FamilyTreeDNA recently released Globetrekker, a great new feature for Big Y customers as part of the Discover tools. You can read about the Discover tools, here.
What Is Globetrekker?
Globetrekker is a new mapping feature that maps your Y-DNA ancestral migration path from Y-Adam in Africa born about 200,000 years ago to where your direct paternal ancestors are found most recently based on:
- The earliest known ancestor (EKA) locations of you, your matches and other testers
- Ancient DNA samples
- Various geographic criteria including elevation, migration corridors, sea levels, and glaciers.
This data-driven model also includes sea levels over time and some climate factors, such as glaciation. Clearly, our ancestors needed access to clean water, food and an environment where they weren’t going to freeze to death. If they had to choose between migrating along a lower level coastal region, or heading straight across the high mountains into the unknown, it’s more likely that they took the lower elevation coastal route with assured food.
Globetrekker displays the “most likely” corridors for you to review.
While you only see your Y-DNA line initially, the map includes 48,000 migration paths for all haplogroups spread across each continent. If you’ve taken the Big Y test, you can view any of the haplogroups in Discover.
And, there’s an integrated tree browser, too.
You can read FamilyTreeDNA’s blog article, written by Goran Runfeldt, head of R&D, here.
Please Note
- Everyone must sign into their own account to use the new Globetrekker tool. To use the rest of the Discover features, everyone can use the public version of the tool, but Globetrekker is for Big Y customers only, which is why you need to sign in. You’ll also receive more information in other categories, such as Notable and Ancient Connections, if you access Discover through your account. The free public version is limited.
- If you’re a project administrator and you normally view your project members’ results through your project (with member-granted authorization, of course) you can’t do that yet with Globetrekker.
- This means that every tester has to sign on using their own kit number and password. FamilyTreeDNA is working on Group Administrator access, so don’t despair if you normally depend on your volunteer administrator to handle things for you and explain. It’s coming.
- The migration map includes only pre-Columbian migrations. In other words, if your EKA is not Native American and is brick-walled in the US, you won’t see it on the map. You’ll see your closest haplogroup location before about 1500.
- These routes will change over time with additional testers whose results will shift and refine the paths.
Best Thing You Can Do
The best things you can do, aside from taking (or upgrading to) a Big Y-700 test are:
- Complete your earliest known ancestor (EKA) information.
- Be SURE to include a country AND a location of origin because that’s the data Globetrekker draws from.
- If your cousins test too, you may be assigned a new, more refined haplogroup, so recruit people. If you don’t know anyone specific, looking at your STR matches is a good resource to find candidates.
Adding Your EKA
To add your EKA and their geographic location, sign in to your account and click on your name, which will display a menu.
Select Account Settings.
Select Genealogy, then Earliest Known Ancestors, then complete the information, including Country, which assigns the flag, among other things. Click on update location to complete or change this location.
Search or place the pin in the correct location. Then click Save.
There are three very important pieces of EKA information that need to be completed to reap all the benefits of the Matches Map, Discover, the Time Tree, the Group Time Tree that includes ancestors, and Globetrekker.
- EKA Name and birth/death date
- Country of Origin field using the dropdown (Please note Native American entries for proven Native ancestors/haplogroups)
- Ancestral Location for specific locations for the Matches Map
While you’re here, enter your direct matrilineal ancestor’s information too – that’s your mother’s mother’s mother’s line, which you’ll need for mitochondrial DNA..
Then, click the orange Save button at the bottom of the page.
Your map location will also appear on your STR Matches Map. You may find relevant matches there, even if they haven’t taken the Big Y test.
There’s immense power in collaboration.
I often reach out to STR panel (12-111 markers) matches and men with the same or similar surnames, asking if they will consider upgrading to the Big Y, sometimes providing testing scholarships. The only way to obtain the most refined haplogroup possible and the most accurate migration path is for multiple people in the same lineage to test AND complete the location information.
Now that we’ve completed our housekeeping, let’s look at Globetrekker.
Globetrekker Quick Test Drive
I’ll be writing about Globetrekker results in detail soon, but for right now, let’s just take a quick spin.
Sign in to your account and click on the Discover Haplogroup Reports under Y-DNA Results and Tools.
You’ll see your Haplogroup Story, of course, and on the left side, you’ll see the Globetrekker link. Click on Globetrekker.
