There’s a lot, a whole lot that DNA testing can tell you. Not just your own tests, but the genetic information carried by your relatives that you do not.
Recently, I’ve been reviewing my brick walls, which led me to realize there are several ancestors who are missing their mitochondrial DNA and/or Y-DNA results. I need these to learn more about my ancestors that can’t be revealed any other way – and to break down those pesky brick walls.
I’ve solved two mysteries recently, one thanks to a Big Y-700 test, and a second very unexpectedly thanks to mitochondrial DNA – both thanks to cousins who tested. These revelations were very encouraging, especially since there’s no way other than DNA for me to break through these brick walls. The mitochondrial test had been sitting there, waiting for what seemed like forever until just the right other person tested.
I am in the process of unlocking several brick-walled ancestors by providing testing scholarships to people who are appropriately descended from known ancestors in those lines.
Don’t leave information on the table. If I were to tell you there even MIGHT be a book available about your family, you’d overturn Heaven and Earth to find it – but you don’t need to do that. All you need to do is order DNA tests for cousins.

All cousins can provide useful autosomal DNA results, but you do need to find appropriate cousins for Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA testing.

I’m sharing the steps for how I accomplish this! You’ll be amazed at what’s out there – and someone may already have tested!
Take Advantage of the Holidays
I’m sharing NOW because it’s the holidays and you’re likely to gather with people you don’t see any other time – and because the best sale of the year for both Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA lasts from now through the end of the year.
These two factors combined mean strike while the iron is hot.

Prices for new tests and bundles are at an all-time low.

If you or your relatives have already taken a lower-level test, now is the time to upgrade to either the Big Y-700 or the mtFull Sequence test.
Step 1 – Test Yourself and Your Known Family
If you’re a male, order both the Big Y-700 test and mitochondrial DNA tests.

Be sure to click on “See More” for more useful tools.

When you receive your results, be sure to click on all of the tabs in your results, and do the same by clicking through to Discover from your account. Discover has 13 more goodies for you to help with your genealogy.

Both your personal page and Discover are essentially chapters of your own personal book about your DNA results. 25 very interesting chapters, to be precise, that are uniquely you.
I’ve written about understanding Y-DNA results here, and mitochondrial results here. My book, Complete Guide to FamilyTreeDNA, covers both along with Discover.
Discover provides robust information for Y-DNA haplogroups. If you’ve taken a Big Y-700 test, you’ll want to click through from your page to receive additional, personalized and more robust information than is available through the free public Discover tool. That said, the public version of Discover is an amazing tool for everyone.
After the new Mitotree is released for mitochondrial DNA, mitochondrial haplogroups will be available in Discover too.
I can’t even begin to stress how important these tools are – in particular the Time Tree, the Group Time Tree for members of group projects, and the Match Time Tree for your own matches.
Who Can Test For What?
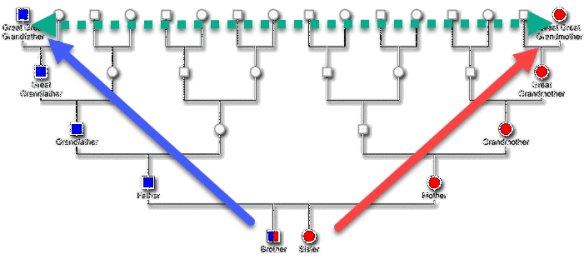
Once you’ve tested yourself, you will want to take a look in your pedigree chart at branches further up your tree to see who can be tested to represent specific ancestors.
Let’s begin with my father’s side.

A mother contributes her mitochondrial DNA to all of her children, so your father carries the mitochondrial DNA of his mother.
If you’re a female, and your father is available to test, you’ll want to test BOTH his mitochondrial DNA and Y-DNA, because there’s no way for you to obtain that information from your own test. Females don’t have a Y chromosome, and men don’t pass on their mitochondrial DNA.
If you’re a male, you can test your own mitochondrial DNA and Y-DNA, but you’ll need to test your father’s mitochondrial DNA to obtain his mother’s. You might still want to test your father’s Y-DNA, however, because you may discover a personal family haplogroup. How cool is that??!! Your own tiny branch on the tree of mankind!
Your father’s mitochondrial DNA provides you with mitochondrial matches and haplogroup information for your paternal grandmother – in this case, Ollie Bolton.

