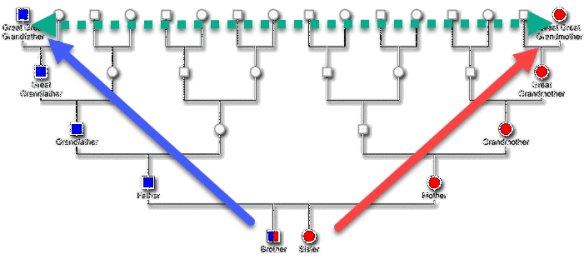
Genetic Affairs released a new AutoKinship tool designed for FamilyTreeDNA’s autosomal Family Finder matches, which also incorporates information from other sources. I must have fallen asleep at the wheel, because AutoKinship has been available for more than six months now.
I’ve been testing this tool with my matches, and it’s an immense help to those of us trying to untangle complicated family relationships using DNA evidence. I don’t know about you, but I have a long list of brick well where I could use help!
How to Use This Guide
This article is long and there are many steps involved – but it’s well worth it at the end.
My suggestion for using this article effectively is to read it through, at least once, to see what you’re going to be doing, and why.
Then, after you get things set up at Genetic Affairs, and any files you want to include, come back and use this article as a step-by-step guide to navigate these new tools.
Here’s the bottom line. The Genetic Affairs tools use matches, along with shared and bucketed matches at FamilyTreeDNA, plus their archived trees, in addition to external GEDCOM files and other information that you can provide in order to create customized, focused clusters and potential family trees for your clustered matches.
These tools combine DNA matching with internal and external trees for the composite best of both types of information.
So grab your favorite drink and let’s get started.
FamilyTreeDNA
AutoKinship works in conjunction with FamilyTreeDNA’s tools, such as Shared Matching, the Matrix tool, and Family Matching, also known as bucketing, which assigns parental sides to your matches using linked matches.
Linked matches are your matches whose relationship to you is known. If you haven’t already, link them to their profile card on your tree by clicking on “Link on Family Tree.” This allows FamilyTreeDNA, by using triangulation, to “bucket” your matches either maternally or paternally – meaning if they are related to you on your maternal side, paternal side, or both.
In my cousin Patricia’s case, the little pink icon by her profile picture shows that she has been bucketed maternally. That occurred when I linked my mother’s DNA to my tree because Patricia matches us both, plus other linked maternal cousins, on the same segments. For bucketing to occur, you don’t have to do anything except link known relatives to their proper place in your tree. FamilyTreeDNA does the rest by assigning your matches either maternally or paternally if they match on common segments.
Upload DNA Files to FamilyTreeDNA from Other Vendors
If you have not taken the Family Finder test at FamilyTreeDNA or uploaded your DNA file from 23andMe (Dec 2010 to present), Ancestry (May 2012 to present), or MyHeritage (March 2019 to May 7, 2025) to FamilyTreeDNA, you should do so now to take advantage of their tools, plus AutoKinship at Genetic Affairs.
What is AutoKinship and Why is it Different?
AutoKinship takes traditional clustering and kicks it up several notches. Instead of just showing you which matches cluster together, it actually attempts to build family trees based on the shared DNA amounts between your matches.
AutoKinship looks at how much DNA your matches share with you, and with each other, and uses that information to predict their relationships. Then AutoKinship builds potential family trees showing how everyone might connect. Additionally, you get to provide input in the process.
The timing couldn’t be better, especially since FamilyTreeDNA recently launched their updated Matrix tool, showing how your matches are related to each other. I wrote about that, here.
Two Steps
There are two primary steps in the AutoKinship process that build on each other. However, within these steps, there are many stepping-stones, so I’ve documented each one.
We’re going to use these tools, one at a time, in order.
I suggest that you join the Genetic Affairs User Group on Facebook for additional support and information.
Using AutoKinship with FamilyTreeDNA
The AutoKinship functionality for FamilyTreeDNA provides an automated approach using both AutoCluster and AutoKinship, together, then AutoLineage, where you can refine the information in a number of ways.