It Takes Two to Tango
Please note the introduction at the top of the Globetrekker page, and don’t get drawn into the beautiful map without reading this part first, along with the Release Announcement, Caveats, and Survey. Please take the survey after you’ve used Globetrekker.
- In order to RECEIVE a detailed haplogroup, it takes at least two people with the variant (mutation) that is then named and becomes the same haplogroup. This is why we recommend that men ask a cousin from the same paternal line to test, or even a father/brother/uncle.
- To MAP the location of a haplogroup on Globetrekker, it takes at least two people with the same haplogroup who have selected a location. Looking at my cousin’s results, I had already entered his EKA and location, but apparently his Big Y matches have not, so there are not two men with R-ZS3700 who have locations specified. I need to contact his matches.
Be sure to enter all of your EKA info. If your cousins have tested, they need to enter their information as well.
- Globetrekker cannot use results for the mapping function without locations.
- Globetrekker cannot use non-Native American haplogroups that are recorded with a location in the Americas. Globetrekker does provide Native American mapping in North and South America when the haplogroup is Native and a location is provided.
- Globetrekker CAN utilize coordinates in the Americas, but a country of origin in Europe or elsewhere pre-Columbus. Globetrekker defaults to the country of origin. Please make sure this information is accurate and not just a guess or oral history.
Locations or at least countries need to be as accurate as possible. If there are only two men with a specific haplogroup, for example, and one enters England and the other enters France, Globetrekker tries to plot the location of that haplogroup someplace in the middle. In this circumstance, probably neither person is happy – both complaining about inaccuracy. Yet another reason why it’s a good thing to help your fellow genealogists.
Therefore, if you notice that you have a Big Y match on either your Big Y match list, or your STR (12-111 panel) matches, and they don’t have an EKA and country listed, with a location displayed on the matches map, PLEASE email them and ask nicely if they will add that info. You can send them a link to this article to explain why providing that information is critically important for them AND the people they match, just like your information is crucial to them. Without location data, Globetrekker paths can’t be calculated correctly, and sometimes not at all. The more data, the greater the accuracy.
After you enter your EKA information and after Big Y results are back, it will be a week or so before Discover and Globetrekker are up to date. Discover is updated weekly, and if a new haplogroup is added, Globetrekker will be up to date the following week.
Drum Roll Please…..
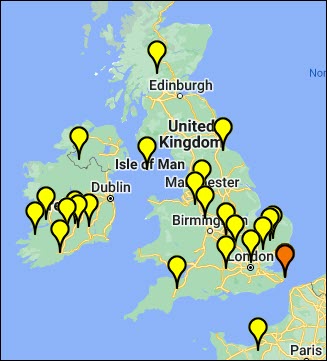
Here it is. The new highly refined Globetrekker migration map. It’s a beauty!
Your end-of-line haplogroup, or the closest one that can be calculated, will be shown in orange. In this case, it’s R-BY490 (circa 1650 CE) because the location of R-ZS3700 (circa 1700 CE) can’t be calculated.
On the map, you can see the various haplogroups that are upstream of haplogroup R-BY490, meaning parent haplogroups.
The path from Y-Adam in Africa is mapped, with the color changing to represent the birth of each major haplogroup in the migration path.
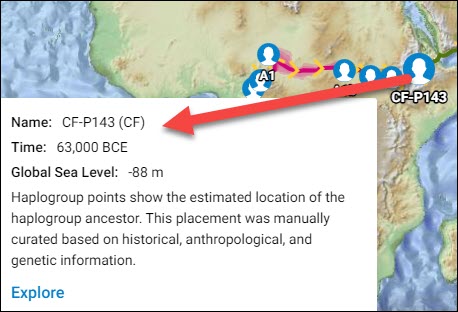
For example, I clicked on the pin for haplogroup CF, which expanded that haplogroup to CF-P143 and showed information about how the haplogroup pin was located on the map – plus the age and sea level difference at the time.
Scroll down on the map until you see the play button. Clicking on that button animates the migration path, beginning with Y-Adam, then progressing to the most current pre-Columbian migration.
In this case, I paused the video at the formation of haplogroup R1.
Notice the glaciation that both forms and recedes. Clearly, your ancestors weren’t living there during glaciation, but humans moved into those areas after the glaciers thawed and retreated.