If your father and his siblings can’t test, then all of the children of your paternal aunts carry your paternal grandmother’s mitochondrial DNA.

If they have no children or they can’t test, then the children of Ollie Bolton’s mother, Margaret Claxton/Clarkson all carry her mitochondrial DNA, and the children of Ollie’s sisters continue the line of descent through all daughters to the current generation.
The male children of Joseph “Dode” Bolton and Margaret Claxton carry his Y-DNA. Fortunately, that’s not one of our missing haplogroups.
Yes, you may have to climb up your tree and climb down various branches to find a testing candidate.
One of the reasons I’m using this example is because, while I have a high-level haplogroup for my grandmother, Ollie Bolton, we need a full sequence tester – and I’m offering a mitochondrial DNA testing scholarship for anyone descending from Margaret Claxton (or her direct female ancestors) through all females to the current generation, which can be male.
Ok, now let’s switch to the maternal side of your tree.

On the other side of your tree, your maternal grandfather or your mother’s brothers will provide the Y-DNA of your mother’s father’s line. Your mother’s uncles or their sons will provide your grandfather’s Y-DNA line, too. In this case, that’s John Whitney Ferverda, who carries the Y-DNA of his father, Hiram Bauke Ferverda/Ferwerda.
Your maternal grandfather or his siblings will provide the mitochondrial DNA of their mother, Evaline Louise Miller.

If they are deceased or can’t test, for mitochondrial DNA, look to the children of Evaline Miller’s daughters or their descendants through all females to the current generation, which can be male.
And yes, in case you’re wondering, I do need Evaline Miller’s mitochondrial line too and am offering a scholarship.
You might have noticed that I’ve been inching my way up my tree. All of my immediate relatives have passed over already, so I’m now looking for testers that I don’t know but who I’m related to.
If you’re seeing family members anytime soon, figure out if their Y-DNA, mitochondrial DNA, or autosomal DNA would be useful for your common genealogy. Take advantage of the opportunity.
Next, you’ll want to figure out which ancestors need haplogroups and locate appropriate cousins.
Step 2 – Identify Ancestors Who Need Haplogroups

Peruse your tree to determine which of your ancestors you need haplogroup information for. To make it easy, on my computer, but never in a public tree anyplace, I store the haplogroup of my ancestor as a “middle name” so I can easily see which ones I have and which ones I need. Sometimes, I have a high-level haplogroup and either need a new tester or someone to upgrade.
Sometimes, I have one tester from a line but need a second for confirmation.
In this example, I’m not missing confirmation on any Y-DNA haplogroups (although I am further upstream on different lines,) but I do need four different mitochondrial DNA lineages.
For easy reference, make a list of all of the lines you can’t confirm with two testers from different children of the same ancestor.
You just might get lucky and discover that someone has already tested!
Step 3 – Check FamilyTreeDNA Projects
Check FamilyTreeDNA Projects to see if someone has already tested to represent those ancestors on your list.
Click here for the Group Project Search. It’s located at the very bottom of the main FamilyTreeDNA page in the footer.
I’m going to use Estes as an example since I’m the volunteer administrator of that project and am very familiar with the lineages.

I’m searching for projects that include the surname Estes.
The projects displayed on the list are projects where the volunteer administrators listed Estes as a possible surname of interest. It doesn’t mean those projects will be of interest to everyone or every line with that surname, but evaluate each project listed.
You probably want the surname project, but if there’s not a surname project for your surname, try alternate spellings or consider checking other projects.
You can see at the bottom that 384 people of both sexes by the surname of Estes have tested at FamilyTreeDNA.
Now, let’s look at the Estes project. Note that not everyone with the Estes surname has joined the Estes project.

I’ve clicked on the “Estes” link which takes me to an additional information page where I can read a description and click to view the project.
For the Estes project, you do not have to join to view the results. Nor does your surname have to be Estes. All Estes descendants of any line are welcome. Everyone can benefit from the Advanced Matching within project feature to see who else you match within the project by selecting a wide range of individual and combined filters.
Click on the Project Website link shown in the search results.