🔹 Step 1: Automated AutoKinship via Genetic Affairs
The first step involves running the AutoKinship tool directly from the Genetic Affairs members’ site. This process is fully automated:
- It starts with the FamilyTreeDNA AutoCluster option, which groups DNA matches into shared clusters based on their connections to each other.
- AutoKinship is then automatically launched on each cluster, adding the DNA tester and generating relationship hypotheses among the group.
- Several family tree models are produced, showing how the matches and the tester could be connected based on shared DNA and cluster structure.
This step is ideal for getting quick insights into how groups of matches may relate.
🔹 Step 2: Refined Clustering & Relationship Analysis Using AutoLineage
After the automated run, downloadable files for AutoLineage are generated. These files allow you to re-import the match, shared matches, and tree data into the AutoLineage web application for further analysis.
This second step offers greater control and customization:
- You can redo the clustering, optionally tweaking parameters to fine-tune how matches are grouped.
- You can redo the common ancestor analysis, optionally tweaking parameters to fine-tune the discovery of MRCAs
- The AutoKinship tool within AutoLineage becomes available again, this time with additional functionality:
- Define known relationships between matches, such as parent-child or cousin relationships
- Define generational information, for instance, if you know certain matches are not on the same generational level
- Integrate MRCA (Most Recent Common Ancestor) data from reconstructed trees, e.g., from the Find Common Ancestors module.
This enhanced phase is especially useful for integrating genealogical trees for targeted clusters.
By combining both steps, automated clustering with AutoKinship, and manual refinement with known or tree-derived relationships using AutoLineage – you can leverage your FamilyTreeDNA data for in-depth relationship exploration.
Let’s Take AutoKinship for a Spin
As always, I’ll walk you through this process step by step, using my own DNA results as an example.
Getting Started
First things first – you’ll need to be a member of Genetic Affairs, so sign up for their free membership, here. Genetic Affairs’ customers purchase “credits” to spend on various features and reports, but you receive 200 free to start.
The automated AutoKinship analysis available on the Genetic Affairs website can be run using credits from the free tier – perfect for exploring the tool without any commitment. This allows users to generate relationship trees for FamilyTreeDNA clusters right away.
To access the more advanced features in the AutoLineage desktop application—including refined clustering, manual relationship input, and integration of MRCA data from reconstructed trees – you’ll need an active subscription.
To get started, sign in to the Genetic Affairs member site, here.
Let’s walk through the process step by step.
We’ll begin by registering a FamilyTreeDNA profile at Genetic Affairs. Click on “Register a new website” to get started.
FamilyTreeDNA account passwords are not stored at Genetic Affairs.
After clicking “Register profile,” you’ll see a message asking you to double-check the credentials for the kit you’re about to use. This is also a good time to log in to your FamilyTreeDNA account directly to make sure there are no pending actions — such as enabling two-factor authentication or accepting updated terms of service.
Once you click “I understand, continue,” you’ll see a list of all registered FamilyTreeDNA profiles at Genetic Affairs.
Locate the kit you want to analyze and click the blue “Start analysis” button.
This opens a guided wizard that walks you through each step of the setup.
First, select AutoKinship and click “Next.”
You’ll then be asked to define several thresholds:
- Minimum and maximum shared cM
- Minimum size of the largest segment
- Minimum cluster size
A quick word of caution here: selecting a very low minimum cM value may actually reduce the number of usable matches. That’s because the system must download shared match data until it either reaches that threshold, or a preset timer expires, which can limit how much data is downloaded. When in doubt, start conservatively. You can always rerun the analysis later and change the parameters. Unfortunately, there’s no way to simoly “get everything” in one run which is, of course, what everyone would do.
Click “Next” to continue.
This section determines which matches will be included in the analysis.
For your first run, I recommend using the top matches within the selected range. This provides a strong foundation and usually produces the clearest results.
Later, once you’re more familiar with the output, you may want to experiment by analyzing only the shared matches of a specific person or group. For now, keep it simple and click “Next.”
Here, you’ll enter your FamilyTreeDNA password (twice) so the system can retrieve the required data.
If you use two-factor authentication, you can enter the 2FA code here, as well. To do that, log in to your FamilyTreeDNA account, retrieve the code from your email, and paste it into the wizard.
