?
We now have answers, so let’s review our evidence.
- Based on the haplogroup of Edmee and Catherine LeJeune both, U6a7a1a, which is clearly NOT of Native American origin, we can conclude that they are NOT Native American through their matrilineal side.
- Native American haplogroups are subsets of five base haplogroups, and U is not one of them.
There’s other information to be gleaned as well.
- Based on the haplogroup of Jeanne LeJeune dit Briard, A2f1a4+12092, plus her daughter’s marriage record, we can conclude that (at least) her mother was Native American.
- Based on Jeanne’s Native American haplogroup alone, we can conclude that she is not the full sister of the Catherine and Edmee LeJeune.
- Based on Jeanne’s birth date, about 1659, it’s clear that she cannot be the full sibling of Catherine born about 1633, and Edmee LeJeune, born about 1624, and was probably a generation too late to be their paternal half sister. Later lack of dispensations also suggests that they were not half-siblings.
- Based on the known Acadian history, confirmed by contemporaneous records, we can state conclusively that Edmee LeJeune was born in France and Catherine probably was as well. The first Acadian settlement did not occur until 1632, and the first known families arrived in 1636.
- Based on the fact that Catherine and Edmee’s haplogroups match, and many of their descendants’ mitochondrial DNA matches exactly, combined with later dispensations, we can conclude that Catherine and Edmee were sisters.
- We can conclusively determine that Catherine and Edmee were NOT Native on their matrilineal side, and given that they were born in France, their father would have been European as well. However, we cannot determine whether their descendants married someone who was either Native or partially Native.
- We know that information for partial haplogroup U6a, provided for HVR1 and HVR1+HVR2-only testers is not necessarily relevant for full sequence haplogroup U6a7a1a.
- The recent Mitotree release has moved the haplogroup “dates” for the LeJeune sisters from about 21,000 years ago for HVR1/HVR2 U6a testers to 50 CE for full sequence testers,. These dates may well be refined in future tree releases.
- Having multiple testers has provided us with an avenue to garner a massive amount of information about the LeJeune sisters, in spite of the fact that their haplogroup was born about 50 CE.
- The LeJeune sisters are related to, but not descended from many very interesting Ancient Connections. Using our Ancient Connections spreadsheet, we can rule out all but one Ancient Connection as being a direct ancestor of the LeJeune sisters, but they are all “haplocousins,” and share common ancestors with the sisters.
- While we cannot rule out the genetically closest Ancient Connection, El Agujero 8, who lived about 1275 CE in the Canary Islands as their direct ancestor, it’s very unlikely. It’s more probable that they share a common ancestor in haplogroup U6a7a1 who lived about 3450 years ago, whose descendants spread both into France by the 1600s and the Canary Islands by the 1200s.
By now, you’re probably thinking to yourself that you know more about my ancestors than your own. The good news is that mitochodnrial DNA testing and mtDNA Discover is available for everyone – so you can learn as much or more about your own ancestors.
Spread Encouragement – Be a Positive Nellie!
Unfortunately, sometimes people are discouraged from mitochondrial DNA testing because they are told that mitochondrial haplogroups are “too old,” and matches “are too distant.” Remember that the MRCA of any two people, or groups of people is sometime between the haplogroup formation date, and the current generation – and that’s the information we seek for genealogy.
Furthermore, it’s those distant matches, beyond the reach of autosomal matching, that we need to break down many brick walls – especially for female ancstors. I offer testing scholarships for ancestors whose mitochondrial DNA is not yet represented. It’s information I can’t obtain any other way, and I’ve broken through many brick walls!
We don’t know what we don’t know, and we’ll never know unless we take the test.
Imagine how much could be gained and how many brick walls would fall if everyone who has tested their autosomal DNA would also take a mitochondrial DNA test.
Which ancestors mitochodrial DNA do you need? The best place to start is with your own, plus your father’s, which gives you both grandmother’s mtDNA and directly up those lines until you hit that brick wall that needs to fall.
Additional Resources
- Mitochondrial DNA Resource Page
- 13 Step to Help Find Your Native American Ancestors
- New Native American Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroups
- Understanding mtDNA Haplogroups
Roberta’s Books:
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – by Roberta Estes, for those ordering the e-book from anyplace, or paperback within the United States
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – for those ordering the paperback outside the US
- The Complete Guide to FamilyTreeDNA – Y-DNA, Mitochondrial, Autosomal and X-DNA – for those ordering the e-book from anyplace, or paperback within the United States
- The Complete Guide to FamilyTreeDNA – Y-DNA, Mitochondrial, Autosomal and X-DNA for those ordering the paperback from outside the US
_____________________________________________________________
Share the Love!
You’re always welcome to forward articles or links to friends and share on social media.
If you haven’t already subscribed (it’s free,) you can receive an e-mail whenever I publish by clicking the “follow” button on the main blog page, here.
You Can Help Keep This Blog Free
I receive a small contribution when you click on some of the links to vendors in my articles. This does NOT increase your price but helps me keep the lights on and this informational blog free for everyone. Please click on the affiliate links in the articles or to the vendors below if you are purchasing products or DNA testing.
Thank you so much.
DNA Purchases and Free Uploads
- FamilyTreeDNA – Y-DNA, mitochondrial and autosomal DNA testing
- MyHeritage DNA – Autosomal DNA test
- AncestryDNA – Autosomal DNA test
- AncestryDNA Plus Traits
- 23andMe Ancestry – Autosomal DNA only, no Health
- 23andMe Ancestry Plus Health
Genealogy Products and Services
- MyHeritage Subscription with Free Trial
- Legacy Family Tree Webinars – Genealogy and DNA classes, subscription-based, some free
- Legacy Family Tree Software – Genealogy software for your computer
- OldNews – Old Newspapers with links to save to MyHeritage trees
- MyHeritage Omni comprehensive “everything included” subscription plan
- Newspapers.com – Search newspapers for your ancestors
- NewspaperArchive – Search different newspapers for your ancestors
My Books
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – by Roberta Estes, for those ordering the e-book from anyplace, or paperback within the United States
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – for those ordering the paperback outside the US
- The Complete Guide to FamilyTreeDNA – Y-DNA, Mitochondrial, Autosomal and X-DNA – for those ordering the e-book from anyplace, or paperback within the United States
- The Complete Guide to FamilyTreeDNA – Y-DNA, Mitochondrial, Autosomal and X-DNA for those ordering the paperback from outside the US
Genealogy Books
- Genealogical.com – Lots of wonderful genealogy research books
- American Ancestors – Wonderful selection of genealogy books
Genealogy Research
- Legacy Tree Genealogists – Professional genealogy research