If you’re searching for a male Estes ancestor, you’ll want to review the project’s Y-DNA Results and the Group Time Tree, for sure, and possibly the Map as well.
Let’s pretend I’m trying to determine if anyone has tested who descends from my ancestor, Abraham Estes, the founding Estes ancestor in Virginia who arrived in the mid-1600s.

In the Estes project, the volunteer administrator has divided the Estes male participants by sons of Abraham, the immigrant. Only three are shown here, but there are several.
Some of the participants have completed their Earliest Known Ancestor information, in the red box. Sometimes people don’t think to update these when they make breakthroughs.
If you descend from Abraham’s son, Sylvester, three men have taken the Big Y-700. That’s the test results you need.
If you descend from Abraham’s son, Abraham, no project participants have taken the Big-Y test to represent that line, although six people have tested, so that’s great news. Maybe you can offer an upgrade scholarship to one or some of those men.
In other words, to establish the haplogroup for that lineage, at least two men need to test or upgrade to the Big Y-700, preferably through two different sons of the common ancestor. A new, more defining haplogroup is often formed every two or three generations for Y-DNA.
Your genetic pedigree chart looks a lot like your genealogy pedigree chart.

Click any image to enlarge
The project Group Time Tree shows selected groups of men who have taken Big Y tests, along with their Earliest Known Ancestor, if they’ve provided the information. This is one of the reasons why the Big Y-700 is so critically important to genealogy. The time granularity is amazing and can answer the question of whether men by the same surname descend from the same common ancestor – and when.
If you’ve taken a Family Finder autosomal test at FamilyTreeDNA, or uploaded an autosomal file from another vendor, you may match one of these men or another male that descends from the Estes line if they, too, have taken an autosomal test.
This same process applies to mitochondrial DNA, but generally surname projects aren’t (as) relevant for mitochondrial DNA since the surname changes every generation. However, sometimes other projects, such as the Acadian AmerIndian Project are quite beneficial if you have Acadian ancestry, or a geographic or regional project like the French Heritage Project, or something like the American Indian Project.
Another great way to find testers is by utilizing your Family Finder test.
Step 4 – Family Finder at FamilyTreeDNA

The next step is to see if you match anyone with the surname you’re searching for by using your autosomal test results, so select your Family Finder Matches.

At FamilyTreeDNA you’ll want to search your matches by the surname you seek. This surname search lists any tester who has that surname, or anyone who has entered that surname in their surname list. Please note that this search does NOT read ancestors in your matches’ trees. You’ll still need to view trees.

Reviewing the 32 Estes Family Finder matches reveals several men, but one man with the Estes surname has already taken a Y-DNA 25-marker test, so he would be an excellent candidate to offer a Big Y-700 upgrade scholarship. If he’s not interested or doesn’t respond, there are several more men to contact.

Click on your match’s name to display the profile card, along with the Earliest Known Ancestors, both Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA haplogroups if they have tested, and the assigned haplogroup based on their testing level.
Craft an email and offer a testing scholarship. This will help both of you. I’ll provide a sample email at the end of this article.
If you match a female with an Estes surname, her father, brother, uncle or cousin may either have already tested or be willing.
If you match someone who has a different surname, that means they have an Estes surname in their surname list and may know a potential tester. If your match has a tree, click to check.
I’ve found that matching through a company where you’ve both tested is the easiest way to encourage someone to take an additional test, but certainly, it’s not the only way.
Step 5 – WikiTree
WikiTree is a quick and easy way to see if anyone has taken a Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA test that should reflect a particular ancestor’s Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA.
I just googled “Moses Estes 1711-1787 WikiTree” and clicked to view.

Each ancestor includes both Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA information, in addition to people who descend from that ancestor through only autosomal lines.

In this case, two men have provided their Y-DNA results that pertain to Moses Estes. They have tested at different levels, which is why they have different haplogroups. That doesn’t mean either is “wrong,” one is just more refined than the other. You can correlate their kit number with the Estes surname project. People often don’t update their haplogroup information at WikiTree when it’s updated at FamilyTreeDNA.
Please note that if the genealogy is wrong, either at WikiTree or individually, the haplogroup may not reflect the appropriate lineage for the ancestor. Check to be sure that there’s no conflict showing between two testers for the same ancestor. For example, the same ancestor clearly can’t have two different base haplogroups, like E and R. The Discover Compare tool can help you evaluate if two haplogroups are in the same part of the Y-DNA tree.
When possible, it’s always best to test a close family member to represent your lineage even if someone else has already tested.