Then click “Next.”
You’ll now see a summary of all the settings you’ve chosen. Take a moment to review everything. When you’re ready, click “Perform analysis” in the bottom right corner.
At this point, the Genetic Affairs servers take over and begin processing your data.
The Results Arrive
When your report is ready, you’ll receive an email with a download link. You can also access it through the notification panel in the top right corner of the Genetic Affairs site.
Downloading the report will result in a zipped file. Save it in a location on your computer where you can find it.
Critical Step
This step is critical and will save you a great deal of frustration: If you’re using a PC, you MUST extract or unzip the files before you can properly use them. I can’t tell you how many people skip this step and then wonder why they’re receiving error messages. Ask me how I know!
This is your zipped file.
If you try to open the HTML file while it’s still zipped, it might appear to work at first, but when you click on any links within the file, you’ll receive an error.
If this happens to you, close everything, right-click on that yellow zipped folder, select “extract all,” and then try again.
Now you’re set up, so on to the fun part – viewing the results.
Exploring Your Results
Once you have everything properly extracted and open the HTML file, you’ll watch your AutoCluster literally fly into place on your screen. I love this part. It’s like watching my family fly into place. I wish the actual genealogy research was this easy.
The new Genetic Affairs reports include significantly more information than previous versions.
You can change what’s displayed using the dropdown menu.
By default, you’ll see the shared cM amounts between your matches, but you can change this to show paternal or maternal information if you’ve identified those lineages by linking your matches.
In my case, my maternal line has fewer matches because my mother’s ancestry includes both recent Dutch and German immigrants, so the majority of my high cM matches are US-centric on my father’s side. My father’s ancestors have been in this country since colonial times, and a lot of testers in the US are looking back to the old country for their origins.
Therefore, in my first several clusters, I see squares with the symbol P, indicating they are paternal matches – designated as such through linked family matches, aka bucketing.
You can see the faint Ps inside the orange cells.
Here’s a close-up so you can see the “P” for paternal. If you haven’t linked your matches, you won’t have bucketed matches. Your Genetic Affairs results don’t require bucketing – it’s just a really beneficial feature.
You can change your AutoCluster settings in several ways. I tend to start with the defaults and then modify from there.
Genetic Affairs functions based on the amount of server time a particular tool takes, so it’s not possible to just “run everything,” or trust me, I would.
The Common Ancestor Magic
In your report, scroll down several sections, and you’ll find Common Ancestors – my favorite feature.
This section shows you the common ancestors that have been identified between your matches’ trees.
Looking at the Common Ancestors cluster report, you can click on three things for each cluster:
- FamilyTreeDNA Trees of Cluster #
- Common Ancestors of Cluster #
- Common Locations of Cluster #
Let’s examine the reconstructed trees based on the common ancestor analysis. The first cluster shows some of my close DNA matches that are descendants of my Vannoy line.
You can see that there are six testers, in addition to me, who descend from Joel Vannoy.
Next, scroll down to the AutoKinship section of your report.
The AutoKinship Analysis
The real treasure lies in the AutoKinship analysis, which is presented in a small table on the main HTML page. When you click on the AutoKinship results for any cluster, you’ll see reconstructed trees based on the shared DNA amounts between matches, meaning between you and each of them, and between each other.
You can see that I have 10 reports available based on the cluster numbers indicated.
I clicked on Cluster 1, which shows some of my close DNA matches who are Vannoy line descendants. This includes testers both with and without trees.
Since the AutoKinship algorithm doesn’t have access to age information, it sometimes struggles with generational differences – but the relationship predictions are still remarkably useful.
Alternative trees are also provided, giving you multiple hypotheses to investigate.
Some matches may not be integrated because of incompatible relationships.
The Next Step with AutoLineage – Adding Genealogical Trees to the Mix
We’ve seen AutoTree and AutoKinship. The new upgraded AutoLineage adds genealogical tree information to genetic information by allowing the user to:
- Import other trees
- Integrate most recent common ancestors (MRCAs) in AutoKinship trees
- Set known relationships
- Provide generational information.
AutoLineage, Genetic Affairs’ online clustering and tree-building tool, has been around for several years but was recently upgraded to create trees based on shared DNA and incorporate genealogical evidence.