You may be surprised at the path your ancient ancestors took, so I encourage you to spend some time with this map, reviewing the approximate path and your parental haplogroups with an open mind.
A legend is located in the far right upper corner to help explain the map details, including Ocean Currents and the various sea level colors.
Notice Doggerland, in dark green, which was a land mass when some haplogroups arrived in what is now the British Isles. Doggerland flooded sometime between 6500 and 6200 BCE, or about 8500 years ago, so it’s sea today. In other coastal locations, some previous land areas are covered by water today. Note the Baltic above, for example. Truthfully, that explains a lot. I knew about Doggerland but not about many of the other coastal regions around the world.
Pay close attention to what’s happening on the map. I noticed that my red pin for the current haplogroup is found in Deal, England, but so is an earlier haplogroup, so the later pin obscures the earlier pin. I enlarged the map and paused the video at 1400 CE so the red pin doesn’t form yet, then clicked on haplogroup R-Z290 that arrived from across the English Channel.
The R-Z290 pin location tells me that my Estes male ancestors arrived from continental Europe around 4650 years ago. My assumption (there’s that word again) had been that the original Estes ancestors arrived, then stayed right in Deal, a coastal village very near Dover, the closest point to the European mainland. According to Globetrekker, that wasn’t at all what happened.
I was initially somewhat skeptical, but then looking at all of the upstream haplogroups, I realized that those 17 haplogroups upstream of R-BY490 had to get into the other parts of the British Isles somehow – and my ancestor clearly descends from those men.
Could my ancestors have crossed back over to the European mainland at some point, then recrossed into Deal? Yes, of course, but without any genetic or other evidence, that’s speculation ONLY, with nothing at all to support it. In other words, that speculation would be based on what I believed all these years and nothing more.
The data-driven genetic scientific evidence tells us that our Estes ancestor arrived in what is today England about 4500 years ago. As you can see, there are a total of 17 points in England that have been reliably placed, not just one or two that might be open to speculation. Additionally, we have ancient DNA evidence.
Notice the functions at the top of the map. Turn on Ancient Connections. You’ll see the little shovels appear when their timeframe and location are relevant to the map migration, then disappear when it isn’t.
Pause the map again, and click on the shovel to display relevant information about the archaeology dig that produced Y-DNA results of sufficient quality to be included. Those ancient samples often anchor haplogroups in a known place at a specific time.
While you’re enjoying different views, try the other options at the top of the Globetrekker map.
Integrated Tree Browser
Scroll down beneath the map to view the integrated tree browser.
This is VERY cool because the tree browser moves in tandem with the map above.
You can see that the migration map shows R-BY487, and on the timeline below, R-BY487 is showing at the top, along with the downstream haplogroups.
R-BY482 (circa 1500 CE), R-BY490 (circa 1650 CE), and R-ZS3700 (circa 1700 CE) are all Estes surname haplogroups. Prior to that, R-BY487 (circa 750 CE) has no associated surname. Surnames hadn’t been adopted yet, but we know approximately where they were living just the same. We can now reference the appropriate historical period in England to determine what was happening when they lived there.
Why the Big Y?
The Big Y test does five things extremely well:
- Scans millions of locations on the Y chromosome looking for mutations that, when compared with other Big Y testers, places men conclusively on their branch, and sometimes on their twig and leaf of the Y-DNA haplotree. Men carrying previously undiscovered mutations from the same line establish a newly named haplogroup.
- Unambiguously matches testers with men who descend from a common ancestor. SNPs, the mutations measured in the Big Y test are not subject to back-mutations and other occasional instabilities that plague the STR markers in the 12-111 panel tests.
- Provides matching to both STR and SNP markers, allowing genealogical connections to men who have taken either type of test. Some people who have taken STR tests have either chosen not to upgrade (yet) or may have passed away. With the Big Y test, those legacy tests, some of which are more than 20 years old, are still useful.
- Provides an estimated date of when the common ancestor lived.
- Reaches reliably back in time, before the age of surnames, allowing testers to peer into the past based on a combination of genetics and history.
In other words, the Big Y test provides the best of both worlds, genealogy for close surname matches and anthropology for ancient matching and migration.