Scan down the list of autosomal testers for that ancestor to see if there’s someone with the Estes surname.
WikiTree provides additional tools to find descendants.

Sign in to WikiTree. You’ll see the ID of the profile you’re viewing – in this case – Estes-167. Click the down arrow and select “Descendants.”

This view shows all descendants through five generations, but you can click on DNA Descendants to see only Y-DNA descendants, X-DNA, or mitochondrial DNA descendants for female ancestors.
You may find people who are living and have added themselves who you can contact to offer a DNA testing scholarship.
Step 6 – MyHeritage
At MyHeritage, you can also search your DNA matches by surname.

Click on “Review DNA Match” to view more detail, including locations. Look to see if you have a Theory of Family Relativity Match which suggests how you may be related. That’s golden!
There’s no Y-DNA information at MyHeritage, BUT, you can search by surname and view DNA matches that either carry that surname or have that surname in their tree as an ancestor.
I have a total of 75 “Estes” matches, and other than the kits that I manage, searching through my matches shows:
- Two Estes men connected to the same small tree, but that’s OK, I’m a genealogist!

- One Estes male match with a Theory of Family Relativity. My lucky day!
You can contact your match easily through the MyHeritage messaging system and offer a DNA testing scholarship at FamilyTreeDNA. You may also want to share your email address.
MyHeritage customers may not be familiar with Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA testing, so you might want to share this article about the 4 Kinds of DNA for Genealogy.
MyHeritage testers can also upload their DNA file to FamilyTreeDNA for free to receive autosomal matches plus a complimentary mid-range Y-DNA haplogroup. This free haplogroup is not even close to the detailed resolution of a Big Y-700 test, but it’s something, and it may well be an enticing first step for people who are only familiar with autosomal testing.
Step 7 – At Ancestry
At Ancestry, select DNA Matches and then search by surname.

You can search by the surname of the tester, which is very useful, or by people who have Estes in their trees.
I started with the surname Estes, because it’s the most straightforward and I may find a perfect male candidate for Y-DNA. If someone’s “screen name” doesn’t show as Estes, they won’t appear in the results of this search. In other words, if your Ancestry screen name is “robertaestes” you won’t show in this search, but “Roberta Estes” will.
For mitochondrial DNA, you would want to search for the surname in your matches’ trees. Unfortunately, you cannot search for the specific ancestor in someone’s tree, at least not directly.
Of my 19 Estes surname matches, ten are males, and of them:
- Three have unlinked trees
- Three have very small linked trees, but I can work on extending those if need be
- Three have public linked trees AND a common ancestor, which means ThruLines
I can review which ancestor we share by clicking on my match’s name

The Estes side of this man’s tree has only one person and is marked “private,” but Ancestry has suggested common ancestors based on other people’s trees. (Yes, I know trees are dicey, but bear with me.)

It’s also worth mentioning that you can be related through multiple lines. I share surnames from Acadian lines with this man, but that really doesn’t matter here because I’m only using autosomal matching to find an Estes male.
Click on “View Relationship” to see our common Estes ancestor’s ThruLine.

The ThruLine shows how Ancestry thinks we’re related on the Estes line.
I can also click on “View ThruLines” to see all Thrulines for John R. Estes, which shows four additional males, some of which did NOT appear in the Estes surname search, and some of which don’t appear further up the tree. In other words, check all Estes ThruLine ancestor generations.
Don’t rely solely on Ancestry’s surname search.

Go directly to your ThruLines on the DNA menu.

Ancestry only reaches back seven generations, which for me is Moses Estes and Luremia Combs. Moses has 95 matches, but he has been given some incorrect children. Again, for this purpose, it doesn’t matter. Within all ThruLine matches, I found three Estes males who all descend through John R. Estes. Check every generation.
However, Luremia Combs shows promise for mitochondrial DNA descendants. Unfortunately, only two of her daughters are represented in ThruLines, and both of their descendants descend through Luremia’s grandsons. That’s too bad, because I need Luremia’s mitochondrial DNA line.