This is where the proverbial rubber meets the road.
Setting Up AutoLineage
Return to the home page at Genetic Affairs and select AutoLineage.
If you’re new to this tool, you’ll see a simplified workflow on the start page that walks you through the process.
First, create a profile representing the DNA test taker – in my case, that’s me.
After creating the profile, you’ll be redirected to the landing page of the profile. From there, you can register DNA tests linked to the profile. From the home page, you can see the different profiles.
You’ll register a new FamilyTreeDNA test specifically for each user whose kit you manage and who took a test.
FamilyTreeDNA is the only DNA testing company for which Genetic Affairs runs automated analyses on their site.
Additionally, you can:
- Include gephi files from GEDmatch which Dr. Patricia Coleman wrote about, here.
- Import GEDCOM files from all companies, or your desktop software. Dr. Coleman published a blog post about that, too.
- Import data from Ancestry using HTML files or copy/paste using a wizard. Dr. Coleman wrote about this methodology, here.
Importing the Data
After registering a FamilyTreeDNA test, you are redirected to the overview of this DNA page, where matches are imported.
Click on “Import matches” and select the CSV file from Genetic Affairs. Here’s where that AutoKinship report we generated earlier comes in handy. The unzipped report contains match and shared match information that we can import directly into AutoLineage.
Navigate to the gephi folder in your report and select the nodes.csv file to import your matches.
After importing the matches, a short dialog shows how many matches were imported.
After closing the dialog box, the DNA matches pane is opened.
You’ll see your DNA matches that were downloaded.
Next, import the shared match information from the edges.csv file in the same gephi folder.
Once both data sets are imported, you’ll see that the ICW (In Common With) column has populated, showing how many shared matches are available for each DNA match.
Clustering in AutoLineage
Now, with the shared match data loaded, you can perform your own clustering analysis.
The wizard allows you to set parameters for which matches to include based on:
- The amount of shared cMs
- Weighted or unweighted clustering
- How much DNA is shared between shared matches
You can also define the cluster characteristics, from sparse to very dense clusters.
Last, you can select the coloring scheme. After setting the parameters, click on “Start Clustering,” at bottom right.
After clustering is finished, the clustering chart is displayed. It looks fairly similar to the ones obtained automatically from Genetic Affairs, but with some differences.
The first thing I noticed is that the large orange cluster 1 in the automated clustering is now mostly represented by the purple cluster 4.
Let’s zoom in on this cluster. By looking more closely at the numbers contained in each cluster, you can already make an estimated guess about the richness in relationship information for cluster members. This cluster has lots of close relationships. Clusters whose matches only share a small amount of DNA with each other are not the best candidates for an AutoKinship analysis because they most likely share a distant common ancestor. Unless, of course, it’s a distant ancestor you’re searching for. (Hello brick wall.)
Adding and Importing Tree Information
Now that we have the new clusters, we could continue to directly run the tree reconstruction on these clusters using the shared DNA information, but let’s wait since we want to include the tree information as well to guide this process.
To use common ancestors, we need to import the available trees that are linked to the DNA matches. Luckily, just like (shared) match information, the tree information is provided with the automated analysis as well. Let’s import the data.
First, navigate to the tree management page. As you can see, no trees have been created or imported. Let’s start the wizard by clicking on the “Import Trees” button.
An “Import tree” wizard pops up, providing different ways to import tree information. It’s also possible to import GEDCOM files or tree data from other resources, but for now, I’m only using the archived trees at FamilyTreeDNA.
Click on the last option and select the files.
Navigate to the matches folder and select the HTML files contained in the folder.
Each file represents a DNA match report, some of which have a tree associated with them.
After importing the trees, they are automatically associated with the concerned DNA matches (using the unique identifier present in each file name). The tree overview page shows which tree is linked to a profile or DNA test, and the amount of DNA shared with the linked DNA match.
If you have created trees for your matches based on your own research (like quick and dirty trees), now is the time to import these using the “Import Tree” wizard again. This is a wonderful feature, because it means you’re not entirely dependant on your match having uploaded a tree themselves.