Lots to Explore
Globetrekker results are available to men who took either the Big Y-500 or the Big Y-700. Those who took the Big Y-500 can upgrade for significantly more refinement and potentially new haplogroups. Men who have not yet tested, or who just ordered one of the STR panels can upgrade to learn about your matches, your haplogroup, and the migration path through history your ancestor trod to arrive where your EKA lived.
I’m looking forward to reviewing all of the kits I manage that have taken the Big Y test. Let me know what you think about your Globetrekker results, and be sure to complete the survey and let FamilyTreeDNA know too.
If you’d like to learn more about your Big Y results, be sure to check out both Discover and Globetrekker. Discover is public, but Big Y testers will receive more information. Globetrekker is for Big Y customers only.
Remember, both will change as more people test and new results come in, so check back often.
The FamilyTreeDNA Big Y Facebook Group
A few weeks ago, FamilyTreeDNA introduced their FamilyTreeDNA Big Y Group on Facebook. As of today, just shy of 8000 people have joined. You do have to agree to follow the rules, but you don’t need to have taken a Big Y test. Lots of people join to learn, including many women who manage Y-DNA tests for family members or people who just want to understand more about one of the three types of tests for genetic genealogy.
You’re welcome to join too, here.
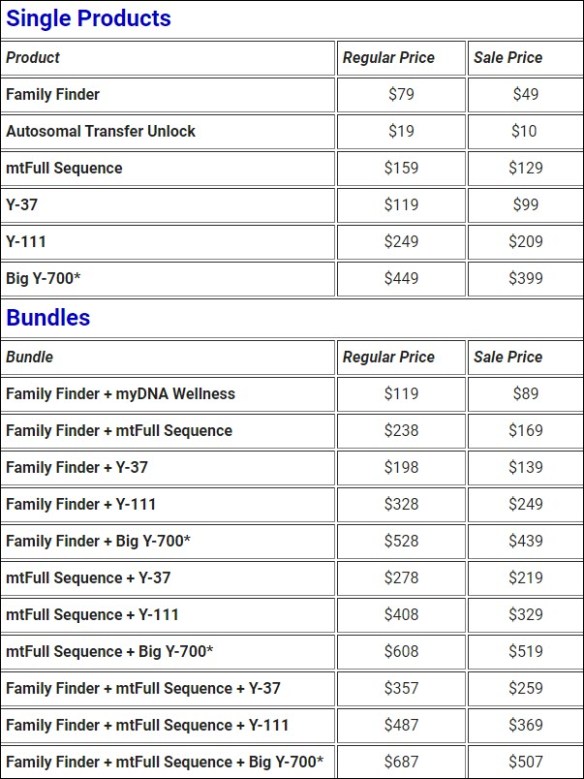
The Summer Sale
Several people have asked when the Big Y or the upgrades would be on sale. The summer sale runs from August 1-31, and all Y-DNA tests and upgrades are included, here.
If you’ve already taken one of the STR panel tests, or the Big Y-500, the Big Y-700 is less expensive when you upgrade. Just sign in to your account and click on the orange Add Ons and Upgrades button at the top right of your page, then on “Upgrades.”
Click here to purchase or upgrade.
_____________________________________________________________
Follow DNAexplain on Facebook, here.
Share the Love!
You’re always welcome to forward articles or links to friends and share on social media.
If you haven’t already subscribed (it’s free,) you can receive an email whenever I publish by clicking the “follow” button on the main blog page, here.
You Can Help Keep This Blog Free
I receive a small contribution when you click on some of the links to vendors in my articles. This does NOT increase the price you pay but helps me to keep the lights on and this informational blog free for everyone. Please click on the links in the articles or to the vendors below if you are purchasing products or DNA testing.
Thank you so much.