It’s easy to message your Ancestry matches. You may want to mention that they can upload their DNA file to FamilyTreeDNA for free where they will receive more matches and males will receive a complimentary mid-level Y-DNA haplogroup.
Please note that, in general, ThruLines need to be evaluated very carefully and are prone to errors, especially if you accept Ancestry’s suggestions of ancestors instead of carefully building out your own tree. Regardless, you can still find Estes cousin matches in your match list and by using ThruLines to find people that do not show up in an “Estes” match search.
Step 8 – At 23andMe
At 23andMe, you can search for anyone who either has the Estes surname or has included that surname in their “Family surnames” list. Keep in mind that your matches at 23andMe are restricted to either 1500 if you don’t have a subscripition, or about 4500 if you do have a subscription.

On my match list, I have two males with the Estes surname.
23andMe provides a mid-level Y-DNA haplogroup. You can’t use this to confirm the lineage when comparing with FamilyTreeDNA, especially given that 23andMe provides no genealogy or user-provided tree, but it is a clue.

Both Estes men at 23andMe have Y-DNA haplogroup R-CTS241. You could use this in some cases to potentially eliminate these matches at 23andMe. For example, if men in your lineage in the Estes project are in haplogroup R and your 23andMe matches are showing as haplogroup E, or any other base haplogroup, their common ancestor is tens of thousands of years ago.
Comparing the 23andMe haplogroup, which in this case is about 4500 years old, to contemporary testers who have taken the Big Y-700, which reaches within a few generations, isn’t terribly useful. These matches are extremely useful to identify individuals to reach out to for further information and potentially offer a Y-DNA testing scholarship at FamilyTreeDNA.
Remember, this also applies to females who have included Estes in their family surnames, given that they may have Estes male relatives.

By clicking to view your match, you can see if they have provided Family Background information, including a link to a family tree someplace.
Sometimes, there’s great information here, and other times, nothing.
You can’t verify this lineage without genealogy information.

I suggest leaving a genealogy-focused message, including where they can see your tree in addition to your Estes connection. Also include your e-mail.
You may want to say that if they descend appropriately, you have a Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA testing scholarship, or you may want to wait to see how they descend. You can also ask if they have already taken a Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA test at FamilyTreeDNA.
Step 9 – FamilySearch and Relatives at RootsTech
We’re getting ready for RootsTech 2025 which takes place in March. In the month or so before the last two RootsTechs, FamilySearch provided an absolutely wonderful tool called “Relatives at RootsTech.”
I’ve written about this several times, but essentially, you can see, by ancestor, other people who are registered both in-person and virtually for RootsTech, and how they descend.

Here’s an example.
In both years, I’ve found several people who descended from common ancestors AND were very willing to take the relevant DNA test. That’s a huge win-win for everyone.
The best part is that because these people have freshly registered for RootsTech, the reply rate is almost 100%.
I’ll write about this as soon as RootsTech makes it available this year. Fingers crossed that they do!
Step 10 – Social Media
Social media wouldn’t be my first choice to find DNA testers, but I have found perfectly willing cousins this way. You may be less successful on Facebook or other social media platforms, but if you’re striking out elsewhere, there’s absolutely no downside to trying.
You can enter a surname and search on Facebook, but I prefer to do a Google search like “Estes genealogy on Facebook” or even just “Estes genealogy,” which will produce far more widespread information, some of which may be irrelevant.