If you don’t import trees from GEDCOMs, you don’t need the linking wizard.
Click on the “Import Tree” wizard and select the GEDCOM option.
Now that we have imported additional trees, we need to associate them with DNA matches.
You can use a wizard to link the unlinked trees to the DNA matches, or link them from each DNA match. The wizard will try to guestimate, based on the content of the tree file name, which DNA match could be associated with the tree. Change the search criteria if it does not provide the correct results.
TIP: Save the GEDCOM files with the name of the linked DNA match as well the shared cM, which speeds up the importing process
Don’t forget to import your own tree. I imported my GEDCOM file from my computer genealogy software and associated it with my profile so it’s included in the common ancestor identification. You can easily upload your GEDCOM from your computer software, or download your tree from either Ancestry or MyHeritage to upload here.
Visit the profile, and select the tree pane. The tree pane only shows a single individual and allows you to add ancestors to it manually. To associate that individual with an existing tree, click on “Link to Existing Tree”.
A wizard will be displayed, which shows all available trees on the left side. Sort by clicking on the “Created” column to display the most recent trees.
Next, you need to select the root person.
I selected my tree.
Next, the right side of the wizard fills with the people in the selected tree. Select the root person, which is me, and click on “Save” in the lower right corner.
Finding Common Ancestors
Now that we have associated a tree with the profile and imported trees for the FamilyTreeDNA matches, it’s time to locate some common ancestors. Fingers crossed!
Go back to the profile and select the profile overview. Scroll down to the “Find common ancestors” section and click on the “Find common ancestors” button.
The “common ancestors” wizard shows trees that are associated with this profile in the table on the left and provides information about the different steps on the right. You can change the settings to make the search more restrictive or more relaxed.
After running the common ancestor identification, a dialog shows the number of trees and tree persons that were used, and the number of common ancestors that were identified.
After the analysis runs, you’ll be able to view all reconstructed trees or filter them based on common ancestors, trees, or linked DNA matches.
Common ancestors, not surprisingly, often align closely with what the automated analysis discovered.
All six testers are now shown descending from our common ancestor, in the approximate location where they will fit in our common tree.
But we aren’t quite finished yet.
The Final AutoKinship Analysis
Finally, we’ve arrived. The earlier steps were necessary to pave the way.
We have the common ancestors and clusters, and it’s time to go back to the clusters to begin the reconstruction of trees using trees combined with DNA.
Click on the profile and go to the clustering results pane. Select the 1x view, which will show the clustering chart.
Now select the matches pane that shows the different matches that are contained in each cluster. Scroll down until you reach your cluster of interest, which is four for me.
After clicking on any cluster, you’ll be redirected to a cluster view with only the information for that particular cluster.
Let’s view purple cluster 4, which looks fairly dense, with only a couple of empty cells, indicating that these shared matches with white cells did not share (enough) DNA with each other to be included in the cluster. Now select the matches pane in the dashboard at the top of this cluster, which displays the matches linked to this specific cluster. As you can see, a button is now available that allows us to run the AutoKinship analysis. Click on the button.
Single cluster matches are displayed.
Now back to the wizard.
The wizard provides several important parameters:
- Maximum number of generations between DNA matches
- Number of trees to analyze in each iteration
- Final number of trees to keep
- Whether to include known relationships and/or MRCA (Most Recent Common Ancestor) relationships
In this example, MRCA relationships were found because we performed the common ancestor identification that resulted in common ancestors between the matches of this cluster.
If you know specific relationships between matches, you can set those manually. Sometimes you might not know the exact relationship, but if you can estimate that a match is one or more generations older or younger than yourself, you can set that too.
In addition to setting the relationship between the test taker (indicated in green in the table) and the DNA matches, it’s also possible to set the relationship between shared matches, if known.
The Hybrid Results
After the analysis has finished, an overview of the identified trees is presented.
The final result is a blended tree where DNA evidence fills in the blanks for matches who haven’t uploaded trees, or you haven’t provided a tree, and known genealogy supports the structure where it exists. This hybrid approach gives us the best of both worlds – the precision of documented genealogy combined with the discovery power of DNA analysis.