DNA Purchases and Free Uploads
- FamilyTreeDNA – Y, mitochondrial and autosomal DNA testing
- MyHeritage DNA – Autosomal DNA test
- MyHeritage FREE DNA file upload – Upload your DNA file from other vendors free
- AncestryDNA – Autosomal DNA test
- 23andMe Ancestry – Autosomal DNA only, no Health
- 23andMe Ancestry Plus Health
Genealogy Products and Services
- MyHeritage FREE Tree Builder – Genealogy software for your computer
- MyHeritage Subscription with Free Trial
- Legacy Family Tree Webinars – Genealogy and DNA classes, subscription-based, some free
- Legacy Family Tree Software – Genealogy software for your computer
- Newspapers.com – Search newspapers for your ancestors
- NewspaperArchive – Search different newspapers for your ancestors
My Book
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – by Roberta Estes, for those ordering the e-book from anyplace, or paperback within the United States
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – for those ordering the paperback outside the US
Genealogy Books
- Genealogical.com – Lots of wonderful genealogy research books
- American Ancestors – Wonderful selection of genealogy books
Genealogy Research
- Legacy Tree Genealogists – Professional genealogy research



















how does Haplo groups change A,B,C etc, if the Y dna doesnt change, thanks Bill
Y DNA is never recombined with the DNA of the spouse. But it does accrue occasional mutations that we can track back in time like breadcrumbs.
The location detail you enter is critical to the accuracy of the results.
My haplogroup is R-FTA30027. I share it with 3 other men with origins in Scotland (me Aberdeenshire, one man Caithness and the othe simply Scotland). The two other men share mutations I don’t have and have been assigned to R-BY91664.
The map shows R-FTA30027 originating in Fife, further south than Aberdeenshire, which may or may not be correct. Take me out of the equation and the map shows R-BY91664 originating even further south in Dumfries and Galloway. I assume this is because of the man who only has Scotland as a locaion. Unfortunately, I don’t think he can be any more specific.
Roberta, I may have missed your commenting on it but note that another Big Y Ingalls cousin and my data did not show up until I asked him to authorize his data being used. They said it takes at least two close matches to create a new group and show it. Do not know if I have explained this correctly but just having cousins have the Big Y test is not the only thing required.
Did you talk to FTDNA?
yDNA and a BigY 500 test had proven ancient roots in Northern Ireland and Raithlin man connections but couldn’t pin point a more recent location in Ireland – until now. I’d only entered Ireland as a possible earliest ancestor location (for my paternal cousin’s yDNA test).His BigY 500 same haplogroup yDNA match with the same earliest ancestor had also just entered Ireland as a location. Globetrekker is showing a location of Galway County, Ireland as a location of our earliest known ancestor, plus one upstream at the same location. It’s a very specific location in Galway County. The kicker is that Ancestry also shows this very specific Galway location on my own autosomnal matches on my paternal surname line. The same ancestral location at two different testing companies – I’m a believer. This opens up a whole new area of research. Woo-hoo!
Thank you for helping clarify aspects of the new Globetrekker Tool. You have helped quell my skepticism.
My biological surname is Fleming. Being a toponymic name the assumption was that my ancestors were originally Scotto-Norman, before which they were Frankish. This was of course a generalization of geographical cultural groups. However, Globetrekker has upended that assertion.
According to the estimates provided, my ancestors were in Northern Wales from 450 ce to 1000 ce before immigrating to Galloway and Dumfries, working their way up to Lanarkshire by 1250. They did travel a route through northwestern europe that had pit stops in the low countries and Flanders but over 1700+ years before the Norman conquest!
However, I do have a question: how accurate do you think the estimates are?
The older estimates are quite accurate and are anchored by ancient DNA. In younger results, it’s an average of information provided by testers. Testers can be wrong. Pay attention to hot spots and ranges along with how many testers have that haplogroup. They can and do move too. Europe is actually a fairly small place.
“The older estimates are quite accurate ” Are we talking about the location of the SNP on the map ? if so what is the range/threshold for the older estimates ? Like100 BC , 1000 BC , 2000 BC etc…
Each SNP has its own range. On the Time Tree, that’s the dashed black line to the left and right of the SNP location.
“The older estimates are quite accurate and are anchored by ancient DNA” Are we talking about the location of a SNP on the Map ?
I was actually referring to the age, but yes, it applies to where those remains were found too. However, the location of a haplogroup can shift some with more testers, especially if they show different locations.
Let me confirm. please.I. have a friend who is using the tool. When he hovers over the last two snps, before it reaches his current / CE country location. It shows the first SNP saying 3000 BC, and 2nd saying 2500 BC and both are in a neighboring country, would those 2 be based on remains found over there?
It could be or from the average of the locations of the people who provide earliest ancestor locations – or a combination of all of that.