That Facebook Google search provided the names of two groups. People join groups because they have an interest, and I’ve had good luck in Facebook genealogy groups.
A Search of “Estes” on Facebook itself, then selecting “people” provided a list of Estes Facebook users.
I’ve had far better luck by joining a group that is focused on Estes genealogy, or even a county genealogy group that includes Estes families, than individuals. People who join any Estes group or project likely have an interest in that surname.
If you have a common surname, or there’s a park named after your surname, like Estes Park, you’ll probably want to focus by using Google searches for Estes genealogy.
The Descendants of Abraham Estes Facebook group has 222 members, of whom at least 31 are males with the Estes surname. Facebook just might be an underestimated resource.
If there isn’t a genealogy-focused group for your surname, you might want to consider starting one and encouraging people to join.
It can’t hurt, and it just might help. Before you start reaching out to random people on Facebook, please do a privacy checkup – I wrote about how, here.
Sale Prices
Remember, the sale prices at FamilyTreeDNA for new tests and upgrades last through year-end.
In my experience, it’s best to test as soon as someone agrees. You never know what will happen otherwise. I’ve had people pass away before they could swab. And yes, we’ve done funeral home swabs, too.
There’s no one-size-fits-all, but here’s a rough draft contact letter.
Potential Contact Letter
You’ll want to include several critical pieces of information.
Essentially:
- Introduce yourself
- Say their full name on their test AND the testing company in the title of an email. I manage many tests and if I receive an email that says, “Hi, can you tell me how we match” without telling me which person they match, I can’t even begin to answer.
- Explain your genealogy connection
- State your purpose in writing
- Explain how a specific test will help them too
- Offer to answer questions
Be sure to modify this letter to reflect your own voice and circumstances. You don’t want this to read like a form letter.
Dear cousin (insert their full name here,)
It was so nice to find our DNA match at <company name> (or we share a common ancestor, or appropriate circumstance.) (If you are managing someone else’s kit, say the name of who they match and explain that you manage their DNA kit.)
I descend from (ancestor plus birth and death date) who lived in Halifax County, Virginia and was married to (spouse.) You can view my tree at (insert link that does not require a subscription for viewing unless you match them on that platform. I use MyHeritage because everyone can view their trees)
I would very much like to confirm that our line descends from Abraham Estes (or relevant information meaning your reason for wanting them to test.)
Given that my surname is x (or I’m a female), we need to test the Y-DNA of a male who is descended from (ancestor) through all males to the current generation. (Or mitochondrial DNA descended through females to the current generation which can be male.)
FamilyTreeDNA provides this testing and shows who you match on that specific line using the Y chromosome (mitochondrial DNA).
This testing may connect us with earlier ancestors. Genetics can be used to determine when we share common Estes ancestors with others who test, where we come from overseas, and when. Even if we match ancient DNA samples that may tell us where our ancestors lived before surnames. In other words, where did we come from?
(Include a nice paragraph, but not a book about your ancestral lineage here.)
I have a DNA testing scholarship for someone from this line and you are the perfect candidate. I would like to take advantage of the current sales. If you’re interested, I only need two things from you.
First, permission so that I can order (or upgrade) and pay for the test, and second, an address where to send the test (unless it’s an upgrade). (If it’s an upgrade at FamilyTreeDNA, they can use a stored sample or will sent them a new kit if there’s not enough DNA.)
If you have any questions, please let me know. I’m very excited that we may be able to learn more about our heritage.
Please email me at xxx or call me at xxx if you have questions.
Your name
I know one person who offers to review results over Zoom. Someone else stresses that the tester’s email is attached to their test and they are always in control of their results. Another person asks them to join a project they manage to assure that they can follow their matches over time.
Customize this communication in your own voice and to fit the circumstances of each match.
It’s just me, but since I’m ordering while the tests are on sale, unless the person uploads their DNA file from another vendor, I add on a Family Finder test too and explain why. You never know if they will match you or another cousin, and they may have that match that eventually breaks down the next brick wall. Shared matches are powerful evidence and it’s a lot easier to add that test on now than try to contact them again later.
You Don’t Know What You Don’t Know
Which ancestors do you need Y-DNA or mitochondrial DNA results for? Methodically check each line.
There’s so much to learn. Don’t leave information on the table by virtue of omission.
Leave no stone unturned!
You don’t know what you don’t know.
Who’s waiting out there for you?
____________________________________________________________
Share the Love!
You’re always welcome to forward articles or links to friends and share on social media.
If you haven’t already subscribed (it’s free,) you can receive an e-mail whenever I publish by clicking the “follow” button on the main blog page, here.
You Can Help Keep This Blog Free
I receive a small contribution when you click on some of the links to vendors in my articles. This does NOT increase your price but helps me keep the lights on and this informational blog free for everyone. Please click on the links in the articles or to the vendors below if you are purchasing products or DNA testing.
Thank you so much.
DNA Purchases and Free Uploads
Genealogy Products and Services
My Books
Genealogy Books
Genealogy Research
Like this:
Like Loading...