I particularly like this approach, because when I identify how a DNA match is related to me from any vendor, I enter their lineage in my desktop genealogy software. Therefore, using that GEDCOM file is the most complete source of my identified relatives.
Testers 1-6 were shown using the regular AutoTree, without the integrated tree, but an additional 11 matches were placed for consideration using all available tools.
I was using this as an experiment because I know how most people in this cluster are related, and those are all placed accurately. There is one person, located on the branch between 1 and 5, who I had no idea how they fit into this puzzle. Now, at least I know where to look.
I can’t imagine trying to do all of this manually.
Why This Matters
For those of us dealing with unknown parent or grandparent situations, poorly documented lines, non-existent trees, or just plain stubborn brick walls, this combination of tools is nothing short of amazing. You can now explore relationship hypotheses even when traditional documentation is scarce.
The reconstructed trees show how common ancestor information provides the template, while the AutoLineage tool fills gaps using shared DNA information. The updated AutoLineage is the genealogical assistant that never gets tired and can deal with relationship possibilities much more effectively than traditional hand-based methods.
In Summary
If you haven’t explored Genetic Affairs recently, give it a look. The integration between AutoKinship and AutoLineage represents a significant step forward in DNA analysis.
While AutoKinship offers valuable insights on its own, its full potential is truly unlocked when you export the data into AutoLineage. The combination creates a comprehensive analysis that was previously impossible.
For researchers dealing with complex family relationships or challenging genealogical puzzles, this hybrid approach that combines matches at FamilyTreeDNA with DNA evidence and genealogical trees could be the key to breaking through stubborn brick walls that nothing else has budged.
Last but not least, I suggest reading Dr. Patricia Coleman’s blog articles about these tools and her methodologies here and here. Patricia works extensively with these tools, and I often recommend her for private autosomal research consultations. Patricia’s 2026 RootsTech Session, DNA Case Study: Finding an 1877 Birth Father with Genetic Affairs, BanyanDNA, and No Birth Record, details her work solving a long-standing problem for my cousin in the Speaks family.
_____________________________________________________________
Share the Love!
You’re always welcome to forward articles or links to friends and share on social media.
Subscribe!
If you haven’t already subscribed, it’s free. You’ll receive an e-mail whenever I publish by clicking the “follow” button at the top of the main blog page, here.
Help Keep This Blog Free
I receive a small commission when you click a vendor link in my articles and purchase that item. This does NOT increase your price but helps me keep the lights on and this informational blog free for everyone. Please click on the affiliate links in the articles or to the vendors below if you are purchasing products or DNA testing.
Thank you so much.
DNA Purchases and Free Uploads
- FamilyTreeDNA – Y-DNA, mitochondrial and autosomal DNA testing
- MyHeritage DNA – Autosomal DNA test
- AncestryDNA – Autosomal DNA test
- AncestryDNA Plus Traits
- 23andMe Ancestry – Autosomal DNA only, no Health
- 23andMe Ancestry Plus Health
Genealogy Products and Services
- MyHeritage Subscription with Free Trial
- Legacy Family Tree Webinars – Genealogy and DNA classes, subscription-based, some free
- Legacy Family Tree Software – Genealogy software for your computer
- OldNews – Old Newspapers with links to save to MyHeritage trees
- MyHeritage Omni comprehensive “everything included” subscription plan
- Newspapers.com – Search newspapers for your ancestors
- NewspaperArchive – Search different newspapers for your ancestors
My Books
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – by Roberta Estes, for those ordering the e-book from anyplace, or paperback within the United States
- DNA for Native American Genealogy – for those ordering the paperback outside the US
- The Complete Guide to FamilyTreeDNA – Y-DNA, Mitochondrial, Autosomal and X-DNA – for those ordering the e-book from anyplace, or paperback within the United States
- The Complete Guide to FamilyTreeDNA – Y-DNA, Mitochondrial, Autosomal and X-DNA for those ordering the paperback from outside the US
Genealogy Books
- Genealogical.com – Lots of wonderful genealogy research books
- American Ancestors – Wonderful selection of genealogy books
Genealogy Research
- Legacy Tree Genealogists – Professional genealogy research